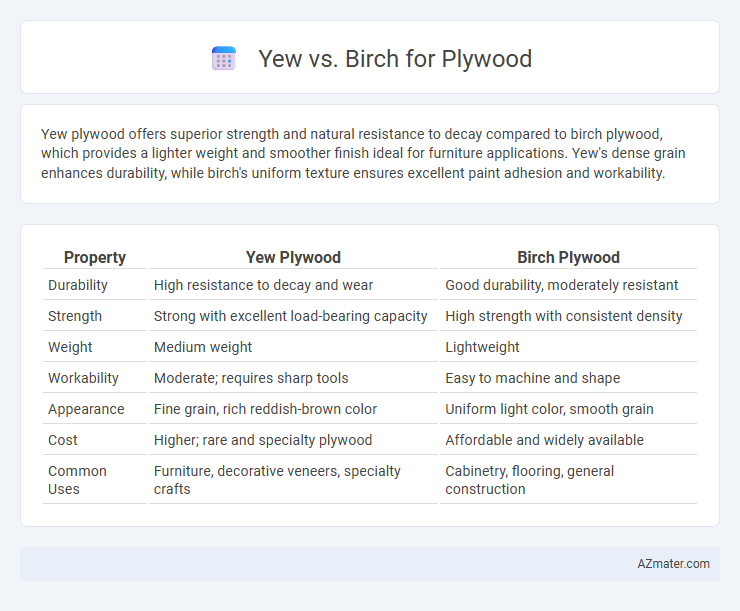
Yew plywood offers superior strength and natural resistance to decay compared to birch plywood, which provides a lighter weight and smoother finish ideal for furniture applications. Yew's dense grain enhances durability, while birch's uniform texture ensures excellent paint adhesion and workability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Yew Plywood | Birch Plywood |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High resistance to decay and wear | Good durability, moderately resistant |
| Strength | Strong with excellent load-bearing capacity | High strength with consistent density |
| Weight | Medium weight | Lightweight |
| Workability | Moderate; requires sharp tools | Easy to machine and shape |
| Appearance | Fine grain, rich reddish-brown color | Uniform light color, smooth grain |
| Cost | Higher; rare and specialty plywood | Affordable and widely available |
| Common Uses | Furniture, decorative veneers, specialty crafts | Cabinetry, flooring, general construction |
Introduction: Yew vs Birch for Plywood
Yew and birch are two popular hardwoods used in plywood production, each offering unique characteristics that influence their applications. Yew plywood is known for its rich color, fine grain, and natural durability, making it ideal for decorative and specialized woodworking projects. Birch plywood stands out for its strength, smooth surface, and resistance to warping, making it a preferred choice for furniture, cabinetry, and structural uses.
Botanical Overview: Yew and Birch Trees
Yew (Taxus baccata) is a slow-growing coniferous tree known for its dense, fine-grained wood, while Birch (Betula spp.) is a fast-growing deciduous tree valued for its light-colored, hard, and flexible timber. Yew wood features a rich reddish-brown hue with natural resistance to decay, making it suitable for high-quality plywood applications requiring durability and aesthetic appeal. Birch plywood is prized for its uniform texture, strength-to-weight ratio, and smooth finish, commonly used in furniture and interior veneers due to its versatility and consistent performance.
Physical Properties Comparison
Yew plywood offers exceptional durability and a fine, even grain, resulting in strong, resilient panels ideal for intricate woodworking and high-stress applications. Birch plywood features a smooth surface with consistent light color and excellent dimensional stability, making it highly resistant to warping and suitable for furniture and cabinetry. While Yew provides superior toughness and a naturally rich finish, birch excels in uniformity and ease of finishing, catering to diverse industrial and decorative needs.
Durability and Longevity
Yew plywood offers exceptional durability due to its dense grain structure, making it highly resistant to wear and decay, which ensures a longer lifespan in demanding applications. Birch plywood is also durable but is generally softer and more prone to dents and scratches compared to yew, reducing its longevity under heavy use. For projects requiring maximum durability and extended service life, yew plywood is often the superior choice, especially in environments exposed to moisture and mechanical stress.
Workability and Machinability
Yew plywood offers moderate workability with a fine, even texture that allows for smooth cutting and shaping, making it suitable for detailed woodworking projects. Birch plywood provides excellent machinability due to its uniform grain and consistent density, enabling clean edges and precise finishes when routed or sanded. The high durability of birch makes it easier to handle in automated machining processes compared to the slightly softer yew wood.
Aesthetic Differences
Yew plywood features a rich, warm reddish-brown tone with fine, interlocked grain patterns, offering a luxurious and classic appearance ideal for high-end furniture and decorative panels. In contrast, birch plywood exhibits a pale, creamy coloration with a more uniform, subtle grain that provides a modern and clean look suited for contemporary interiors and cabinetry. The aesthetic choice between yew and birch plywood hinges on desired visual warmth and grain complexity, with yew delivering depth and character while birch ensures brightness and minimal visual distraction.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Yew plywood offers a durable, dense wood option with slower growth rates, potentially leading to higher environmental costs due to longer harvesting cycles compared to birch, which is fast-growing and widely managed in sustainable forestry operations. Birch plywood's sustainability benefits include efficient resource use through rapid regeneration and certification under programs like FSC, minimizing ecological footprint and promoting biodiversity. Choosing birch plywood supports sustainable construction practices by balancing durability with reduced deforestation and carbon emissions.
Cost and Availability
Yew plywood typically commands a higher price due to the wood's rarity and limited availability, making it less accessible for large-scale projects. Birch plywood is more widely available and cost-effective, favored for its consistent quality and abundance in North American and European markets. The cost efficiency and accessibility of birch plywood make it the preferred choice for budget-conscious applications requiring sturdy, smooth veneer.
Best Applications for Each Wood
Yew plywood is prized for its fine grain, durability, and rich color, making it ideal for high-end furniture, decorative veneers, and artistic woodworking projects where visual appeal and strength are paramount. Birch plywood, known for its uniform texture, strength, and resistance to warping, excels in cabinetry, flooring, and structural applications where stability and a smooth finish are essential. Selecting yew plywood enhances luxury and aesthetic value, while birch plywood is best suited for functional, everyday uses requiring robustness and consistent performance.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Yew and Birch for Plywood
Yew plywood offers exceptional durability and a rich, warm aesthetic ideal for high-end furniture and decorative applications, while birch plywood is renowned for its strength, affordability, and light color, making it suitable for general construction and cabinetry. The choice between yew and birch plywood depends on project requirements such as cost sensitivity, visual appeal, and structural needs. Prioritize yew plywood for premium, visually striking projects and birch plywood for versatile, budget-friendly solutions with reliable performance.
Infographic: Yew vs Birch for Plywood
 azmater.com
azmater.com