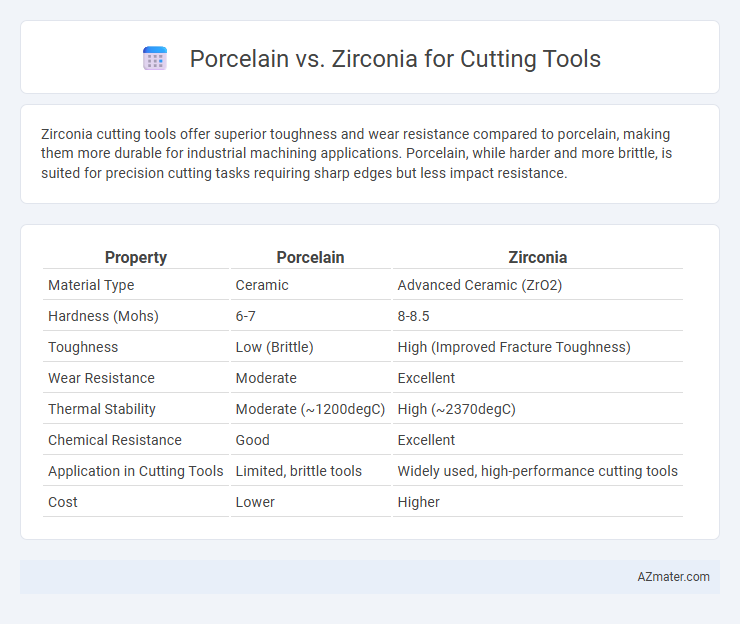
Zirconia cutting tools offer superior toughness and wear resistance compared to porcelain, making them more durable for industrial machining applications. Porcelain, while harder and more brittle, is suited for precision cutting tasks requiring sharp edges but less impact resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Porcelain | Zirconia |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Ceramic | Advanced Ceramic (ZrO2) |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 6-7 | 8-8.5 |
| Toughness | Low (Brittle) | High (Improved Fracture Toughness) |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate (~1200degC) | High (~2370degC) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Application in Cutting Tools | Limited, brittle tools | Widely used, high-performance cutting tools |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Advanced Cutting Tool Materials
Porcelain and zirconia represent two advanced materials used in cutting tools, each offering distinct mechanical properties and wear resistance. Zirconia, known for its exceptional toughness, high fracture resistance, and thermal stability, is increasingly favored in precision machining and dental instrument applications. Porcelain, while offering excellent hardness and aesthetic qualities, typically lacks the durability required for high-stress cutting environments, making zirconia a superior choice for demanding industrial uses.
Understanding Porcelain as a Cutting Tool Material
Porcelain as a cutting tool material offers high hardness and excellent resistance to wear, making it suitable for precision cutting applications. Its brittleness, however, limits its use to low-impact operations where sharp, fine edges are essential. Compared to zirconia, porcelain provides superior thermal stability but requires careful handling to prevent chipping and breakage during machining tasks.
Exploring Zirconia in Cutting Tool Applications
Zirconia exhibits superior toughness and wear resistance compared to traditional porcelain, making it increasingly favored for cutting tool applications where durability is critical. Its high fracture toughness and thermal stability enable cutting tools to maintain sharpness and precision under intense mechanical stress and elevated temperatures. Innovations in zirconia composites further enhance tool lifespan and performance, outpacing the limitations typically encountered with porcelain materials in industrial machining environments.
Mechanical Properties Comparison: Porcelain vs Zirconia
Zirconia exhibits superior mechanical properties compared to porcelain, featuring higher flexural strength typically around 900-1200 MPa versus porcelain's 60-90 MPa, making it more resistant to fracture under stress. Zirconia's fracture toughness ranges from 6 to 10 MPa*m^0.5, significantly outperforming porcelain's 1-2 MPa*m^0.5, which results in enhanced durability and longevity in cutting tool applications. The hardness of zirconia, approximately 1200 Vickers hardness (HV), surpasses porcelain's lower hardness, providing better wear resistance essential for efficient cutting performance.
Wear Resistance and Durability
Zirconia cutting tools exhibit superior wear resistance compared to porcelain, thanks to their high fracture toughness and ability to withstand abrasive conditions. Porcelain, while offering excellent hardness, tends to be more brittle, resulting in lower durability under heavy cutting stresses. The combination of zirconia's mechanical strength and superior thermal stability makes it the preferred choice for long-lasting, wear-resistant cutting applications.
Thermal Stability in High-Speed Operations
Zirconia exhibits superior thermal stability compared to porcelain, making it the preferred material for high-speed cutting tool applications where heat resistance is critical. Zirconia's ability to maintain hardness and structural integrity at elevated temperatures reduces tool wear and enhances cutting precision during intensive machining processes. Porcelain, while thermally stable at lower temperatures, tends to degrade or crack under the extreme heat generated in high-speed operations, limiting its effectiveness in demanding industrial environments.
Sharpness and Edge Retention
Zirconia cutting tools demonstrate superior sharpness and edge retention compared to porcelain due to their higher fracture toughness and wear resistance. The dense microstructure of zirconia maintains a sharp cutting edge longer under high-stress machining conditions, reducing frequent tool replacement. Porcelain, while harder, tends to chip and wear faster, limiting its effectiveness in applications requiring sustained precision and durability.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Zirconia cutting tools offer higher cost-effectiveness due to their superior toughness and longer tool life compared to porcelain, reducing replacement frequency and downtime. While porcelain tools are generally more affordable initially, their lower durability leads to increased maintenance and replacement costs. Zirconia's widespread industrial availability ensures consistent supply, whereas porcelain tools may face limited availability in specialized applications.
Best Use Cases: Porcelain vs Zirconia Tools
Zirconia cutting tools excel in high-stress applications due to their superior toughness and resistance to chipping, making them ideal for heavy-duty machining and aerospace components. Porcelain tools offer excellent wear resistance and are best suited for precision cutting in electronics and medical device manufacturing where fine detail and smooth finishes are essential. Selecting between porcelain and zirconia depends on the operational demands, with zirconia favored for durability and porcelain for precision.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Cutting Tools
Zirconia cutting tools offer superior toughness, wear resistance, and fracture strength compared to porcelain, making them ideal for high-precision and heavy-duty machining applications. Porcelain tools, while more cost-effective and corrosion-resistant, are better suited for low-stress, light-duty cutting tasks where brittleness is less of a concern. Selecting the right material depends on balancing performance requirements, cost constraints, and the specific machining environment to optimize tool longevity and cutting efficiency.
Infographic: Porcelain vs Zirconia for Cutting Tool
 azmater.com
azmater.com