Padauk offers rich, warm tonal qualities and excellent sustain, making it ideal for guitar necks and fingerboards. Maple provides bright, clear sound with strong projection, commonly used for violins and drum shells.
Table of Comparison
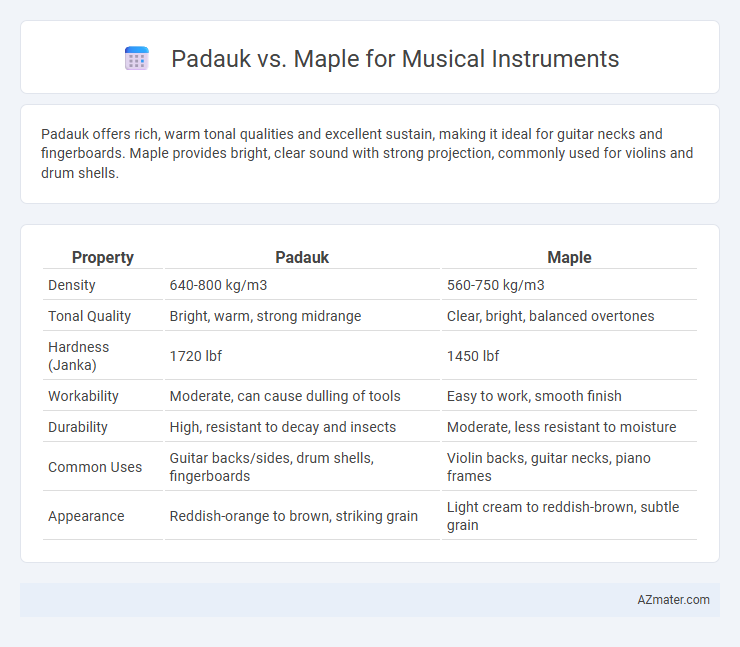
| Property | Padauk | Maple |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 640-800 kg/m3 | 560-750 kg/m3 |
| Tonal Quality | Bright, warm, strong midrange | Clear, bright, balanced overtones |
| Hardness (Janka) | 1720 lbf | 1450 lbf |
| Workability | Moderate, can cause dulling of tools | Easy to work, smooth finish |
| Durability | High, resistant to decay and insects | Moderate, less resistant to moisture |
| Common Uses | Guitar backs/sides, drum shells, fingerboards | Violin backs, guitar necks, piano frames |
| Appearance | Reddish-orange to brown, striking grain | Light cream to reddish-brown, subtle grain |
Introduction to Padauk and Maple in Musical Instruments
Padauk wood, prized for its striking reddish hue and dense, oily texture, offers excellent acoustic properties and durability, making it ideal for crafting guitar bodies and drum shells that require rich tonal resonance and sustain. Maple, known for its bright, clear tonal qualities and smooth grain, is a preferred choice for necks and fretboards in string instruments as well as drum shells, providing stability and sharp attack. Both woods contribute unique sound characteristics and aesthetics, influencing the tonal warmth and projection in musical instruments.
Physical Properties of Padauk vs Maple
Padauk wood, known for its high density and hardness, offers exceptional durability and resistance to wear, making it ideal for musical instruments that require longevity and strength. Maple, slightly less dense but with a tighter, more consistent grain, provides superior tonal clarity and resonance, favored in instruments like violins and guitars. Both woods exhibit stability, yet Padauk's natural oils enhance moisture resistance, while maple's fine grain allows for easier carving and shaping in precision instrument crafting.
Acoustic Characteristics of Padauk and Maple
Padauk offers a warm, rich tone with pronounced midrange frequencies, making it ideal for guitars and percussion instruments that require strong resonance and sustain. Maple produces a bright, clear sound with excellent projection and a tight low end, often favored in violins and drum shells for its articulate and balanced acoustic properties. The choice between Padauk and Maple depends on the desired tonal quality, with Padauk enhancing warmth and fullness, while Maple emphasizes clarity and brightness.
Workability and Crafting Differences
Padauk offers superior workability for musical instrument crafting due to its moderate density and natural oils, which enhance smooth cutting and reduce tool wear, making it ideal for intricate detailing and shaping. Maple, known for its hardness and fine, uniform grain, provides excellent durability and a consistent surface finish but requires sharper tools and more effort to achieve precise cuts, especially in curved or delicate parts. Crafting instruments with Padauk generally results in faster production times and easier fretwork, whereas Maple demands greater skill but yields a bright, clear tonal quality favored in high-end guitars and violins.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Padauk wood exhibits exceptional durability with high resistance to decay and insect attack, making it ideal for long-lasting musical instruments. Maple, renowned for its hardness and shock resistance, provides a stable structure that withstands frequent use without warping or cracking. When comparing longevity, Padauk's natural oils contribute to sustained resilience, while Maple's dense grain ensures consistent tonal quality over time.
Aesthetic Appeal: Grain and Color
Padauk wood displays a vibrant reddish-orange hue with a pronounced, interlocking grain that enhances the visual depth of musical instruments. Maple offers a lighter, creamy color with subtle, consistent grain patterns, often featuring a figured or flame effect prized for its elegance. The choice between Padauk and Maple depends on whether a bold, warm aesthetic or a classic, refined appearance is desired for the instrument's design.
Common Musical Instruments Using Padauk
Padauk wood is highly valued in musical instrument craftsmanship for its rich tonal quality and durability, commonly used in electric guitar bodies, drum shells, and stringed instrument fingerboards. Unlike maple, which offers bright resonance and is often favored for violin backs and acoustic guitar tops, padauk provides a warm, midrange-focused sound that enhances the instrument's depth. Its natural hardness and stability make padauk ideal for instruments requiring robust construction and sustain, such as electric guitar necks and djembe drums.
Popular Musical Instruments Made with Maple
Maple is a preferred wood for making musical instruments like violins, guitars, and drums due to its bright tonal qualities, durability, and attractive grain patterns. Popular instruments such as Fender Stratocaster guitars and drum shells often feature maple, providing a clear, articulate sound with excellent sustain. In contrast, Padauk, known for its rich reddish hue and dense structure, is less common but used for unique instruments requiring warm midrange tones and robust resonance.
Cost and Availability of Padauk vs Maple
Padauk wood is generally more affordable than maple, making it a cost-effective choice for musical instrument construction without compromising tonal quality. While maple is widely available, especially in North America and Europe, padauk, sourced primarily from Africa and Southeast Asia, may have limited supply depending on regional imports. The cost advantage of padauk often depends on the rarity of specific maple grades, with premium maple varieties commanding higher prices due to demand in high-end instrument manufacturing.
Choosing the Right Tonewood: Padauk or Maple?
Padauk offers a warm, rich tonal quality with strong midrange presence, making it ideal for instruments needing a robust, resonant sound, while Maple provides bright, clear tones with excellent sustain and a balanced frequency response favored in many guitars and violins. The density and grain structure of Padauk contribute to its punchy sound and natural resonance, whereas Maple's hardness and fine grain produce sharp attack and clarity. Selecting the right tonewood depends on the desired tonal character and responsiveness, with Padauk suited for a warmer, fuller voice and Maple preferred for brightness and articulation in musical instruments.
Infographic: Padauk vs Maple for Musical Instrument
 azmater.com
azmater.com