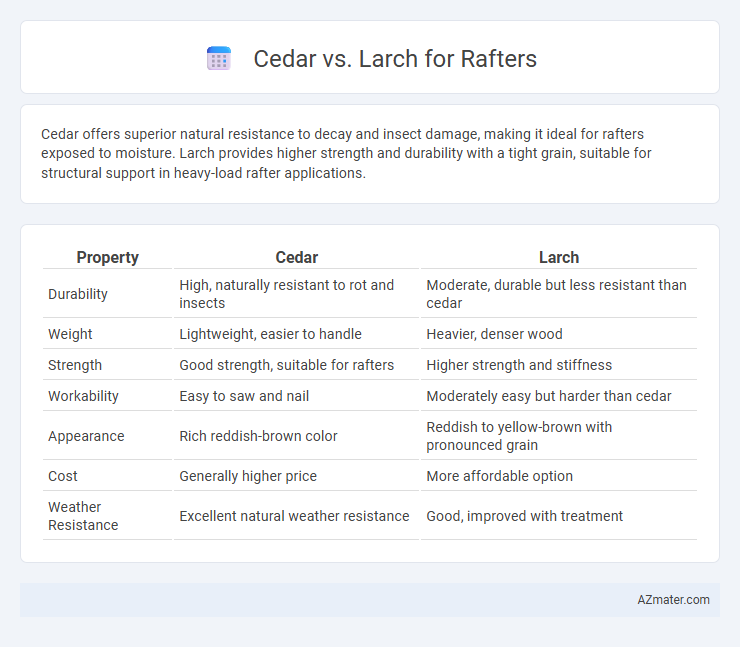
Cedar offers superior natural resistance to decay and insect damage, making it ideal for rafters exposed to moisture. Larch provides higher strength and durability with a tight grain, suitable for structural support in heavy-load rafter applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Cedar | Larch |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High, naturally resistant to rot and insects | Moderate, durable but less resistant than cedar |
| Weight | Lightweight, easier to handle | Heavier, denser wood |
| Strength | Good strength, suitable for rafters | Higher strength and stiffness |
| Workability | Easy to saw and nail | Moderately easy but harder than cedar |
| Appearance | Rich reddish-brown color | Reddish to yellow-brown with pronounced grain |
| Cost | Generally higher price | More affordable option |
| Weather Resistance | Excellent natural weather resistance | Good, improved with treatment |
Introduction: Cedar vs Larch for Rafters
Cedar and larch are popular wood choices for rafters, each offering distinct advantages in durability and aesthetics. Cedar is naturally resistant to decay and insects, making it ideal for long-lasting roofing structures, while larch provides exceptional strength and a robust grain pattern that enhances structural integrity. Selecting between cedar and larch depends on specific project requirements, including environmental exposure and desired lifespan of the rafters.
Wood Properties: Cedar and Larch Overview
Cedar offers excellent resistance to decay and insect damage due to its natural oils, making it highly durable for rafters in various climates. Larch is known for its exceptional strength, density, and stiffness, providing superior structural support while maintaining good resistance to moisture and wear. Both woods are favored for their stability and longevity, but cedar's lighter weight and natural preservative qualities often make it preferable in environments prone to humidity and pests.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Cedar rafters are prized for their natural resistance to decay and insect damage, offering strong durability and a lightweight structure ideal for long-term performance in harsh weather conditions. Larch provides exceptional strength with its dense, fibrous grain, making it highly resistant to bending and structural stress, often used in heavy load-bearing applications. Both woods demonstrate excellent durability, but cedar excels in moisture resistance while larch offers superior mechanical strength, crucial for robust rafter construction.
Weather Resistance and Longevity
Cedar rafters offer superior weather resistance due to natural oils that repel moisture, insects, and decay, providing exceptional longevity even in harsh conditions. Larch, while denser and harder, resists rot and fungal attacks well but may require treatment to enhance durability in wet climates. Cedar's lightweight and stable properties make it ideal for long-lasting rafters exposed to varying weather patterns.
Weight and Workability of Rafters
Cedar rafters are known for their lightweight properties, typically weighing around 23 pounds per cubic foot, which makes them easier to handle and install compared to larch, which is denser and weighs approximately 36 pounds per cubic foot. The superior workability of cedar stems from its fine, uniform grain and softer texture, allowing for smoother cuts and less tool wear, whereas larch's harder, resinous nature demands more effort and durable tools during fabrication. Choosing cedar can result in faster installation times and reduced labor costs due to its manageable weight and ease of shaping, while larch offers enhanced strength but requires greater physical handling and cutting precision.
Aesthetic Appeal and Color Differences
Cedar rafters are prized for their rich, warm reddish-brown tones that deepen over time, enhancing outdoor structures with a classic, elegant appearance. Larch offers a lighter, yellowish hue with distinctive grain patterns that create a rustic and natural aesthetic ideal for contemporary designs. Both woods age beautifully, but cedar's uniform color and smooth texture provide a premium finish, while larch's unique knots add character and visual interest.
Cost Analysis: Cedar vs Larch
Cedar rafters generally cost more than larch due to cedar's higher demand and natural resistance to decay and insects, which reduces long-term maintenance expenses. Larch offers a more budget-friendly option, providing strong structural support with moderate durability, making it suitable for cost-conscious projects. When evaluating cost analysis, consider cedar's longevity and lower upkeep against larch's initial savings and adequate performance for typical rafter applications.
Maintenance Requirements for Each Wood
Cedar rafters require minimal maintenance due to their natural resistance to rot, insects, and decay, making them ideal for long-lasting roof structures. Larch rafters need more frequent upkeep, including regular sealing or staining to prevent moisture absorption and fungal growth, as this wood is less naturally durable than cedar. Both options benefit from periodic inspections to address any potential damage, but cedar offers a lower-maintenance solution overall.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Cedar rafters offer superior sustainability due to their natural resistance to decay, reducing the need for chemical treatments and extending the lifespan of roofing structures. Larch wood, known for its fast growth and carbon sequestration capabilities, contributes significantly to reforestation efforts and has a lower environmental footprint during harvesting. Both species provide renewable resources, but cedar's durability and larch's rapid renewability make them environmentally responsible choices for sustainable construction.
Which Wood Is Best for Rafters?
Cedar offers superior natural resistance to decay and insects, making it an excellent choice for rafters exposed to moisture. Larch is denser and harder than cedar, providing greater structural strength and durability under heavy loads. For rafters, cedar is best suited for longevity and weather resistance, while larch excels where strength and load-bearing capacity are the primary concerns.
Infographic: Cedar vs Larch for Rafter
 azmater.com
azmater.com