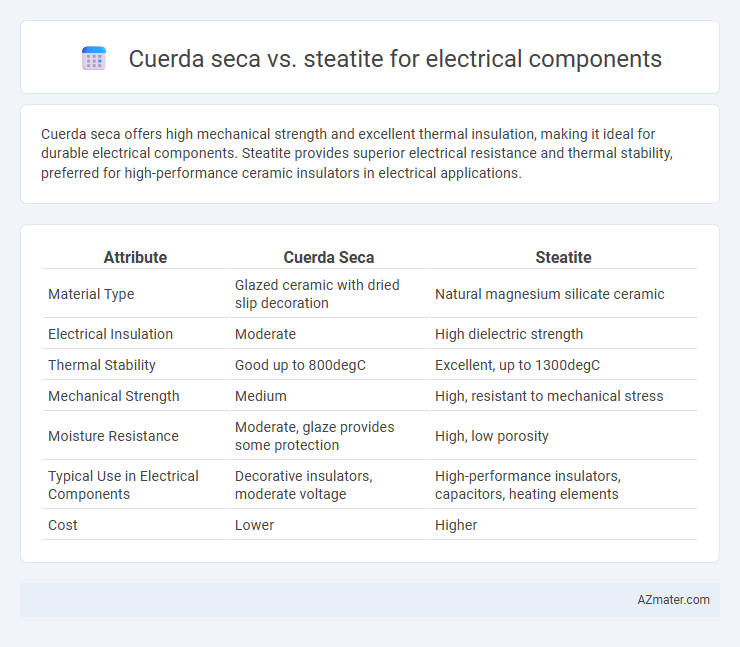
Cuerda seca offers high mechanical strength and excellent thermal insulation, making it ideal for durable electrical components. Steatite provides superior electrical resistance and thermal stability, preferred for high-performance ceramic insulators in electrical applications.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Cuerda Seca | Steatite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glazed ceramic with dried slip decoration | Natural magnesium silicate ceramic |
| Electrical Insulation | Moderate | High dielectric strength |
| Thermal Stability | Good up to 800degC | Excellent, up to 1300degC |
| Mechanical Strength | Medium | High, resistant to mechanical stress |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate, glaze provides some protection | High, low porosity |
| Typical Use in Electrical Components | Decorative insulators, moderate voltage | High-performance insulators, capacitors, heating elements |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Cuerda Seca and Steatite in Electrical Components
Cuerda seca and steatite materials serve distinct purposes in electrical component manufacturing, with cuerda seca primarily used for decorative ceramic insulators and steatite renowned for its high dielectric strength and thermal stability. Steatite, a dense ceramic composed mainly of magnesium silicate, provides excellent electrical insulation and mechanical strength in components like bushings and insulators. Cuerda seca, involving a slip-resist glaze process, enhances aesthetic appeal while offering moderate electrical insulation but is less favored for high-performance electrical applications compared to steatite.
Material Composition: Cuerda Seca vs Steatite
Cuerda Seca is a ceramic material composed primarily of clay mixed with metallic oxides to create intricate decorative patterns through a resin resist technique, offering moderate electrical insulation properties suited for artistic electrical components. Steatite, a dense, high-purity magnesium silicate ceramic, exhibits superior electrical insulation, high dielectric strength, and excellent thermal stability, making it ideal for high-performance electrical insulators and semiconductor substrates. The material composition difference results in Cuerda Seca having more aesthetic versatility while Steatite delivers enhanced durability and reliability in electrical applications.
Electrical Insulation Properties Compared
Cuerda seca and steatite differ significantly in electrical insulation properties for electrical components, with steatite offering superior dielectric strength and lower electrical conductivity. Steatite's dense ceramic structure provides excellent resistance to high voltage and temperature fluctuations, making it ideal for high-performance insulators and electrical bushings. In contrast, cuerda seca, primarily a decorative ceramic technique, exhibits lower insulating capacity and is less suited for critical electrical insulation applications.
Thermal Resistance and Performance
Cuerda seca and steatite differ significantly in thermal resistance and performance for electrical components. Steatite ceramic exhibits high thermal resistance, typically above 1200degC, making it ideal for insulation in high-temperature environments, whereas cuerda seca, primarily a decorative ceramic technique, lacks the specialized thermal properties required for electrical insulation. Steatite's superior mechanical strength and dielectric properties enhance component longevity and efficiency under thermal stress compared to the relatively lower thermal resilience of cuerda seca materials.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Cuerda seca ceramics exhibit excellent mechanical strength and durability due to their dense microstructure and robust glaze application, making them suitable for high-stress electrical components. Steatite, a magnesium silicate ceramic, offers high mechanical strength and superior resistance to thermal shock and electrical insulation, which enhances its long-term durability in electrical parts. Both materials provide reliable mechanical performance, but steatite generally outperforms cuerda seca in durability under extreme thermal and electrical conditions.
Manufacturing Processes and Ease of Fabrication
Cuerda seca involves applying colored glazes separated by a resist paste and requires kiln firing, making the manufacturing process intricate and time-consuming compared to Steatite, which is fabricated from compacted and sintered talc-based material through pressing and firing. Steatite offers superior ease of fabrication with its machinability and consistency, allowing for precise shaping and drilling essential for electrical components. The robust and homogeneous nature of Steatite minimizes defects during manufacturing, whereas cuerda seca's layered glaze process increases complexity and potential for glaze cracking or imperfections.
Cost Analysis: Cuerda Seca vs Steatite
Cuerda seca offers lower initial manufacturing costs due to simpler production techniques and readily available materials, making it cost-effective for high-volume applications. Steatite, while more expensive upfront, provides superior durability and thermal resistance, reducing long-term maintenance and replacement expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership, steatite's benefits often justify its higher price in demanding electrical component environments.
Common Applications in the Electrical Industry
Cuerda seca is commonly used for high-voltage insulators and decorative electrical components due to its excellent dielectric properties and thermal resistance. Steatite is favored in electronic substrates, capacitors, and insulator parts because of its high mechanical strength and exceptional electrical insulation at elevated temperatures. Both materials are essential in ensuring reliability and efficiency in electrical applications, with cuerda seca suited for outdoor and high-voltage environments, while steatite excels in compact, high-performance electronic components.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cuerda seca glazing uses water-based pigments and low-energy firing processes, resulting in a reduced carbon footprint and minimal hazardous waste compared to steatite, which requires energy-intensive extraction and production methods involving mining talc. Steatite's mining disrupts ecosystems and generates significant waste, while cuerda seca's artisanal techniques promote sustainability through lower resource consumption and biodegradable materials. Choosing cuerda seca for electrical components aligns with eco-friendly manufacturing goals and supports a circular economy by leveraging natural, non-toxic substances.
Choosing the Best Material for Electrical Components
Steatite offers superior electrical insulation and thermal stability compared to cuerda seca, making it ideal for high-performance electrical components. Its low dielectric constant and high resistance to thermal shock ensure efficient operation in demanding environments. Selecting steatite enhances durability and reliability, crucial for minimizing energy loss and preventing component failure.
Infographic: Cuerda seca vs Steatite for Electrical component
 azmater.com
azmater.com