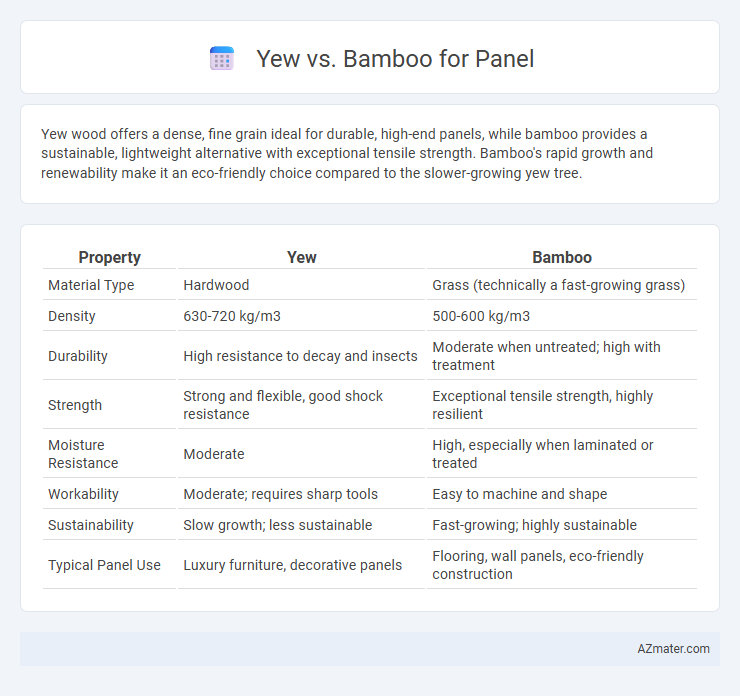
Yew wood offers a dense, fine grain ideal for durable, high-end panels, while bamboo provides a sustainable, lightweight alternative with exceptional tensile strength. Bamboo's rapid growth and renewability make it an eco-friendly choice compared to the slower-growing yew tree.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Yew | Bamboo |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Hardwood | Grass (technically a fast-growing grass) |
| Density | 630-720 kg/m3 | 500-600 kg/m3 |
| Durability | High resistance to decay and insects | Moderate when untreated; high with treatment |
| Strength | Strong and flexible, good shock resistance | Exceptional tensile strength, highly resilient |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate | High, especially when laminated or treated |
| Workability | Moderate; requires sharp tools | Easy to machine and shape |
| Sustainability | Slow growth; less sustainable | Fast-growing; highly sustainable |
| Typical Panel Use | Luxury furniture, decorative panels | Flooring, wall panels, eco-friendly construction |
Introduction to Yew and Bamboo Panels
Yew panels, derived from the slow-growing Taxus tree, offer exceptional durability and a rich reddish-brown color, making them ideal for high-quality cabinetry and decorative wall treatments. Bamboo panels, produced from fast-growing grass, provide sustainable and eco-friendly options with a light, natural appearance, superior flexibility, and resistance to moisture and insects. Both materials serve distinct purposes: yew excels in traditional, luxurious applications, while bamboo suits modern, sustainable designs.
Botanical Overview: Yew vs Bamboo
Yew (Taxus spp.) is an evergreen conifer known for its dense, fine-grained wood rich in taxane alkaloids, while bamboo, a fast-growing grass from the Poaceae family, features hollow, segmented culms with high tensile strength. Yew wood typically exhibits a smooth texture and deep reddish-brown color, favored for detailed paneling and durability in fine woodworking. Bamboo's cellular structure offers exceptional flexibility and sustainability, making it ideal for lightweight, eco-friendly panels with natural resistance to moisture and pests.
Physical Properties and Appearance
Yew wood exhibits a fine, smooth texture with a rich, warm reddish-brown hue complemented by subtle grain patterns, offering durability and moderate hardness ideal for paneling. Bamboo panels, renowned for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, possess a uniform, light golden color and a smooth surface, providing resistance to moisture and wear. The choice between Yew and Bamboo panels hinges on desired aesthetics and functional demands, with Yew favoring traditional warmth and Bamboo offering sustainable resilience.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Yew wood panels exhibit exceptional durability due to their dense grain and natural resistance to rot and insect damage, often lasting several decades when properly maintained. Bamboo panels, known for their rapid growth and eco-friendliness, offer strong tensile strength but may require treatment to enhance moisture resistance and prevent degradation over time. When comparing longevity, yew typically outperforms bamboo in harsh environmental conditions, while bamboo can provide a sustainable option with a shorter lifespan unless engineered for durability.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Yew wood is a dense, slow-growing timber that offers long-lasting durability but has a higher environmental impact due to its slow regeneration rate and limited availability. Bamboo, known for its rapid growth and ability to sequester carbon efficiently, is a highly sustainable alternative, regenerating within 3-5 years and reducing deforestation pressures. Choosing bamboo panels significantly lowers the carbon footprint and supports sustainable harvesting practices compared to the more resource-intensive yew wood.
Workability and Ease of Installation
Yew wood offers superior workability due to its fine grain and smooth texture, allowing for precise cuts and detailed finishes in panel construction. Bamboo, while harder and more fibrous, requires specialized tools for cutting and fastening, which can complicate installation but provides exceptional durability and resilience. Panels made from yew are easier to install in intricate applications, whereas bamboo panels demand careful handling and expertise to achieve a secure and stable fit.
Cost Comparison: Yew Panels vs Bamboo Panels
Yew panels generally have a higher cost due to the wood's rarity and slower growth rates compared to bamboo, which is widely cultivated and rapidly renewable. Bamboo panels offer a more budget-friendly option with lower production costs and faster harvesting cycles, making them ideal for cost-sensitive projects. When comparing durability and aesthetic value, the initial savings on bamboo panels can be offset by the premium appeal and longevity of yew panels in high-end applications.
Applications in Interior Design and Construction
Yew wood offers exceptional durability and a fine grain, making it ideal for high-end interior paneling and decorative accents where rich texture and warm hues are desired. Bamboo panels provide a sustainable, lightweight alternative with natural flexibility and moisture resistance, suitable for modern designs emphasizing eco-friendly materials and dynamic aesthetics. Both materials enhance interior construction; yew excels in traditional, elegant settings, while bamboo supports contemporary, minimalist environments with its sleek, uniform appearance.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Yew wood panels require minimal maintenance due to their natural resistance to decay and insects, needing only occasional cleaning and oiling to preserve their rich color and texture. Bamboo panels demand more frequent care, including sealing to prevent moisture damage and regular cleaning to avoid mold growth, especially in humid environments. Both materials benefit from controlled indoor conditions and timely repairs to extend their lifespan and maintain aesthetic appeal.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Yew and Bamboo for Panels
Yew panels offer superior durability and a rich, deep grain ideal for high-end, long-lasting interior finishes, while bamboo panels provide excellent sustainability, rapid renewability, and a lighter aesthetic suited for eco-friendly designs. Selecting between yew and bamboo depends on project priorities: prioritize yew for luxury and longevity, or bamboo for environmental impact and modern style. Both materials deliver unique benefits, making them suitable for different architectural and design intentions.
Infographic: Yew vs Bamboo for Panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com