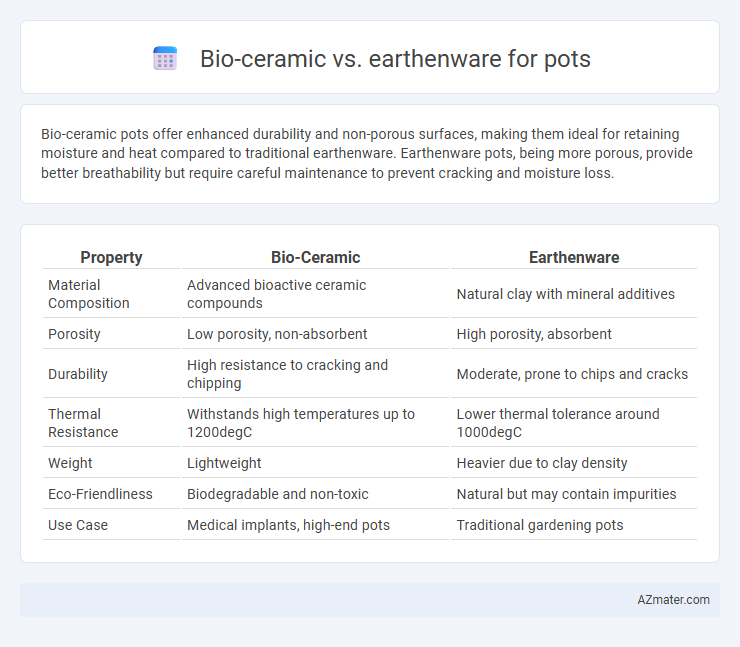
Bio-ceramic pots offer enhanced durability and non-porous surfaces, making them ideal for retaining moisture and heat compared to traditional earthenware. Earthenware pots, being more porous, provide better breathability but require careful maintenance to prevent cracking and moisture loss.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bio-Ceramic | Earthenware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Advanced bioactive ceramic compounds | Natural clay with mineral additives |
| Porosity | Low porosity, non-absorbent | High porosity, absorbent |
| Durability | High resistance to cracking and chipping | Moderate, prone to chips and cracks |
| Thermal Resistance | Withstands high temperatures up to 1200degC | Lower thermal tolerance around 1000degC |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier due to clay density |
| Eco-Friendliness | Biodegradable and non-toxic | Natural but may contain impurities |
| Use Case | Medical implants, high-end pots | Traditional gardening pots |
Introduction to Bio-ceramic and Earthenware Pots
Bio-ceramic pots are crafted using advanced ceramic materials that offer enhanced durability, thermal insulation, and non-porous surfaces, making them ideal for modern cooking needs. Earthenware pots, traditionally made from natural clay, provide excellent heat retention but are porous and require seasoning or glazing to prevent moisture absorption. Both types serve distinct culinary purposes, with bio-ceramic pots excelling in longevity and hygiene, while earthenware pots promote slow, even cooking with a rustic flavor profile.
Material Composition: Bio-ceramic vs Earthenware
Bio-ceramic pots are crafted from advanced materials combining natural minerals and bioactive compounds, resulting in enhanced durability, heat retention, and antibacterial properties. Earthenware pots consist primarily of clay fired at lower temperatures, making them porous and less durable but highly breathable for plant roots. The bio-ceramic material offers superior strength and non-porous surfaces compared to the traditional, more fragile and porous earthenware composition.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Bio-ceramic pots exhibit superior durability and strength compared to traditional earthenware due to their advanced composition of bioactive materials and high-temperature firing processes. Earthenware pots, while aesthetically pleasing and porous, are more prone to cracking and chipping under stress or temperature fluctuations. The enhanced resilience of bio-ceramic makes it ideal for long-term use in both indoor and outdoor gardening environments.
Temperature Resistance and Heat Distribution
Bio-ceramic pots offer superior temperature resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 1,200degC without cracking, making them ideal for high-heat cooking and oven use. Earthenware pots, typically fired at lower temperatures around 1,000degC, are more porous and less durable under intense heat, which can lead to thermal shock and cracking. Heat distribution in bio-ceramic is more even and consistent due to its dense composition, while earthenware has slower, uneven heat conduction that affects cooking performance.
Health and Safety: Non-toxic and Eco-friendliness
Bio-ceramic pots are prized for their non-toxic composition, often made from natural minerals that do not leach harmful chemicals, making them safer for food storage and cooking. Earthenware, while also natural, can sometimes contain lead or other heavy metals in older or lower-quality glazes, raising health concerns if not properly certified non-toxic. Bio-ceramics generally offer enhanced eco-friendliness by using sustainably sourced materials and lower-energy manufacturing processes compared to traditional earthenware production.
Moisture Retention and Breathability
Bio-ceramic pots excel in moisture retention due to their dense, non-porous structure, which minimizes water evaporation and keeps soil consistently hydrated. Earthenware, characterized by its porous composition, promotes superior breathability, allowing air and moisture to pass through the walls, which helps prevent root rot and provides natural aeration. Choosing between bio-ceramic and earthenware depends on plant species' water needs and preferred soil moisture levels, balancing retention with breathability for optimal growth.
Cooking Performance and Flavor Impact
Bio-ceramic pots offer superior heat retention and even heat distribution, enhancing cooking performance and preserving food moisture and nutrients effectively. Earthenware pots excel at slow cooking by allowing gradual heat absorption but may result in uneven temperature spots, affecting cooking consistency. Flavor impact from bio-ceramic is minimal and neutral, while earthenware imparts a subtle earthy aroma that can enrich the taste of traditional dishes.
Cleaning and Maintenance Requirements
Bio-ceramic pots feature non-porous surfaces that resist stains and bacteria, making them easier to clean and maintain compared to earthenware, which is porous and can absorb moisture and oils, causing potential odors and discoloration over time. Earthenware requires gentle cleaning with mild detergents and avoiding harsh scrubbing to prevent cracks and preserve glaze integrity, while bio-ceramic can withstand more rigorous cleaning methods, including dishwasher use. Regular sealing is necessary for earthenware to maintain its waterproof qualities, whereas bio-ceramic pots typically do not require resealing, enhancing their convenience and longevity in maintenance.
Cost and Accessibility
Bio-ceramic pots typically offer higher durability and advanced thermal properties but come at a premium price compared to earthenware, which remains more affordable for everyday use. Earthenware pots are widely accessible in local markets and favored for their rustic aesthetic and lightweight nature, making them ideal for casual gardeners and budget-conscious buyers. The cost-efficiency and availability of earthenware make it a popular choice, while bio-ceramic appeals to those seeking long-term investment in quality and performance.
Making the Right Choice: Which Pot is Best?
Bio-ceramic pots offer superior durability and non-toxic properties, making them ideal for health-conscious cooking and long-term use, while earthenware pots provide excellent heat retention and traditional aesthetics that enhance slow-cooked flavors. Choosing the right pot depends on your cooking style: bio-ceramics excel in modern, versatile applications with easy maintenance, and earthenware suits rustic, slow-cooking methods where flavor infusion is key. Consider factors like thermal conductivity, porosity, and intended use to determine which material aligns best with your culinary needs.
Infographic: Bio-ceramic vs Earthenware for Pot
 azmater.com
azmater.com