Alder wood offers a lightweight, affordable option with a smooth grain and warm reddish-brown tone, while walnut provides a durable, premium hardwood featuring rich dark brown hues and intricate grain patterns. Choose alder for budget-friendly, easy-to-work material and walnut for long-lasting elegance and high-end appeal in table construction.
Table of Comparison
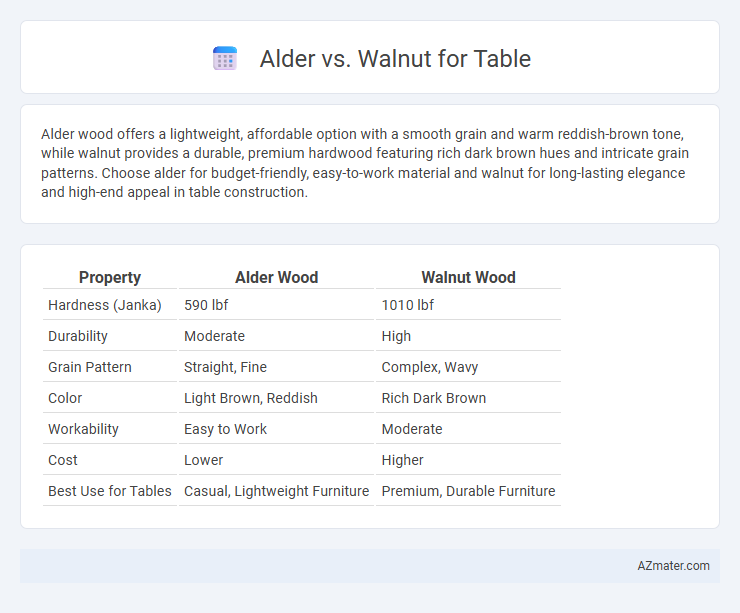
| Property | Alder Wood | Walnut Wood |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Janka) | 590 lbf | 1010 lbf |
| Durability | Moderate | High |
| Grain Pattern | Straight, Fine | Complex, Wavy |
| Color | Light Brown, Reddish | Rich Dark Brown |
| Workability | Easy to Work | Moderate |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Best Use for Tables | Casual, Lightweight Furniture | Premium, Durable Furniture |
Introduction to Alder and Walnut Woods
Alder wood is a lightweight, soft hardwood known for its fine, even texture and warm, reddish-brown hues, making it ideal for crafting aesthetically pleasing and affordable furniture. Walnut wood is a dense, strong hardwood prized for its rich chocolate-brown color, striking grain patterns, and exceptional durability, often used in high-end tables and fine woodworking. Both woods offer unique characteristics in terms of workability and finish, with alder being easier to shape and walnut providing a more luxurious, long-lasting surface.
Key Differences Between Alder and Walnut
Alder wood is softer and lighter with a pale, reddish-brown tone, while walnut is denser and darker, featuring rich chocolate-brown hues that deepen over time. Walnut offers superior durability and resistance to wear, making it ideal for high-use tables, whereas alder is more budget-friendly and easier to work with due to its softness. Grain patterns in walnut tend to be more pronounced and decorative, compared to the more subtle, uniform grain of alder.
Appearance and Grain Patterns
Alder wood features a smooth, fine grain with a consistent, light brown to reddish hue, providing a warm, uniform appearance ideal for casual and rustic table designs. Walnut boasts a rich, dark chocolate brown color with intricate, swirling grain patterns and occasional knots, creating a striking, elegant look perfect for high-end, statement furniture pieces. The contrast between Alder's subtle grain and Walnut's bold grain patterns influences the visual impact and style direction of tables crafted from these woods.
Durability and Hardness Comparison
Walnut is significantly harder and more durable than alder, with a Janka hardness rating of approximately 1,010 compared to alder's 590, making it more resistant to dents and scratches for table surfaces. Walnut's dense grain structure contributes to its superior strength and longevity, ideal for heavy-use areas such as dining or work tables. Alder, while softer and less durable, offers a more affordable option with a smoother finish, but it requires more care to prevent damage over time.
Workability and Ease of Crafting
Alder wood offers excellent workability due to its softness and uniform grain, making it easier to cut, shape, and sand compared to walnut. Walnut, while harder and denser, provides a smoother finish but requires sharper tools and more effort during crafting to achieve detailed designs. Craftsmen often prefer alder for intricate carvings and quick projects, whereas walnut is favored for durable, high-end tabletops requiring refined detail.
Cost and Availability Factors
Alder wood is generally more affordable than walnut, making it a budget-friendly option for table construction without sacrificing quality. Walnut, valued for its rich color and durability, tends to have a higher price point due to limited supply and slower growth rates. Availability of alder is widespread and consistent across North America, while walnut is less abundant and often sourced from select regions, impacting procurement ease and cost.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Alder wood, known for its fast growth rate and renewable sourcing, offers a more sustainable option compared to Walnut, which takes longer to mature and is often harvested from older, less abundant trees. Walnut production generally has a higher environmental impact due to slower regeneration and greater resource demands, making it less eco-friendly for table manufacturing. Choosing Alder supports reduced deforestation and promotes sustainable forestry practices without compromising durability or aesthetic appeal.
Alder vs Walnut: Table Longevity
Alder wood offers moderate durability with a Janka hardness of approximately 590, making it softer and more prone to dents and scratches than walnut, which boasts a higher Janka hardness of around 1010. Walnut tables typically provide enhanced longevity due to their greater resistance to wear, impact, and environmental factors. Properly maintained walnut furniture can last several decades, while alder furniture may require more frequent refinishing to preserve its appearance and structural integrity.
Best Uses for Alder and Walnut Tables
Alder wood excels for indoor tables due to its soft texture, warm color, and easy stain acceptance, making it ideal for rustic or casual settings. Walnut offers superior durability and a rich, dark finish, perfect for high-end dining tables that require longevity and an elegant look. Both woods suit different aesthetics: Alder is best for affordable, customizable furniture, while Walnut suits premium, heirloom pieces.
Choosing the Right Wood for Your Table
Alder offers a soft texture and warm, light tones ideal for casual and budget-friendly tables, while walnut provides a rich, dark color and exceptional durability suited for high-end, long-lasting furniture. Walnut's tight grain and natural resistance to wear make it perfect for heirloom-quality tabletops, whereas alder's ease of staining allows for versatile finishes that mimic more expensive woods. Selecting between alder and walnut depends on your desired aesthetic, durability needs, and budget, with walnut favored for elegance and strength, and alder chosen for affordability and customization.
Infographic: Alder vs Walnut for Table
 azmater.com
azmater.com