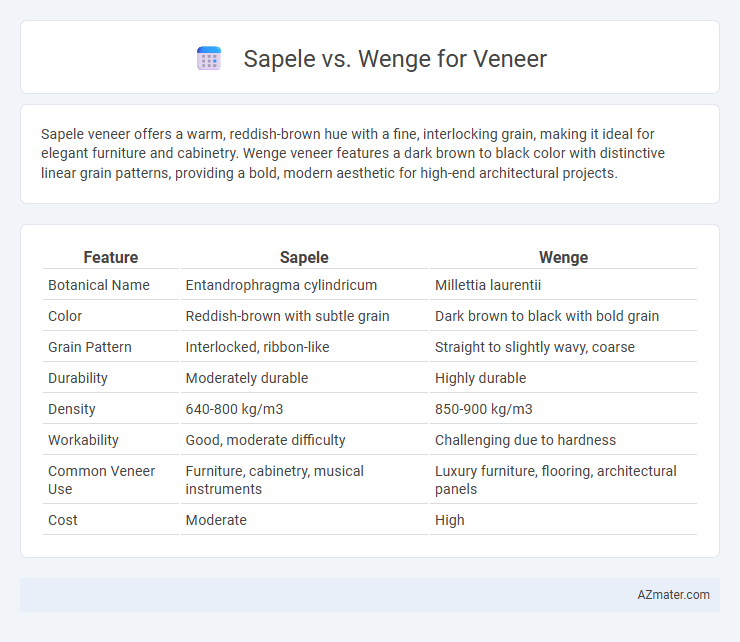
Sapele veneer offers a warm, reddish-brown hue with a fine, interlocking grain, making it ideal for elegant furniture and cabinetry. Wenge veneer features a dark brown to black color with distinctive linear grain patterns, providing a bold, modern aesthetic for high-end architectural projects.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sapele | Wenge |
|---|---|---|
| Botanical Name | Entandrophragma cylindricum | Millettia laurentii |
| Color | Reddish-brown with subtle grain | Dark brown to black with bold grain |
| Grain Pattern | Interlocked, ribbon-like | Straight to slightly wavy, coarse |
| Durability | Moderately durable | Highly durable |
| Density | 640-800 kg/m3 | 850-900 kg/m3 |
| Workability | Good, moderate difficulty | Challenging due to hardness |
| Common Veneer Use | Furniture, cabinetry, musical instruments | Luxury furniture, flooring, architectural panels |
| Cost | Moderate | High |
Introduction to Sapele and Wenge Veneer
Sapele veneer, derived from the African Sapele tree, offers a rich reddish-brown color with fine, interlocked grain patterns ideal for high-end furniture and cabinetry. Wenge veneer, harvested from the Wenge tree native to Central Africa, features a dark brown to black hue with distinctive straight grains that provide a dramatic, modern appearance. Both veneers are prized for their durability, aesthetic appeal, and versatility in luxury interior design applications.
Botanical Origins and Growth Regions
Sapele veneer originates from *Entandrophragma cylindricum*, a hardwood tree native to tropical West Africa, particularly Ghana, Nigeria, and Ivory Coast, while Wenge comes from *Millettia laurentii*, found primarily in the Congo Basin of Central Africa. Both species thrive in humid, tropical climates but differ in their ecological niches, with Sapele favoring slightly drier conditions and Wenge growing in wetter, swampy areas. These distinct botanical origins and growth regions influence the density, grain pattern, and coloration of the veneers, making each wood unique for specific decorative applications.
Appearance and Grain Patterns
Sapele veneer exhibits a warm, reddish-brown hue with a fine, interlocked grain pattern that creates a shimmering effect known as "chatoyancy," enhancing its visual appeal in furniture and cabinetry. Wenge veneer is characterized by a deep, dark brown to black color with bold, straight, and pronounced grain lines that provide a striking, dramatic contrast ideal for modern and luxurious interior designs. Both woods offer unique aesthetics, with Sapele leaning towards elegance and warmth, while Wenge delivers a robust, contemporary look with its distinctive grain patterns.
Color Characteristics and Aging
Sapele veneer exhibits a warm reddish-brown color with subtle golden highlights that deepen and develop a richer, more lustrous patina as it ages. In contrast, Wenge veneer features a dark chocolate-brown base with pronounced black streaks that maintain their intense contrast over time, often darkening slightly but retaining its dramatic appearance. Both woods offer striking visual appeal, but Sapele's color evolves more noticeably with age, while Wenge's distinct grain pattern remains consistently bold.
Physical Properties and Durability
Sapele veneer offers a medium density of approximately 640 kg/m3, providing excellent stability and moderate hardness, making it resistant to wear and dents in furniture applications. Wenge veneer is denser, around 830 kg/m3, with high hardness and exceptional durability, ideal for heavy-use surfaces and flooring due to its resistance to abrasion and impact. Both species exhibit good natural resistance to decay and insects, but Wenge's greater density enhances its long-term durability in demanding environments.
Workability and Machining Ease
Sapele veneer offers excellent workability with a fine, consistent grain that cuts and sands smoothly, making it ideal for precision machining. Wenge veneer, while visually striking with its dark, bold streaks, is denser and harder, often requiring sharper tools and slower feed rates for clean cuts. Both veneers provide durability, but Sapele's machinability generally leads to fewer tool wear issues and a faster production process in veneer applications.
Common Applications in Veneer
Sapele veneer is widely used in furniture making, cabinetry, and decorative wall panels due to its rich reddish-brown hue and fine grain that adds elegance and warmth to interiors. Wenge veneer is favored for high-end flooring, musical instruments, and modern furniture, prized for its dark, dramatic coloring and striking, coarse grain pattern that creates a bold visual statement. Both woods are chosen for veneer applications where durability and aesthetic appeal are paramount, with Sapele offering a more traditional look and Wenge providing a contemporary, exotic finish.
Cost and Market Availability
Sapele veneer is generally more affordable and widely available due to its abundant supply from West African forests, making it a popular choice in the veneer market. Wenge veneer, sourced primarily from Central Africa, tends to be more expensive and less accessible because of its limited availability and higher demand in luxury woodworking. Cost differences reflect supply constraints and regional logging restrictions that impact Wenge more significantly than Sapele.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
Sapele veneer is often favored for its certified sustainable harvesting practices and lower environmental impact due to faster growth rates compared to Wenge, which is sourced from slow-growing trees primarily in Central Africa. Wenge veneer faces higher sustainability concerns because overharvesting and illegal logging threaten its population, leading to stricter trade regulations under CITES. Choosing Sapele supports responsible forestry certification and reduces ecological harm, while Wenge requires careful sourcing to ensure compliance with conservation efforts.
Choosing Between Sapele and Wenge for Your Project
Sapele veneer offers a warm, reddish-brown hue with fine, interlocked grain, making it ideal for elegant, classic interiors, while Wenge veneer features a dark brown to black coloration with prominent, straight grain, perfect for bold, contemporary designs. Both woods provide hardness and durability, but Wenge tends to be denser and more resistant to wear, suited for high-traffic areas or furniture surfaces subjected to heavy use. Selecting between Sapele and Wenge hinges on the desired aesthetic impact and functional requirements, balancing Sapele's rich warmth against Wenge's striking contrast and toughness.
Infographic: Sapele vs Wenge for Veneer
 azmater.com
azmater.com