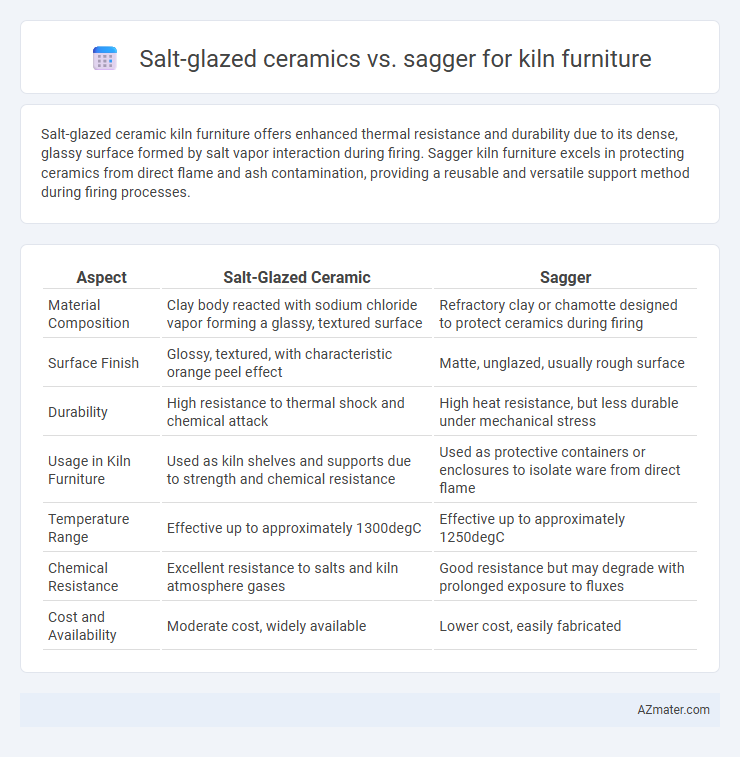
Salt-glazed ceramic kiln furniture offers enhanced thermal resistance and durability due to its dense, glassy surface formed by salt vapor interaction during firing. Sagger kiln furniture excels in protecting ceramics from direct flame and ash contamination, providing a reusable and versatile support method during firing processes.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Salt-Glazed Ceramic | Sagger |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Clay body reacted with sodium chloride vapor forming a glassy, textured surface | Refractory clay or chamotte designed to protect ceramics during firing |
| Surface Finish | Glossy, textured, with characteristic orange peel effect | Matte, unglazed, usually rough surface |
| Durability | High resistance to thermal shock and chemical attack | High heat resistance, but less durable under mechanical stress |
| Usage in Kiln Furniture | Used as kiln shelves and supports due to strength and chemical resistance | Used as protective containers or enclosures to isolate ware from direct flame |
| Temperature Range | Effective up to approximately 1300degC | Effective up to approximately 1250degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to salts and kiln atmosphere gases | Good resistance but may degrade with prolonged exposure to fluxes |
| Cost and Availability | Moderate cost, widely available | Lower cost, easily fabricated |
Introduction to Kiln Furniture Materials
Salt-glazed ceramics and sagger materials serve distinct roles in kiln furniture, crucial for supporting and protecting ceramics during firing. Salt-glazed ceramics offer a durable, glassy surface formed by salt vapor reacting with silica in the body, providing excellent resistance to thermal shock and chemical attack. Saggers, typically made from refractory clay or ceramic composites, form protective containers that shield delicate wares from direct flame and ash, maintaining consistent kiln atmospheres and preventing glaze defects.
What is Salt-Glazed Ceramic?
Salt-glazed ceramic is a type of pottery surface created by introducing salt vapor into the kiln at high temperatures, which reacts with the silica in the clay body to form a glassy, textured coating. This glaze results in a durable, slightly glossy, and often orange-peel textured finish that enhances the ceramic's resistance to wear and thermal shock. Compared to saggers, which act as protective containers in kilns, salt glazing directly affects the pottery surface by chemically altering it during firing.
Understanding Sagger: Definition and Uses
Sagger is a protective container made from refractory materials used in kiln firing to shield ceramics from direct flame and ash contamination, ensuring a controlled atmosphere during the firing process. It is commonly used to achieve specific surface effects, such as on salt-glazed ceramics, by preventing direct salt vapors from damaging delicate textures while still allowing chemical reactions to occur. Understanding the role of saggers in kiln furniture helps optimize firing results by balancing protection and exposure, crucial for producing high-quality salt-glazed pottery.
Key Differences in Manufacturing Processes
Salt-glazed ceramic kiln furniture undergoes a unique manufacturing process where salt is introduced into the kiln at high temperatures, reacting with the silica in the clay body to create a durable glassy surface. In contrast, sagger kiln furniture is produced by shaping and firing refractory clay or materials without the addition of salt, providing a protective container for ware during firing. The key difference lies in the salt glazing step, which imparts a distinctive texture and increased chemical resistance to the ceramic, while saggers rely on their structural design for protection.
Thermal Performance in High-Temperature Kilns
Salt-glazed ceramics exhibit superior thermal shock resistance and maintain structural integrity under rapid temperature fluctuations, making them ideal for high-temperature kiln furniture applications. Sagger kiln furniture, typically made from refractory clay or alumina, offers excellent thermal insulation and stability but may have lower resistance to thermal shock compared to salt-glazed options. The enhanced thermal performance of salt-glazed ceramics helps reduce warping and extend kiln furniture lifespan in intense firing environments above 1300degC.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Salt-glazed ceramics exhibit enhanced durability due to their glassy, fused surface formed during the salt-firing process, which provides excellent resistance to thermal shock and abrasion. Sagger kiln furniture, composed primarily of refractory clays and sometimes alumina, offers robust mechanical strength and prolonged lifespan under consistent high-temperature firing conditions. While salt-glazed ceramic kiln furniture boasts superior surface hardness, saggers typically ensure longer service life in industrial kiln environments by maintaining structural integrity through repeated thermal cycles.
Impact on Final Ceramic Product Quality
Salt-glazed ceramics produce a unique, textured surface with enhanced durability and chemical resistance, improving the final product's aesthetic and functional qualities. In contrast, saggers protect ceramics during firing, preventing direct flame contact and contamination, which ensures a cleaner, more uniform finish. The choice between salt glazing and sagger use directly influences surface quality, texture, and overall integrity of the final ceramic ware in kiln firing processes.
Cost Analysis: Salt-Glazed Ceramic vs Sagger
Salt-glazed ceramic kiln furniture generally incurs higher production costs due to the complex glazing process and material durability requirements, but offers superior resistance to chemical and thermal stress. In contrast, sagger kiln furniture is more cost-effective with lower initial expenses, as it utilizes simpler materials and manufacturing techniques, though it may require more frequent replacement. Long-term cost analysis reveals salt-glazed ceramic's durability reduces replacement frequency, potentially offsetting higher upfront investment compared to sagger alternatives.
Environmental Considerations and Safety
Salt-glazed ceramics release sodium chloride vapors during firing, which pose environmental challenges by contributing to air pollution and requiring specialized ventilation systems to protect worker health. Saggers made from refractory materials contain kiln atmospheres, reducing emissions and ensuring higher safety for kiln operators by limiting exposure to harmful gases. Choosing saggers enhances environmental compliance and workplace safety compared to the salt glazing process in kiln furniture applications.
Choosing the Right Kiln Furniture for Your Needs
Choosing the right kiln furniture depends on your firing requirements, with salt-glazed ceramics benefiting from salt-glazed kiln shelves that resist the corrosive effects of salt vapors and high temperatures. Saggers provide excellent protection for ceramics that require an enclosed environment to prevent direct flame contact, enhancing surface quality and reducing defects. Evaluating factors such as firing atmosphere, temperature range, and desired finish will guide the selection between durable salt-glazed options and protective saggers to optimize kiln performance and ceramic outcomes.
Infographic: Salt-glazed ceramic vs Sagger for Kiln furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com