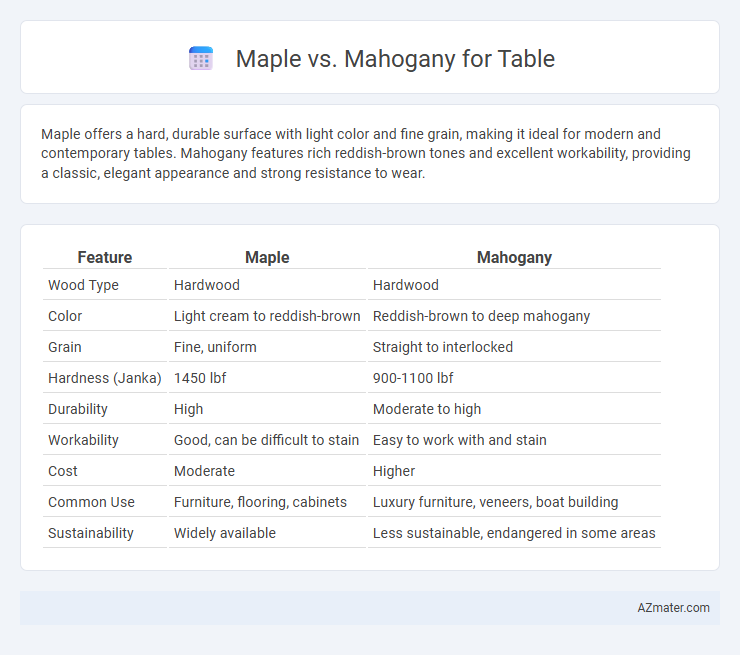
Maple offers a hard, durable surface with light color and fine grain, making it ideal for modern and contemporary tables. Mahogany features rich reddish-brown tones and excellent workability, providing a classic, elegant appearance and strong resistance to wear.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Maple | Mahogany |
|---|---|---|
| Wood Type | Hardwood | Hardwood |
| Color | Light cream to reddish-brown | Reddish-brown to deep mahogany |
| Grain | Fine, uniform | Straight to interlocked |
| Hardness (Janka) | 1450 lbf | 900-1100 lbf |
| Durability | High | Moderate to high |
| Workability | Good, can be difficult to stain | Easy to work with and stain |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
| Common Use | Furniture, flooring, cabinets | Luxury furniture, veneers, boat building |
| Sustainability | Widely available | Less sustainable, endangered in some areas |
Maple vs Mahogany for Table: An Overview
Maple offers a lighter color and higher hardness rating around 1450 on the Janka scale, ideal for durable, scratch-resistant tables. Mahogany provides rich reddish-brown hues with a Janka rating near 900, valued for its elegant appearance and smooth grain. Choosing between maple and mahogany depends on preferences for durability versus aesthetic warmth in table design.
Appearance and Grain Patterns
Maple wood features a light, creamy color with a smooth, consistent grain pattern that enhances modern and minimalist table designs. Mahogany offers a rich, reddish-brown hue with a more pronounced, open grain pattern that adds warmth and character to traditional or classic furniture styles. Choosing between maple and mahogany depends on the desired aesthetic impact and the balance between subtlety and visual richness in table appearance.
Hardness and Durability Comparison
Maple exhibits a Janka hardness rating of approximately 1450, making it a highly durable hardwood ideal for tables subjected to daily use and heavy wear. Mahogany, with a slightly lower Janka rating around 900 to 1100 depending on the species, offers moderate hardness but superior resistance to decay and moisture. While maple provides exceptional scratch and dent resistance for long-lasting table surfaces, mahogany excels in stability and color retention, contributing to its timeless aesthetic appeal in furniture design.
Weight Differences: Maple vs Mahogany
Maple is denser and heavier than mahogany, with an average weight of around 44-47 lbs per cubic foot compared to mahogany's 32-36 lbs per cubic foot. This significant weight difference affects table stability and portability, making maple tables sturdier but less easy to move. Choosing between maple and mahogany depends on whether a heavier, more durable surface or a lighter, more manageable table is preferred.
Workability: Crafting Tables with Maple or Mahogany
Maple offers excellent workability for crafting tables due to its fine, even grain and hardness, which allows for smooth sanding and detailed carving while resisting wear. Mahogany, known for its straight, coarse grain and medium hardness, excels in ease of machining and finishing, providing a rich, polished appearance with less effort. Both woods accommodate various joinery techniques, but maple's density may require sharper tools for precision, whereas mahogany's softer texture facilitates faster shaping and refinishing.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Maple is generally more affordable and widely available compared to mahogany, making it a popular choice for budget-conscious table projects. Mahogany tends to be more expensive due to its limited supply and luxurious appeal, often sourced from specific tropical regions with strict harvesting regulations. Availability challenges and higher costs make mahogany tables a premium investment, whereas maple offers a cost-effective and accessible alternative without compromising sturdiness.
Maintenance and Longevity
Maple tables require less maintenance due to their hard, dense grain that resists dents and scratches, making them ideal for high-use areas. Mahogany, though more prone to surface marks, offers exceptional longevity with proper care thanks to its natural oils that protect the wood from moisture and decay. Both woods benefit from regular cleaning and occasional refinishing to preserve their appearance and durability over time.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Maple wood, sourced primarily from sustainably managed forests in North America, offers a lower environmental impact due to its faster growth rates and efficient carbon sequestration. Mahogany, often harvested from tropical rainforests, faces challenges related to deforestation, habitat loss, and slower regrowth, making its sustainability more questionable without certified sourcing such as FSC. Choosing FSC-certified maple or mahogany ensures reduced ecological footprints and supports responsible forestry practices.
Table Design Styles: Best Uses for Each Wood
Maple's light color and fine, consistent grain make it ideal for modern and Scandinavian table designs, offering a sleek, minimalist aesthetic that complements clean lines and light interiors. Mahogany's rich, reddish-brown hue and pronounced grain pattern suit classic, traditional, and antique-style tables, adding warmth and elegance to formal dining rooms or vintage-inspired spaces. Both woods provide durability, but maple's hardness lends itself well to high-traffic or contemporary settings, while mahogany enhances luxury and timeless appeal in crafted, heirloom-quality furniture.
Final Verdict: Choosing Between Maple and Mahogany for Your Table
Maple offers exceptional durability and a lighter, consistent grain, making it ideal for tables requiring heavy use and a modern aesthetic. Mahogany provides rich, warm tones with natural resistance to decay, perfect for elegant, traditional designs and longevity. The final choice depends on your preference for style and durability: opt for maple for a robust, contemporary table or mahogany for a classic, luxurious piece.
Infographic: Maple vs Mahogany for Table
 azmater.com
azmater.com