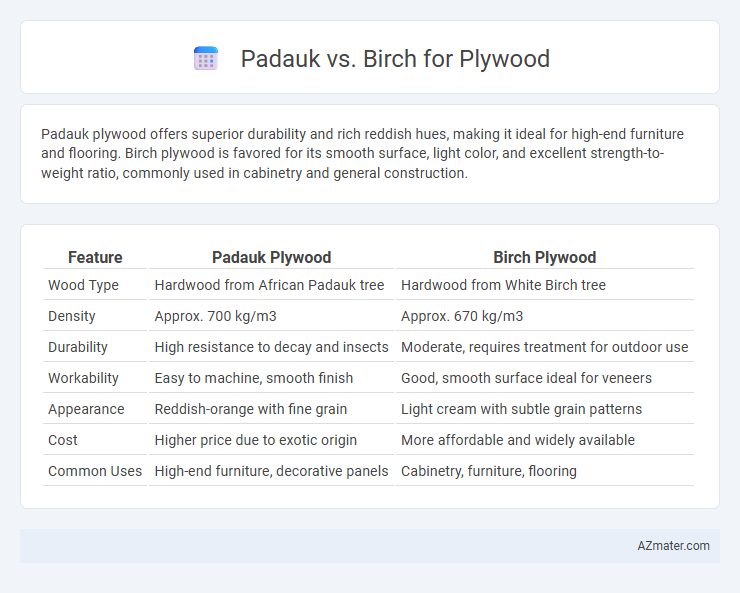
Padauk plywood offers superior durability and rich reddish hues, making it ideal for high-end furniture and flooring. Birch plywood is favored for its smooth surface, light color, and excellent strength-to-weight ratio, commonly used in cabinetry and general construction.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Padauk Plywood | Birch Plywood |
|---|---|---|
| Wood Type | Hardwood from African Padauk tree | Hardwood from White Birch tree |
| Density | Approx. 700 kg/m3 | Approx. 670 kg/m3 |
| Durability | High resistance to decay and insects | Moderate, requires treatment for outdoor use |
| Workability | Easy to machine, smooth finish | Good, smooth surface ideal for veneers |
| Appearance | Reddish-orange with fine grain | Light cream with subtle grain patterns |
| Cost | Higher price due to exotic origin | More affordable and widely available |
| Common Uses | High-end furniture, decorative panels | Cabinetry, furniture, flooring |
Introduction to Padauk and Birch for Plywood
Padauk and Birch are two distinct hardwoods commonly used in plywood manufacturing, valued for their durability and aesthetic appeal. Padauk, known for its rich reddish-orange hue and natural resistance to decay, offers excellent strength and stability, making it ideal for high-end furniture and decorative applications. Birch plywood, characterized by its pale color and smooth grain, provides superior workability and uniform strength, often favored in cabinetry and structural uses due to its consistent performance and affordability.
Botanical Origins and Availability
Padauk plywood is derived from several species within the Pterocarpus genus, primarily Pterocarpus soyauxii, native to tropical Africa, known for its durability and rich reddish hue. Birch plywood comes from Betula species, predominantly Betula pendula and Betula papyrifera, native to temperate regions of Europe, Asia, and North America, valued for its fine grain and pale color. Availability of Padauk plywood is limited and often costly due to slow growth and restricted geographic range, while Birch plywood is widely accessible and economical, benefiting from faster growth rates and extensive forestry management.
Color and Grain Comparison
Padauk plywood features a vivid reddish-orange hue that deepens over time, creating a striking visual appeal, while birch plywood displays a light cream to pale yellow color with a subtle, uniform grain. Padauk's distinctive coarse, interlocked grain pattern contrasts with birch's fine, straight grain, offering more texture and character in finished surfaces. The choice between padauk and birch plywood often depends on the desired warmth and boldness of color versus a lighter, more neutral aesthetic.
Strength and Durability: Padauk vs Birch
Padauk plywood exhibits superior strength and durability compared to birch, boasting a higher density and natural resistance to decay and insect damage, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. Birch plywood, while strong and stable, is less dense and more prone to moisture damage, requiring additional sealing for outdoor or high-moisture environments. The inherent hardness and toughness of Padauk contribute to its longer lifespan and better performance under stress in structural projects.
Workability and Machining
Padauk plywood offers superior workability due to its smooth texture and natural oils, allowing for easy cutting, sanding, and shaping with minimal dulling of tools. Birch plywood, known for its fine grain and uniform texture, provides excellent machining capabilities with consistent results in drilling, routing, and finishing processes. The density of birch ensures less splintering and chip-out, while padauk's hardness demands sharper tools but yields a highly polished surface.
Moisture Resistance and Stability
Padauk plywood exhibits superior moisture resistance compared to birch plywood due to its dense and oily grain structure, which naturally repels water and reduces swelling. Birch plywood, while strong and stable under dry conditions, tends to absorb moisture more readily, leading to potential warping or delamination over time. For applications requiring enhanced durability in humid or wet environments, padauk plywood offers better long-term stability and performance than birch.
Cost and Market Value
Padauk plywood commands a higher market value due to its rich reddish hue, durability, and resistance to decay, making it a premium choice for luxury furniture and high-end applications. Birch plywood is more cost-effective, offering consistent performance and strength at a lower price, widely favored in construction and cabinetry for budget-conscious projects. The cost disparity reflects Padauk's rarity and aesthetic appeal versus Birch's availability and versatility in the marketplace.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Padauk plywood offers superior sustainability due to its fast growth rate and ability to regenerate quickly in tropical forests, reducing deforestation pressures compared to birch, which grows more slowly in temperate zones. Birch plywood, while durable and widely used, often involves harvesting from older forests, raising concerns about habitat disruption and carbon sequestration loss. Choosing padauk supports more sustainable forestry practices and lower environmental footprints, making it a greener option for responsible plywood production.
Best Applications for Padauk Plywood
Padauk plywood is highly valued for its rich reddish-brown color, exceptional durability, and resistance to decay, making it ideal for high-end furniture, decorative veneers, and flooring applications. Its natural hardness and dimensional stability allow it to withstand heavy use and environmental changes, which is crucial for cabinetry and architectural millwork. Unlike birch plywood, which is lighter and often chosen for cost-effective projects, Padauk plywood excels in luxury interior finishes and outdoor projects requiring both aesthetic appeal and long-lasting performance.
Best Uses for Birch Plywood
Birch plywood is highly valued for its strength, smooth finish, and light color, making it ideal for furniture, cabinetry, and cabinetry where a clean, modern look is desired. It offers excellent stability and fine grain, suitable for painting and veneers, enhancing aesthetic versatility in interior design projects. Compared to Padauk plywood, which is more decorative and resistant to decay, birch remains the preferred choice for applications requiring structural integrity and ease of finishing.
Infographic: Padauk vs Birch for Plywood
 azmater.com
azmater.com