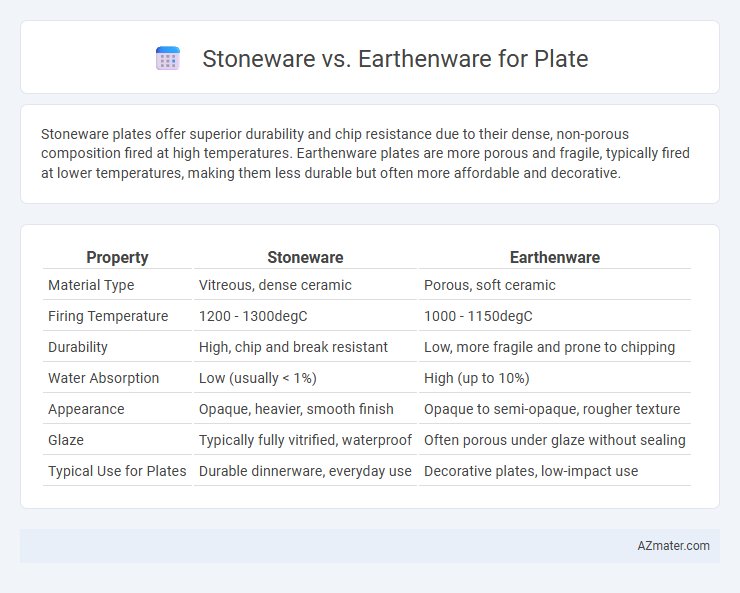
Stoneware plates offer superior durability and chip resistance due to their dense, non-porous composition fired at high temperatures. Earthenware plates are more porous and fragile, typically fired at lower temperatures, making them less durable but often more affordable and decorative.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Stoneware | Earthenware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Vitreous, dense ceramic | Porous, soft ceramic |
| Firing Temperature | 1200 - 1300degC | 1000 - 1150degC |
| Durability | High, chip and break resistant | Low, more fragile and prone to chipping |
| Water Absorption | Low (usually < 1%) | High (up to 10%) |
| Appearance | Opaque, heavier, smooth finish | Opaque to semi-opaque, rougher texture |
| Glaze | Typically fully vitrified, waterproof | Often porous under glaze without sealing |
| Typical Use for Plates | Durable dinnerware, everyday use | Decorative plates, low-impact use |
Introduction to Stoneware and Earthenware Plates
Stoneware plates are made from dense, non-porous clay fired at high temperatures between 1,200degC and 1,300degC, resulting in durable, chip-resistant dinnerware ideal for everyday use. Earthenware plates are crafted from porous clay fired at lower temperatures ranging from 1,000degC to 1,150degC, producing lightweight and more fragile dishes with a rustic appearance. These fundamental differences in material composition and firing temperature significantly affect the strength, texture, and usability of each type of plate.
Key Differences Between Stoneware and Earthenware
Stoneware plates are fired at higher temperatures, typically between 1,200degC and 1,300degC, resulting in a denser, more durable, and non-porous material compared to earthenware, which is fired at lower temperatures around 1,000degC to 1,150degC, making it more porous and less durable. Stoneware has a more vitreous, glass-like surface that resists chipping and staining, while earthenware is more porous and prone to absorbing liquids and stains unless glazed. The color of stoneware ranges from gray to brown tones due to its dense composition, whereas earthenware generally appears red, orange, or tan because of its higher iron content in the clay.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Process
Stoneware plates are made from dense, non-porous clay fired at high temperatures between 1,200degC and 1,300degC, resulting in a durable, vitrified material ideal for everyday use. Earthenware plates use a more porous clay fired at lower temperatures between 1,000degC and 1,150degC, which produces a softer, more fragile surface prone to chipping but often favored for decorative purposes. The manufacturing process of stoneware involves longer firing times and higher heat to achieve its strength and water resistance, while earthenware's lower firing preserves its porous texture and allows for vibrant glazes.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Stoneware plates exhibit superior durability and strength compared to earthenware due to their higher firing temperature, which results in a denser, non-porous ceramic structure. Earthenware plates, fired at lower temperatures, tend to be more porous and less resistant to chipping or cracking under impact. The vitrification process in stoneware enhances its robustness, making it ideal for everyday use and heavy handling.
Porosity and Water Absorption Rates
Stoneware plates have lower porosity and water absorption rates, typically below 0.5%, making them more durable and resistant to staining compared to earthenware. Earthenware is more porous, with water absorption rates ranging from 5% to 10%, which makes it more prone to chipping and less suitable for everyday use. The denser composition of stoneware creates a non-porous surface ideal for plates that require longevity and resistance to moisture.
Aesthetic Qualities: Colors, Textures, and Glazes
Stoneware plates feature rich, earthy tones and a dense, smooth texture, often enhanced by glossy or matte glazes that highlight natural variations. Earthenware plates typically showcase warmer, more rustic colors with a slightly porous texture, allowing for vibrant, hand-painted or crackled glazes that emphasize a handcrafted feel. Both materials offer distinct aesthetic qualities, with stoneware providing a refined, durable finish and earthenware presenting a charming, artisanal appearance.
Suitability for Everyday Use and Special Occasions
Stoneware plates offer superior durability and resistance to chipping, making them ideal for everyday use and suitable for dishwasher and microwave convenience. Earthenware plates, with their porous nature and more delicate glaze, provide a rustic aesthetic better suited for special occasions and decorative settings where gentle handling is preferred. Choosing between stoneware and earthenware depends on balancing daily practicality with the desired elegance for formal dining experiences.
Maintenance, Cleaning, and Care Needs
Stoneware plates are highly durable and resistant to chips and cracks, making them easier to maintain with regular use, and they are usually dishwasher safe, requiring minimal special care. Earthenware plates, being more porous and delicate, demand gentle hand washing to avoid damage and should not be exposed to extreme temperature changes to maintain their integrity. Proper care for stoneware involves occasional seasoning or sealing, while earthenware benefits from thorough drying to prevent moisture absorption and staining.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Stoneware plates typically cost more than earthenware due to their denser composition and higher firing temperatures, resulting in greater durability and chip resistance. Earthenware is more widely available and generally less expensive, making it a popular choice for budget-conscious consumers and casual dining. Availability of stoneware may be limited to specialty stores or higher-end brands, while earthenware can be easily found in most home goods retailers.
Which is Better for Plates: Stoneware or Earthenware?
Stoneware is superior for plates due to its durability, resistance to chipping, and non-porous surface that resists stains and odors. Earthenware, while more porous and less durable, offers a rustic aesthetic but requires sealing to prevent moisture absorption. For everyday use, stoneware plates provide long-lasting performance and easier maintenance compared to earthenware.
Infographic: Stoneware vs Earthenware for Plate
 azmater.com
azmater.com