Fir offers superior strength and durability for doors, making it ideal for high-traffic areas. Poplar is lightweight and more affordable but less resistant to dents and moisture, suitable for interior doors with minimal wear.
Table of Comparison
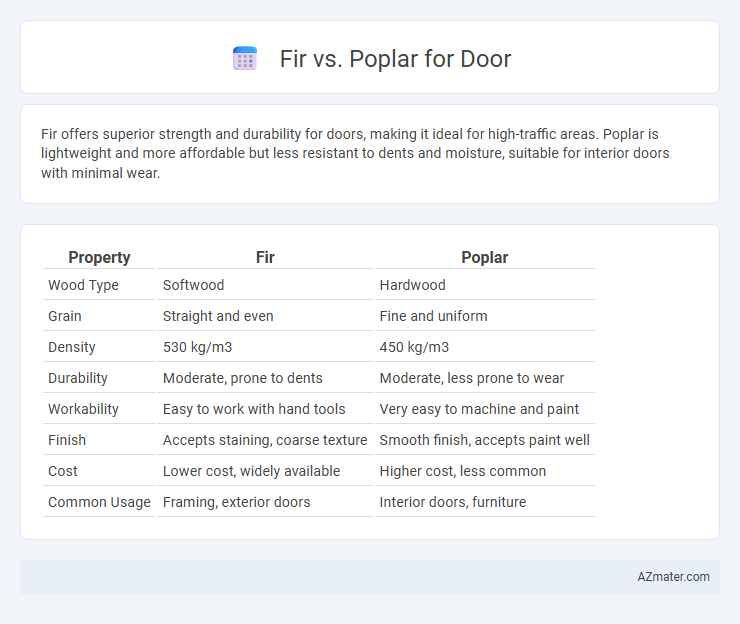
| Property | Fir | Poplar |
|---|---|---|
| Wood Type | Softwood | Hardwood |
| Grain | Straight and even | Fine and uniform |
| Density | 530 kg/m3 | 450 kg/m3 |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to dents | Moderate, less prone to wear |
| Workability | Easy to work with hand tools | Very easy to machine and paint |
| Finish | Accepts staining, coarse texture | Smooth finish, accepts paint well |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely available | Higher cost, less common |
| Common Usage | Framing, exterior doors | Interior doors, furniture |
Introduction to Fir and Poplar Wood
Fir wood, known for its strength and durability, is commonly used in door construction due to its fine, straight grain and resistance to warping, making it ideal for exterior doors. Poplar wood, prized for its affordability and ease of machining, features a softer texture with a smooth finish, often selected for interior doors and painted applications. Both woods offer distinct advantages: Fir delivers robustness and longevity, while Poplar provides versatility and cost-effectiveness for door manufacturing.
Key Characteristics of Fir for Doors
Fir wood, known for its straight grain and uniform texture, offers excellent strength and durability, making it a reliable choice for doors. Its natural resistance to warping and shrinking ensures long-lasting stability, while the light reddish-brown hue provides an attractive, warm aesthetic. Fir's ease of finishing and sanding enhances its versatility for both interior and exterior door applications.
Key Characteristics of Poplar for Doors
Poplar is a lightweight hardwood known for its smooth texture and uniform grain, making it easy to paint and finish for door applications. Its moderate strength and resistance to warping ensure durability and stability in interior doors. Poplar's affordability and workability make it a popular choice for custom door designs requiring a refined, consistent appearance.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Fir wood offers superior durability and strength compared to poplar, making it more suitable for doors that require long-lasting structural integrity. Fir's dense grain and natural resistance to warping contribute to a robust door frame capable of withstanding heavy use and environmental stress. In contrast, poplar tends to be softer and less durable, making it better suited for interior doors or decorative elements rather than high-traffic entry points.
Appearance and Grain Differences
Fir wood features a straight, uniform grain with a pale reddish-brown hue that darkens over time, offering a smooth and consistent appearance ideal for modern doors. Poplar typically exhibits a more varied grain pattern with occasional knots and a lighter, yellowish to greenish tint, providing a more rustic or natural look. The distinct grain textures and color variations between fir and poplar significantly influence the visual appeal and style of doors in residential and commercial settings.
Workability and Ease of Finishing
Fir offers excellent workability due to its straight grain and soft texture, making it easy to cut, shape, and fasten with minimal effort. Poplar is also highly workable, featuring a fine, even texture that sands smoothly and holds paint and stains well, resulting in an excellent finish. Both woods provide ease of finishing, but Poplar's uniform grain often yields a more consistent, high-quality painted surface.
Cost Comparison: Fir vs. Poplar
Fir doors generally have a lower cost due to the wood's widespread availability and faster growth rate, making fir an economical choice for budget-conscious projects. Poplar tends to be moderately priced, slightly higher than fir, because of its smoother finish and better paint adhesion which reduces the need for extensive surface preparation. Comparing long-term value, fir offers affordability upfront, while poplar may reduce refinishing costs, impacting overall lifecycle expenses.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Fir wood, known for its rapid growth and renewable qualities, offers a lower environmental impact compared to poplar due to its efficient carbon sequestration and minimal chemical processing during door manufacturing. Poplar, while also a fast-growing species, often involves more intensive farming practices that can affect soil health and biodiversity, thereby reducing its overall sustainability. Choosing fir doors supports sustainable forestry practices and reduces carbon footprint, making it a preferable option for eco-conscious construction.
Best Applications for Fir Doors
Fir doors are ideal for exterior and interior applications due to their strength, durability, and resistance to warping. The fine, straight grain of fir makes it excellent for door frames and panels that require a smooth finish and stability. Fir's ability to hold paint and stain well ensures long-lasting aesthetics, particularly in high-traffic areas exposed to varying weather conditions.
Best Applications for Poplar Doors
Poplar doors are best suited for interior applications due to their smooth texture and stability, making them ideal for painted finishes that complement modern and traditional decor. Fir, being denser and more durable, is preferred for exterior doors exposed to weather variations. Poplar's affordability and workability make it a popular choice for lightweight, decorative interior door designs where moisture resistance is less critical.
Infographic: Fir vs Poplar for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com