Boron carbide offers exceptional hardness and chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-performance pots in industrial applications. Terra cotta provides natural insulation and breathability, perfect for traditional gardening pots but less durable under extreme conditions.
Table of Comparison
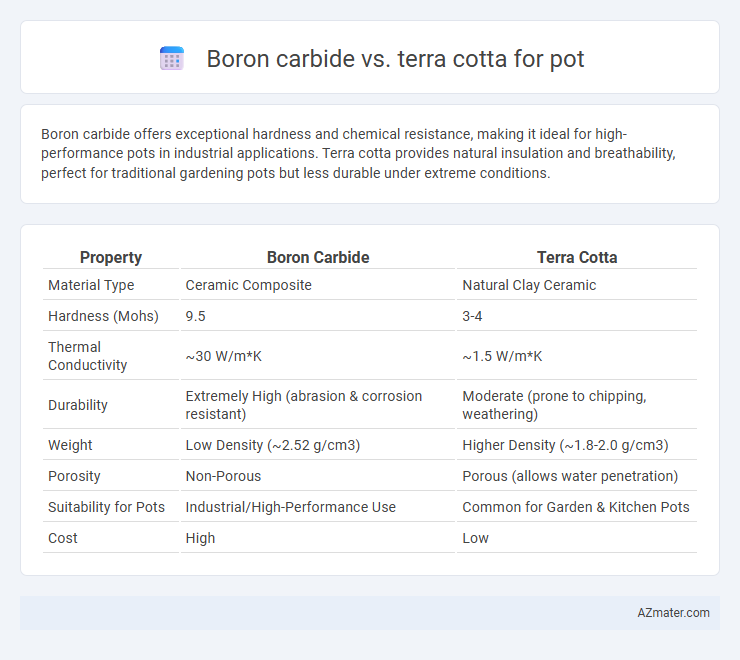
| Property | Boron Carbide | Terra Cotta |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Ceramic Composite | Natural Clay Ceramic |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 9.5 | 3-4 |
| Thermal Conductivity | ~30 W/m*K | ~1.5 W/m*K |
| Durability | Extremely High (abrasion & corrosion resistant) | Moderate (prone to chipping, weathering) |
| Weight | Low Density (~2.52 g/cm3) | Higher Density (~1.8-2.0 g/cm3) |
| Porosity | Non-Porous | Porous (allows water penetration) |
| Suitability for Pots | Industrial/High-Performance Use | Common for Garden & Kitchen Pots |
| Cost | High | Low |
Introduction to Boron Carbide and Terra Cotta Pots
Boron carbide is an exceptionally hard ceramic material known for its high strength, wear resistance, and chemical stability, often used in advanced industrial applications rather than traditional pottery. Terra cotta pots, made from natural clay, are porous and breathable, allowing moisture control and root aeration ideal for plant growth. While boron carbide offers durability and resistance to extreme conditions, terra cotta remains popular for gardening due to its natural insulating properties and classic aesthetic.
Material Composition and Properties
Boron carbide is an extremely hard ceramic material composed primarily of boron and carbon atoms, known for its exceptional abrasion resistance, high melting point above 2400degC, and low density, making it ideal for industrial applications requiring durability and wear resistance. Terra cotta, made from natural clay containing silica, alumina, and iron oxide, is porous, relatively soft, and fired at lower temperatures around 1000degC, resulting in a brittle, earthy material commonly used for decorative and gardening pots. The fundamental difference lies in boron carbide's superior hardness and chemical stability compared to terra cotta's porous structure and moisture absorption, which significantly influences their respective suitability for high-impact or decorative pot uses.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Boron carbide exhibits exceptional hardness and impact resistance, making it significantly more durable and stronger than terra cotta, which is a porous ceramic material prone to chipping and cracking under stress. Terra cotta pots are susceptible to weathering and mechanical damage, especially in freeze-thaw conditions, whereas boron carbide's robust molecular structure provides superior resistance to abrasion and environmental wear. For applications requiring high strength and long-lasting durability, boron carbide offers unparalleled performance compared to the more traditional terra cotta pots.
Porosity and Water Retention
Boron carbide pots exhibit extremely low porosity, resulting in minimal water absorption and superior resistance to moisture-related damage, making them ideal for plants requiring well-drained soil. Terra cotta pots have high porosity, allowing significant water evaporation and air exchange, which benefits plants needing drier conditions but necessitates more frequent watering. The difference in water retention between boron carbide, with its almost impermeable surface, and porous terra cotta significantly affects soil moisture levels and irrigation frequency.
Thermal Insulation Capabilities
Boron carbide offers exceptional thermal insulation capabilities with a high melting point of 2763degC and low thermal conductivity, making it suitable for applications requiring heat resistance and durability. Terra cotta, composed of porous clay fired at lower temperatures (typically around 1000degC), provides moderate thermal insulation but lacks the extreme heat tolerance seen in boron carbide. Boron carbide's advanced ceramic properties enable better protection against thermal shock and maintain stability in high-temperature environments compared to traditional terra cotta pots.
Weight and Portability
Boron carbide pots are significantly lighter than terra cotta, making them more portable for activities such as camping or outdoor cooking. The high strength-to-weight ratio of boron carbide ensures durability without added bulk, whereas terra cotta pots are fragile and heavier due to their dense ceramic composition. Consequently, boron carbide offers enhanced ease of transport and handling compared to traditional terra cotta pots.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Options
Boron carbide pots offer a sleek, modern aesthetic with smooth, dark finishes that complement contemporary design schemes. Terra cotta pots provide a warm, rustic appearance with their natural reddish-brown hues and textured surfaces, ideal for traditional or Mediterranean styles. While boron carbide allows for diverse shapes and minimalistic designs due to its durability, terra cotta pots excel in handcrafted, artisanal appeal with varied glazing and surface patterns.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Boron carbide pots are highly durable and resistant to wear, reducing the need for frequent replacement and minimizing waste, but their manufacturing involves energy-intensive processes and mining of raw materials, which can contribute to environmental degradation. Terra cotta pots are made from natural clay, making them more eco-friendly and biodegradable; they require less energy to produce and can help regulate plant moisture naturally, supporting sustainable gardening practices. Choosing terra cotta aligns better with circular economy principles, while boron carbide offers longevity that may offset initial environmental costs over time.
Cost and Availability
Boron carbide pots are significantly more expensive due to their advanced manufacturing process and specialized applications, making them less common in typical pottery markets. Terra cotta pots are widely available and affordable, produced from natural clay with low-cost firing techniques, making them a popular choice for gardening and decorative uses. The high cost and limited availability of boron carbide pots restrict their use mainly to industrial or high-performance contexts.
Best Uses and Recommendations
Boron carbide is a highly durable, lightweight ceramic commonly used in industrial applications like armor plating and abrasives, unsuitable for typical plant pots due to its hardness and cost. Terra cotta offers excellent breathability and moisture regulation, making it ideal for outdoor and indoor plant pots where root aeration and natural temperature control are priorities. For gardening, terra cotta is recommended for its affordability, ease of use, and beneficial effect on plant health, while boron carbide lacks practical application in standard pot production.
Infographic: Boron carbide vs Terra cotta for Pot
 azmater.com
azmater.com