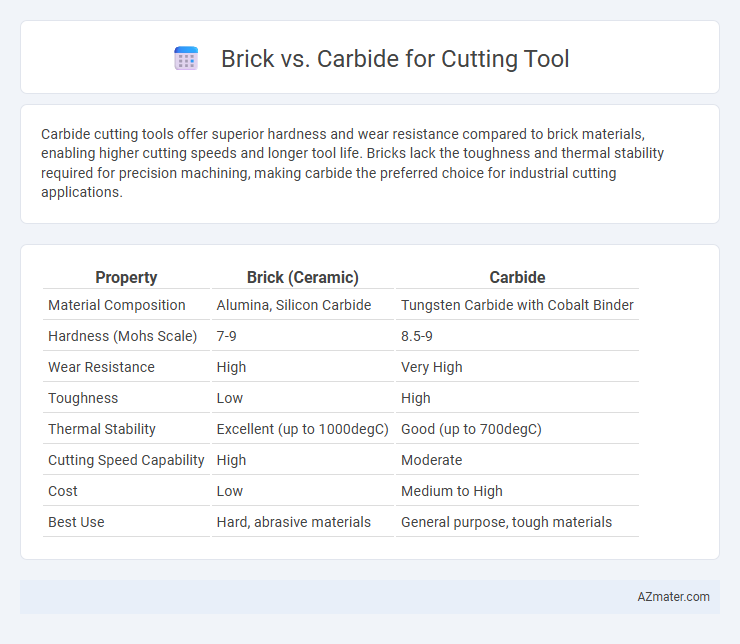
Carbide cutting tools offer superior hardness and wear resistance compared to brick materials, enabling higher cutting speeds and longer tool life. Bricks lack the toughness and thermal stability required for precision machining, making carbide the preferred choice for industrial cutting applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Brick (Ceramic) | Carbide |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Alumina, Silicon Carbide | Tungsten Carbide with Cobalt Binder |
| Hardness (Mohs Scale) | 7-9 | 8.5-9 |
| Wear Resistance | High | Very High |
| Toughness | Low | High |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent (up to 1000degC) | Good (up to 700degC) |
| Cutting Speed Capability | High | Moderate |
| Cost | Low | Medium to High |
| Best Use | Hard, abrasive materials | General purpose, tough materials |
Introduction to Cutting Tools: Brick vs Carbide
Cutting tools are essential in manufacturing processes, with brick and carbide being two common materials. Brick cutting tools, typically made from ceramic composites, offer cost-effective solutions but lack durability and wear resistance compared to carbide tools. Carbide cutting tools, composed of tungsten carbide particles bonded with cobalt, provide superior hardness, heat resistance, and longevity, making them ideal for high-precision and high-speed machining applications.
Material Composition: Understanding Brick and Carbide
Brick cutting tools are primarily composed of clay, silica, and other natural minerals, which provide moderate hardness and thermal resistance suitable for basic masonry tasks. Carbide tools consist mainly of tungsten carbide particles bonded with a metallic binder like cobalt, offering exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and heat tolerance for precision cutting and heavy-duty applications. The distinct material compositions result in carbide outperforming brick tools in durability and cutting efficiency across various industrial processes.
Performance Comparison: Cutting Efficiency
Carbide cutting tools deliver significantly higher cutting efficiency compared to brick-based tools due to their superior hardness and wear resistance, allowing for faster material removal rates and prolonged tool life. The thermal stability of carbide enables it to maintain sharp cutting edges at elevated temperatures, reducing downtime caused by frequent tool changes. In contrast, brick materials, lacking comparable mechanical properties, show rapid degradation and lower precision in cutting applications.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Carbide cutting tools offer significantly higher durability and wear resistance compared to brick-based tools due to their superior hardness and ability to maintain a sharp edge under high temperatures and abrasive conditions. Cemented carbide tools resist deformation and abrasive wear, making them ideal for prolonged use in machining metals and hard materials. In contrast, brick cutting tools, typically made from ceramic or refractories, lack the toughness and wear resistance of carbide, resulting in shorter tool life and more frequent replacements.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Longevity
Carbide cutting tools demand a higher initial investment compared to brick tools due to advanced material composition and manufacturing processes. Despite greater upfront costs, carbide offers superior longevity and wear resistance, reducing replacement frequency and long-term expenses. Brick tools, while cheaper initially, often require more frequent replacements, escalating cumulative costs over time.
Application Suitability: Where Each Excels
Carbide cutting tools excel in high-speed machining, precision cutting, and toughness necessary for metals, alloys, and hardened materials. Brick tools, typically made of ceramic or refractory materials, are better suited for rough cutting, shaping softer materials, and applications with lower temperature and stress demands. Carbide's superior hardness and thermal resistance make it ideal for industrial environments requiring durability and sustained cutting performance.
Maintenance and Sharpening Needs
Carbide cutting tools demand less frequent sharpening due to their superior hardness and wear resistance compared to brick tools, which require regular maintenance to maintain cutting accuracy. Brick tools often need more frequent edge restoration and regrinding as they wear down faster, impacting productivity. Proper sharpening techniques and equipment prolong carbide tool life, while brick tools benefit from routine inspections to prevent premature failure.
Safety Considerations for Each Material
Brick cutting tools typically pose fewer safety risks due to their lower hardness and reduced brittleness, minimizing the chances of tool shattering during use. Carbide cutting tools, while offering superior durability and cutting precision, require careful handling and proper protective equipment to prevent injury from sharp edges and potential chip breakage. Proper training and adherence to safety protocols are essential when using carbide tools to mitigate hazards associated with high-speed cutting and material fracturing.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Carbide cutting tools offer greater durability and longer lifespan compared to brick tools, reducing the frequency of replacements and waste generation, which supports sustainability goals. Manufacturing carbide tools typically involves higher energy consumption and mining of rare metals, raising environmental concerns related to resource extraction and carbon emissions. In contrast, brick tools are often composed of more abundant materials with lower manufacturing impacts but require more frequent replacement, resulting in increased material waste over time.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Cutting Tool Material
Carbide cutting tools outperform brick materials in hardness, wear resistance, and durability, making them ideal for high-speed and precision machining applications. Brick tools are typically limited to low-impact, non-metal cutting tasks due to their brittleness and lower thermal tolerance. Selecting carbide ensures enhanced tool life and machining efficiency, especially in demanding industrial environments.
Infographic: Brick vs Carbide for Cutting Tool
 azmater.com
azmater.com