Eucalyptus veneer offers high density and durability with a naturally rich grain, making it ideal for heavy-use furniture, while maple veneer provides a smoother texture and lighter color, preferred for modern and uniform wood finishes. Both materials balance strength and aesthetics, but eucalyptus excels in hardness and sustainability compared to maple.
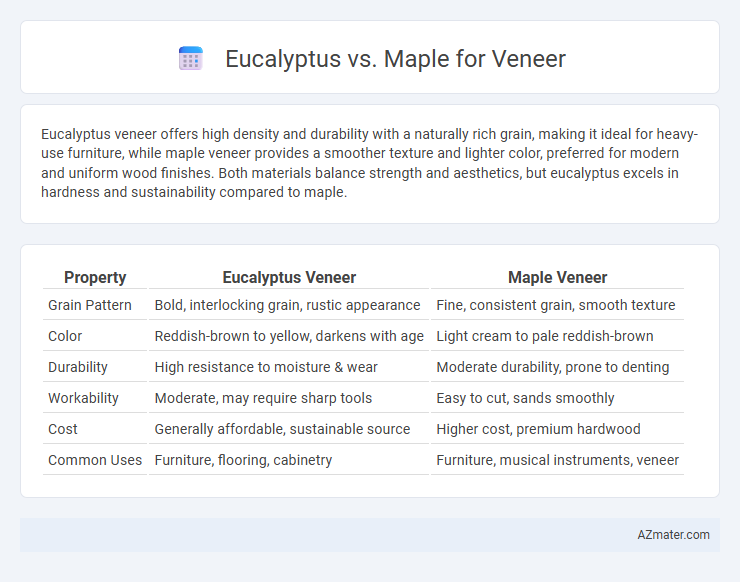
Table of Comparison
| Property | Eucalyptus Veneer | Maple Veneer |
|---|---|---|
| Grain Pattern | Bold, interlocking grain, rustic appearance | Fine, consistent grain, smooth texture |
| Color | Reddish-brown to yellow, darkens with age | Light cream to pale reddish-brown |
| Durability | High resistance to moisture & wear | Moderate durability, prone to denting |
| Workability | Moderate, may require sharp tools | Easy to cut, sands smoothly |
| Cost | Generally affordable, sustainable source | Higher cost, premium hardwood |
| Common Uses | Furniture, flooring, cabinetry | Furniture, musical instruments, veneer |
Introduction to Eucalyptus and Maple Veneer
Eucalyptus veneer offers a durable and sustainable option with a distinctive grain pattern and warm, reddish-brown hues, making it ideal for contemporary furniture and interior design. Maple veneer is prized for its light color, smooth texture, and fine grain, providing a classic, clean appearance commonly used in cabinetry, flooring, and musical instruments. Both eucalyptus and maple veneers provide versatility and aesthetic appeal, but eucalyptus emphasizes eco-friendliness and robustness, while maple highlights uniformity and subtle elegance.
Botanical Origins and Global Availability
Eucalyptus veneer originates from the Eucalyptus genus native primarily to Australia, known for its rapid growth and sustainability, whereas Maple veneer comes from the Acer genus widespread across North America, Europe, and Asia, valued for its hardness and fine grain. Eucalyptus trees are predominantly harvested in plantation settings in Australia, South America, and Africa, offering a renewable resource with increasing global supply. Maple, with a more limited growth rate and distribution largely in temperate climates, remains more regionally confined but is prized for its consistent quality and aesthetics in veneer production.
Physical Appearance and Grain Patterns
Eucalyptus veneer features a warm, reddish-brown hue with subtle, uniform grain patterns that create a smooth and contemporary aesthetic. Maple veneer offers a lighter, creamy to pale yellow color with a fine, consistent grain that often includes distinctive birdseye or curly figure variations, providing a brighter and more visually textured surface. Both woods present unique visual characteristics that influence the design choice for furniture and interior applications based on desired warmth and grain complexity.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Eucalyptus veneer is known for its impressive durability, boasting high resistance to wear and moisture, which makes it a reliable choice for heavy-use applications. Maple veneer offers exceptional strength with a dense grain structure, providing excellent stability and resistance to impact and deformation. Both species perform well in veneer form, but eucalyptus tends to excel in moisture resistance, while maple is preferred for its superior hardness and structural integrity.
Workability and Machinability
Eucalyptus veneer offers good workability with its moderate hardness and fine, even grain, making it suitable for both hand and machine tools without excessive wear. Maple veneer is denser and harder, providing a smooth, consistent surface but requiring sharper tools and slower machining speeds to avoid tear-out. Both woods machine well, but eucalyptus is generally preferred for quicker production due to its lesser tool dulling and easier sanding properties.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Eucalyptus veneer offers rapid growth rates and high carbon sequestration, making it a more sustainable option compared to slower-growing maple. Its ability to thrive on marginal lands reduces deforestation pressure on natural forests, whereas maple harvesting often involves old-growth trees with longer regrowth periods. Life cycle assessments indicate eucalyptus plantations generally have lower water and pesticide inputs, contributing to a reduced environmental footprint in veneer production.
Cost and Market Value Considerations
Eucalyptus veneer generally offers a more cost-effective option due to its faster growth rate and abundant supply, making it ideal for budget-conscious projects. Maple veneer commands higher market value because of its smooth texture, durability, and popularity in premium furniture and cabinetry. Choosing between the two involves balancing initial veneer cost against long-term market demand and end-product valuation.
Common Applications in Furniture and Design
Eucalyptus veneer offers a striking, fine-grained texture ideal for contemporary furniture, cabinetry, and decorative panels, prized for its durability and resistance to warping. Maple veneer features a smooth, light-toned appearance commonly used in traditional and modern furniture, flooring, and millwork, valued for its hardness and ability to take stains evenly. Both wood veneers enhance aesthetic appeal and structural integrity, with eucalyptus preferred for bold design statements and maple favored for classic, versatile styles.
Maintenance and Longevity
Eucalyptus veneer offers robust resistance to wear and environmental stress, requiring minimal maintenance with periodic cleaning and occasional sealing to preserve its natural finish. Maple veneer is known for its dense, fine grain that enhances durability but demands regular polishing and protection from moisture to maintain its appearance over time. Both eucalyptus and maple veneers provide long-lasting aesthetics, though eucalyptus generally outperforms maple in humidity resistance, extending its longevity in variable climates.
Choosing the Right Veneer: Eucalyptus vs Maple
Eucalyptus veneer offers a durable, sustainable option with distinct grain patterns that enhance modern and rustic designs, while Maple veneer provides a smooth, fine-grained surface ideal for uniform, clean aesthetics in cabinetry or furniture. Eucalyptus tends to resist moisture and pests better, making it suitable for high-traffic or humid environments, whereas Maple's hardness and light color allow for versatile staining and finishing techniques. Selecting between eucalyptus and maple veneers depends on desired aesthetics, durability requirements, and environmental conditions of the installation space.
Infographic: Eucalyptus vs Maple for Veneer
 azmater.com
azmater.com