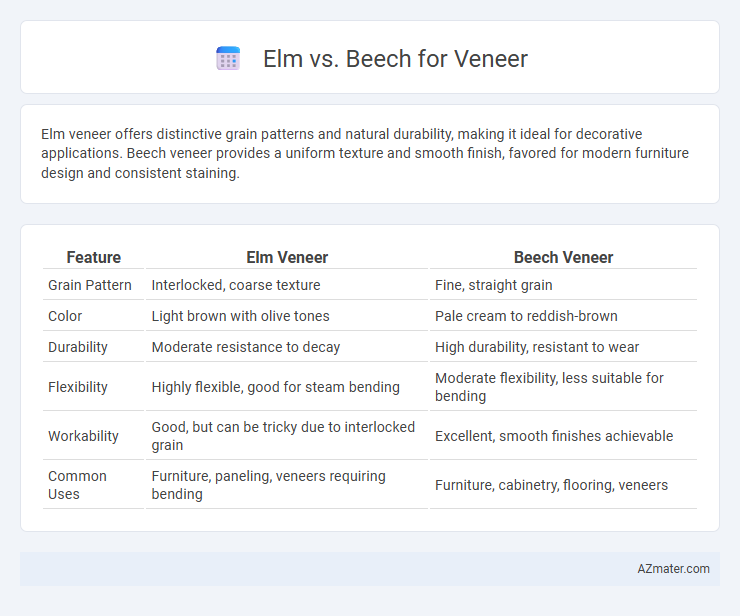
Elm veneer offers distinctive grain patterns and natural durability, making it ideal for decorative applications. Beech veneer provides a uniform texture and smooth finish, favored for modern furniture design and consistent staining.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Elm Veneer | Beech Veneer |
|---|---|---|
| Grain Pattern | Interlocked, coarse texture | Fine, straight grain |
| Color | Light brown with olive tones | Pale cream to reddish-brown |
| Durability | Moderate resistance to decay | High durability, resistant to wear |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, good for steam bending | Moderate flexibility, less suitable for bending |
| Workability | Good, but can be tricky due to interlocked grain | Excellent, smooth finishes achievable |
| Common Uses | Furniture, paneling, veneers requiring bending | Furniture, cabinetry, flooring, veneers |
Introduction to Elm and Beech Veneer
Elm veneer offers a distinctive grain pattern characterized by interlocking fibers and a warm, honey-brown hue that enhances furniture and interior paneling with natural texture and durability. Beech veneer is prized for its fine, consistent grain and pale cream color, providing a smooth, elegant surface ideal for modern cabinetry and decorative veneers. Both woods are valued for their workability and strength, making them popular choices in woodworking and design projects.
Botanical Overview: Elm vs Beech
Elm (genus Ulmus) and Beech (genus Fagus) differ significantly in botanical characteristics affecting veneer quality. Elm trees, belonging to the Ulmaceae family, are deciduous hardwoods known for their interlocking grain which provides strength and resistance to splitting, making elm veneer unique in texture and durability. Beech trees, members of the Fagaceae family, offer a finer, uniform grain with a pale cream color, prized in veneer for its smooth finish and excellent stain absorption, commonly used in furniture and cabinetry.
Aesthetic Differences in Veneer Appearance
Elm veneer showcases distinctive interlocking grain patterns with a rich, warm hue ranging from light brown to reddish tones, creating a rustic and dramatic visual appeal. Beech veneer features a fine, straight grain with a uniform, pale cream to light pink coloration, offering a clean and contemporary look ideal for minimalist designs. The contrasting grain complexity and color saturation between Elm's bold texture and Beech's subtle uniformity make them suitable for different aesthetic preferences in veneer applications.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Elm veneer offers moderate durability with good resistance to splitting due to its interlocking grain, making it suitable for furniture and paneling that require flexibility. Beech veneer is known for its high strength and hardness, providing excellent wear resistance and structural stability, ideal for heavy-use surfaces and cabinetry. While elm provides better shock resistance, beech outperforms in overall strength and longevity for veneer applications.
Workability and Machining Properties
Elm veneer offers excellent workability with its interlocking grain that resists splitting during machining, providing a smooth finish suitable for furniture and paneling. Beech veneer is highly regarded for its uniform texture and hardness, making it easy to machine with minimal tool wear while delivering consistent edges and surfaces. Both woods perform well under machining processes, but Elm's open grain requires careful handling to prevent tear-out, whereas Beech's fine grain allows for cleaner cuts and finer detailing.
Cost Comparison: Elm vs Beech Veneer
Elm veneer typically costs more than beech veneer due to its unique grain patterns and limited availability, making it a premium choice for furniture and interior design. Beech veneer offers a more economical option with consistent grain and widespread use in mass-produced items, providing good value without compromising quality. The price difference between elm and beech veneer generally reflects the rarity and aesthetic appeal of elm compared to the practical affordability of beech.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Elm veneer is often favored for its durability and natural resistance to pests, contributing to a longer lifecycle and reduced need for chemical treatments, which enhances its environmental sustainability. Beech veneer, sourced from rapidly growing, widely replanted forests, tends to have a lower carbon footprint due to efficient regeneration and high yield per hectare. Both woods support sustainable forestry when harvested responsibly, but beech's faster growth rate and higher availability make it a more eco-friendly option in large-scale veneer production.
Common Applications and Uses
Elm veneer is commonly used in furniture making, cabinetry, and decorative paneling due to its attractive interlocking grain and durability. Beech veneer is favored for flooring, plywood, and kitchen utensils because of its hardness, fine texture, and light color that easily accepts stains. Both woods provide strong, visually appealing surfaces ideal for interior design and woodworking applications.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Elm veneer requires moderate maintenance due to its open grain structure, which can absorb moisture and stains if not properly sealed, necessitating regular cleaning with a damp cloth and occasional polishing to maintain its appearance. Beech veneer offers lower maintenance as its tight grain resists moisture and staining better, allowing for easier cleaning with mild detergents and minimal polishing. Both wood veneers benefit from avoiding excessive exposure to direct sunlight and humidity to prevent warping and discoloration, preserving their durability and aesthetic appeal.
Choosing the Right Veneer for Your Project
Elm veneer offers a distinctive interlocking grain pattern that provides strong durability and a warm, rustic aesthetic ideal for traditional or craftsman-style furniture. Beech veneer features a tight, consistent grain with a pale creamy color, making it perfect for modern designs seeking a smooth, uniform surface that can be easily stained or finished. Selecting between elm and beech veneers depends on the desired visual texture and project durability, with elm favoring character and hardness, while beech emphasizes versatility and subtle elegance.
Infographic: Elm vs Beech for Veneer
 azmater.com
azmater.com