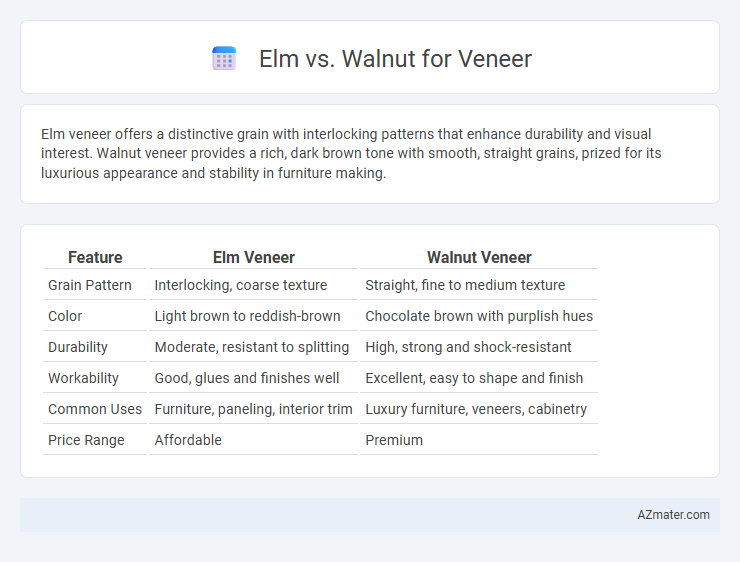
Elm veneer offers a distinctive grain with interlocking patterns that enhance durability and visual interest. Walnut veneer provides a rich, dark brown tone with smooth, straight grains, prized for its luxurious appearance and stability in furniture making.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Elm Veneer | Walnut Veneer |
|---|---|---|
| Grain Pattern | Interlocking, coarse texture | Straight, fine to medium texture |
| Color | Light brown to reddish-brown | Chocolate brown with purplish hues |
| Durability | Moderate, resistant to splitting | High, strong and shock-resistant |
| Workability | Good, glues and finishes well | Excellent, easy to shape and finish |
| Common Uses | Furniture, paneling, interior trim | Luxury furniture, veneers, cabinetry |
| Price Range | Affordable | Premium |
Introduction to Elm and Walnut Veneer
Elm veneer features a distinctive grain pattern with interlocking fibers, offering a warm, rustic appearance ideal for traditional and contemporary furniture designs. Walnut veneer is prized for its rich, deep brown color and smooth texture, providing a luxurious finish that enhances high-end cabinetry and decorative surfaces. Both veneers are durable and versatile, making them popular choices for interior woodworking projects.
Botanical Origins and Wood Characteristics
Elm veneer, derived from trees of the Ulmus genus, is renowned for its interlocking grain pattern that offers both strength and a distinctive wavy appearance. Walnut veneer, sourced from Juglans species, features a straight to irregular grain with a rich, deep chocolate-brown color and occasional purple hues, prized for its elegance and durability. Both woods provide excellent stability for veneer applications, but Elm's coarse texture contrasts with Walnut's fine, smooth finish, making each suitable for different aesthetic and structural requirements.
Color and Grain Differences
Elm veneer features a rich golden to reddish-brown hue with irregular and open grain patterns that often showcase striking interlocking and wavy textures, making it ideal for achieving a rustic or traditional look. Walnut veneer displays a deep, rich chocolate brown color with subtle purples and greys, characterized by a straighter, more uniform grain that provides a sleek, contemporary aesthetic. The distinct color contrast and grain complexity of elm offer warmth and character, while walnut's smooth grain and darker tone lend a refined and elegant appearance to furniture and cabinetry.
Durability and Hardness Comparison
Elm veneer offers moderate durability with a Janka hardness rating around 830, making it suitable for light to medium wear applications. Walnut veneer, with a higher Janka hardness rating of approximately 1010, provides greater resistance to dents and scratches, ideal for high-traffic areas. Choosing walnut ensures enhanced hardness and longevity, while elm presents a softer, more flexible option for veneer projects.
Veneer Workability and Machining
Elm veneer offers excellent workability due to its interlocking grain, which provides stability and reduces the risk of splitting during machining. Walnut veneer is prized for its smooth texture and consistent grain, allowing for precise cutting and shaping with minimal tear-out. Both veneers respond well to sanding and finishing, but walnut generally yields a finer surface, ideal for high-quality veneer applications.
Cost and Market Availability
Walnut veneer is generally more expensive than elm due to its rich color, fine grain, and high demand in luxury furniture markets. Elm veneer offers a more economical option with moderate durability and an attractive interlocking grain, making it easier to source in bulk for various woodworking projects. Market availability favors elm, which is more abundant and sustainable, whereas walnut's limited supply and premium status contribute to higher costs and selective market presence.
Common Uses in Interiors and Furniture
Elm veneer is prized for its interlocking grain and durability, making it ideal for traditional furniture, paneling, and cabinetry that require a warm, textured appearance. Walnut veneer, valued for its rich dark tones and fine grain, is commonly used in high-end furniture, decorative wall panels, and luxury interior accents, providing a sophisticated and elegant finish. Both veneers enhance interior aesthetics, with elm offering rustic charm and walnut delivering classic luxury.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Trends
Elm veneer showcases a distinctive interlocking grain pattern and warm, golden-brown hues that add rustic charm and natural texture to interiors. Walnut veneer, prized for its rich chocolate-brown color and straight, fine grain, aligns with contemporary design trends favoring sleek, sophisticated aesthetics. Both woods enhance furniture and paneling, but walnut's luxurious appeal often dominates upscale modern and mid-century designs, while elm's character suits vintage and artisanal styles.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Elm veneer offers a sustainable choice due to its fast growth and regional abundance, resulting in lower transportation emissions and less habitat disruption. Walnut veneer, while prized for its rich color and durability, often comes from slower-growing trees that require longer harvest cycles, impacting forest regeneration rates. Both woods benefit from certified sourcing like FSC, but elm generally has a lower carbon footprint and higher renewability in veneer applications.
Choosing Between Elm and Walnut Veneer
Choosing between elm and walnut veneer hinges on factors like grain pattern, color, and durability. Elm veneer features interlocking grain with a light to medium brown tone, offering a rustic and textured appearance ideal for traditional or eclectic designs. Walnut veneer presents a smoother grain with rich, dark brown hues and excellent hardness, making it suitable for high-end furniture requiring elegance and longevity.
Infographic: Elm vs Walnut for Veneer
 azmater.com
azmater.com