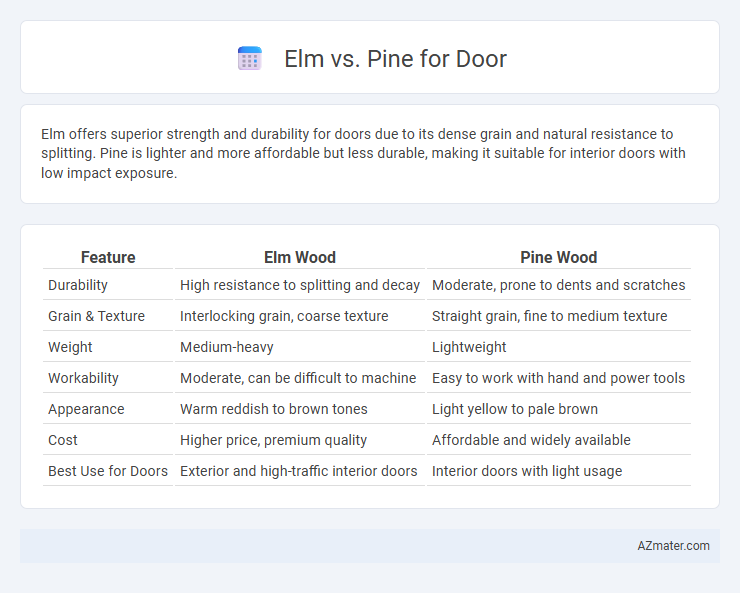
Elm offers superior strength and durability for doors due to its dense grain and natural resistance to splitting. Pine is lighter and more affordable but less durable, making it suitable for interior doors with low impact exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Elm Wood | Pine Wood |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High resistance to splitting and decay | Moderate, prone to dents and scratches |
| Grain & Texture | Interlocking grain, coarse texture | Straight grain, fine to medium texture |
| Weight | Medium-heavy | Lightweight |
| Workability | Moderate, can be difficult to machine | Easy to work with hand and power tools |
| Appearance | Warm reddish to brown tones | Light yellow to pale brown |
| Cost | Higher price, premium quality | Affordable and widely available |
| Best Use for Doors | Exterior and high-traffic interior doors | Interior doors with light usage |
Introduction: Elm vs Pine Doors
Elm doors offer exceptional durability and natural resistance to wear, making them ideal for high-traffic areas, while pine doors provide a lightweight and cost-effective option with a smooth surface perfect for painting. Elm's dense grain structure enhances its strength and resistance to moisture, contrasting with pine's softer texture, which may dent more easily but allows for easier customization. Choosing between elm and pine doors depends on balancing durability needs against budget and aesthetic preferences.
Wood Characteristics Overview
Elm wood features a coarse, interlocking grain that provides excellent resistance to splitting, making it ideal for durable door construction. Pine, characterized by its straight grain and softer texture, offers ease of machining and a lighter weight, though it is less resistant to dents and wear. Elm's higher density and moisture resistance contribute to superior longevity, while Pine's affordability and availability make it a popular choice for budget-conscious projects.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Elm wood offers exceptional durability due to its interlocking grain, making it highly resistant to splitting and ideal for door construction in high-traffic areas. Pine, while easier to work with and more affordable, lacks the same strength and tends to dent or scratch more easily under stress. Doors made from elm provide superior long-term resilience and structural integrity compared to pine doors, especially in environments subject to frequent impacts or heavy use.
Aesthetic Appearance and Grain Patterns
Elm wood showcases a distinctive interlocking grain pattern that creates unique, wavy textures ideal for rustic or traditional door designs. Pine offers a lighter, more uniform grain with knots that add character but provide a simpler, more casual aesthetic suited for cottage or country-style doors. The choice between elm's rich, textured appearance and pine's clean, soft grains depends on the desired visual impact and interior design style.
Resistance to Moisture and Warping
Elm wood offers moderate resistance to moisture and warping, making it suitable for doors exposed to varying humidity, thanks to its interlocking grain that reduces deformation. Pine, being a softwood, is less resistant to moisture and more prone to warping and swelling, requiring proper sealing and maintenance for durability in moist environments. Choosing elm for doors in humid or fluctuating climates ensures better structural stability and longevity compared to pine.
Cost and Availability
Elm door materials generally offer moderate cost with good availability in most regions, making them a practical choice for budget-conscious projects. Pine doors typically cost less than Elm, providing an economical option, especially where availability is high due to its widespread growth and faster harvesting cycles. Both woods are commonly available, but Pine benefits from larger supply chains and lower price points, influencing overall affordability.
Maintenance and Longevity
Elm offers exceptional durability and resistance to wear, making it a low-maintenance choice for doors exposed to heavy use. Pine requires regular sealing and refinishing to protect against moisture and wear but is easier to repair due to its softer grain. Longevity favors Elm as it naturally withstands decay and damage longer, often lasting several decades with minimal upkeep.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Elm wood demonstrates notable environmental benefits due to its rapid growth rate and high carbon sequestration capacity, promoting sustainable forestry practices. Pine wood, widely available and fast-growing, supports renewable resource management but often requires chemical treatments that may impact eco-friendliness. Choosing elm for doors reduces carbon footprint and encourages biodiversity, while pine remains a versatile, cost-effective option with moderate sustainability credentials.
Best Applications for Each Wood
Elm wood, known for its interlocking grain and durability, excels in crafting sturdy exterior doors due to its resistance to splitting and warping under various weather conditions. Pine, characterized by its light weight and softer texture, is ideal for interior doors where ease of machining and affordability are prioritized. Elm's natural strength makes it suitable for heavy-use areas, while pine offers versatility and a smooth finish for decorative purposes.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Elm and Pine for Doors
Elm offers superior durability and resistance to moisture, making it ideal for exterior doors that require long-lasting strength and weather resistance. Pine is a cost-effective, lightweight option that works well for interior doors where ease of customization and a smooth finish are priorities. Selecting between elm and pine depends on the door's location and functional needs, with elm suited for heavy-duty use and pine favored for budget-friendly, decorative applications.
Infographic: Elm vs Pine for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com