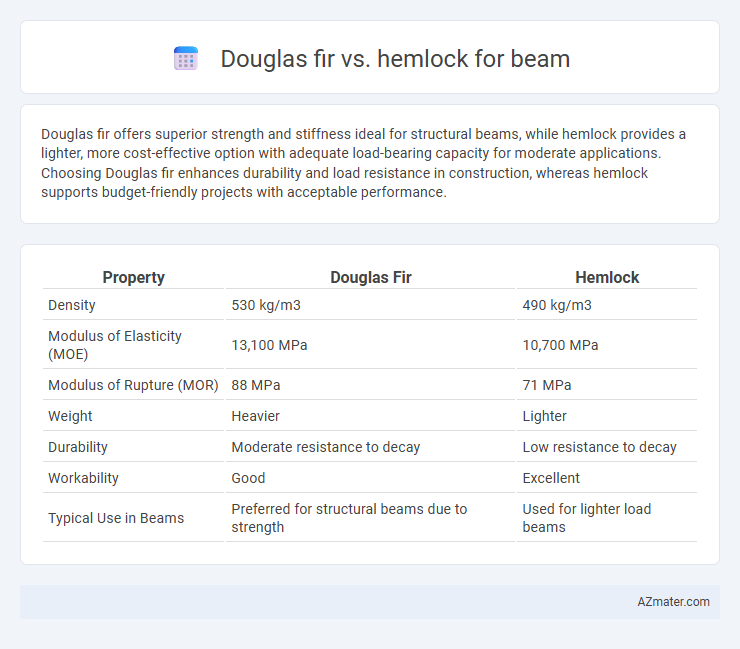
Douglas fir offers superior strength and stiffness ideal for structural beams, while hemlock provides a lighter, more cost-effective option with adequate load-bearing capacity for moderate applications. Choosing Douglas fir enhances durability and load resistance in construction, whereas hemlock supports budget-friendly projects with acceptable performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Douglas Fir | Hemlock |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 530 kg/m3 | 490 kg/m3 |
| Modulus of Elasticity (MOE) | 13,100 MPa | 10,700 MPa |
| Modulus of Rupture (MOR) | 88 MPa | 71 MPa |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Durability | Moderate resistance to decay | Low resistance to decay |
| Workability | Good | Excellent |
| Typical Use in Beams | Preferred for structural beams due to strength | Used for lighter load beams |
Introduction to Douglas Fir and Hemlock Beams
Douglas fir beams are renowned for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for structural applications requiring durability and load-bearing capacity. Hemlock beams offer a straight grain and uniform texture, providing reliable stability and ease of machining in construction projects. Both species are favored for their resistance to warping and attractive finish, but Douglas fir tends to outperform Hemlock in tensile strength and stiffness.
Wood Strength and Structural Performance
Douglas fir exhibits superior wood strength and structural performance compared to hemlock, with a higher modulus of elasticity (about 12,100 MPa) and greater bending strength (approximately 104 MPa). This makes Douglas fir beams more suitable for heavy load-bearing applications and long-span structures, offering enhanced durability and resistance to deformation. Hemlock, while still structurally reliable, has a lower stiffness and strength profile, limiting its use in high-stress beam installations.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Douglas fir beams exhibit superior durability and longevity compared to Hemlock, thanks to their dense grain structure and natural resistance to decay and insect damage. Hemlock, while lighter and easier to work with, is more susceptible to moisture and fungal attacks, reducing its lifespan in structural applications. For long-term beam installations, Douglas fir provides enhanced strength retention and greater resilience in harsh environmental conditions.
Workability and Ease of Installation
Douglas fir beams offer superior workability due to their straight grain and uniform texture, making them easier to saw and nail with minimal splintering. Hemlock beams, while slightly harder and denser, may require more effort during cutting and fastening but provide good dimensional stability. Both woods are relatively easy to install, though Douglas fir's lighter weight and smoother surface can speed up handling and fitting on site.
Resistance to Decay and Insects
Douglas fir exhibits higher resistance to decay and insect infestations compared to Hemlock, making it a preferred choice for beams in exterior or moist environments. The natural resin content in Douglas fir enhances its durability, while Hemlock is more susceptible to fungal decay and insect damage without proper treatment. Selecting Douglas fir beams effectively reduces maintenance costs and extends structural lifespan in challenging conditions.
Cost Differences and Budget Considerations
Douglas fir beams generally cost more than hemlock due to their superior strength, density, and durability, making them ideal for structural applications requiring high load-bearing capacity. Hemlock offers a more budget-friendly option with adequate strength for lighter loads, but it is less resistant to decay and may require additional treatment or maintenance. Selecting between Douglas fir and hemlock depends on balancing upfront material costs against long-term durability and maintenance expenses within the project's budget.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Douglas fir beams are favored for their rapid growth rate and carbon sequestration capabilities, making them a more sustainable option compared to hemlock. Hemlock's slower growth and less efficient carbon storage result in a higher environmental impact over the lifecycle of the beam. Selecting Douglas fir supports sustainable forestry practices due to its abundance and renewability in managed forests.
Aesthetic Qualities and Grain Patterns
Douglas fir beams showcase a rich, warm reddish-brown hue with prominent, straight grain patterns that offer a bold and rustic aesthetic, making them ideal for exposed structural elements in traditional and modern designs. Hemlock beams present a lighter, creamy to pale pinkish tone with finer, more uniform grains that produce a smoother, subtle texture, preferred for a clean and elegant appearance. Both wood types provide distinct visual appeal, with Douglas fir emphasizing robust character and Hemlock highlighting understated refinement in architectural applications.
Common Applications in Construction
Douglas fir beams are preferred in construction for their high strength-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for heavy-load-bearing structures such as floor joists, roof trusses, and bridge components. Hemlock beams, while less strong than Douglas fir, are commonly used in non-structural or light framing applications including interior trim, paneling, and decorative beams. The natural durability and dimensional stability of Douglas fir often result in longer-lasting support elements, whereas Hemlock is favored for its ease of machining and aesthetic appeal in finishes.
Choosing the Right Wood: Douglas Fir or Hemlock
Douglas Fir offers superior strength and stiffness, making it a top choice for structural beams in construction where load-bearing capacity is critical. Hemlock, while more affordable and easier to work with due to its fine grain, is less durable and has lower resistance to decay, which may limit its use in heavy structural applications. Selecting Douglas Fir over Hemlock ensures enhanced performance and longevity in beam installations, particularly in demanding architectural or engineering projects.
Infographic: Douglas fir vs Hemlock for Beam
 azmater.com
azmater.com