Basswood offers a lightweight, fine-grained surface ideal for detailed carving and smooth paint finishes in door construction. Alder provides a denser, stronger option with a rich, warm color and natural resistance to dents, making it suitable for durable, stained doors.
Table of Comparison
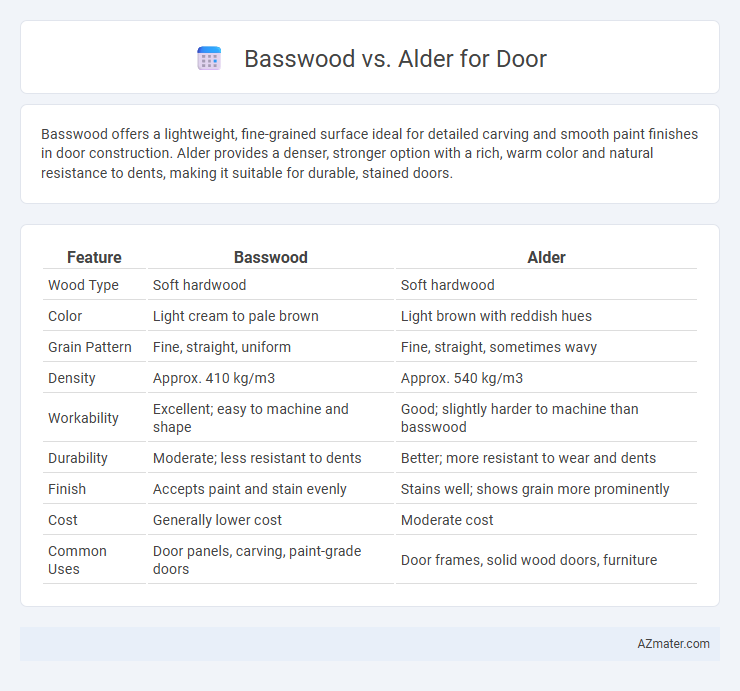
| Feature | Basswood | Alder |
|---|---|---|
| Wood Type | Soft hardwood | Soft hardwood |
| Color | Light cream to pale brown | Light brown with reddish hues |
| Grain Pattern | Fine, straight, uniform | Fine, straight, sometimes wavy |
| Density | Approx. 410 kg/m3 | Approx. 540 kg/m3 |
| Workability | Excellent; easy to machine and shape | Good; slightly harder to machine than basswood |
| Durability | Moderate; less resistant to dents | Better; more resistant to wear and dents |
| Finish | Accepts paint and stain evenly | Stains well; shows grain more prominently |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Moderate cost |
| Common Uses | Door panels, carving, paint-grade doors | Door frames, solid wood doors, furniture |
Introduction to Basswood and Alder
Basswood is a lightweight, fine-grained hardwood known for its smooth texture and excellent workability, making it a popular choice for painted interior doors. Alder wood features a warm, reddish-brown hue with a straight grain and medium density, offering durability and a natural aesthetic for both stained and natural finish doors. Both Basswood and Alder provide stable, versatile options, but Basswood excels in paint adhesion, while Alder is favored for rich, rustic interiors.
Key Characteristics of Basswood
Basswood is prized for its fine, even texture and lightweight nature, making it an excellent choice for door construction where ease of handling is important. Its pale, creamy color provides a smooth, uniform surface that accepts paint and stain exceptionally well, ensuring a high-quality finish. The wood's stability and resistance to warping enhance door durability, contrasting with alder's more pronounced grain and slightly heavier weight.
Key Characteristics of Alder
Alder wood is prized for its fine, consistent grain and warm reddish-brown hue, making it an excellent choice for doors requiring a smooth, elegant finish. Compared to basswood, alder is denser and more durable, providing superior resistance to dents and wear over time. Its natural stability minimizes warping and shrinking, ensuring longevity and maintaining door integrity in varying environmental conditions.
Appearance and Grain Comparison
Basswood doors feature a light, creamy color with a fine, uniform grain pattern that offers a smooth and elegant appearance, ideal for painted finishes and a sleek look. Alder doors exhibit a warmer, reddish-brown tone with a more pronounced, varied grain that enhances natural wood aesthetics and adds character to rustic or traditional designs. Both woods provide distinct visual textures, with basswood favoring subtlety and alder emphasizing rich, natural warmth in door applications.
Durability and Strength Differences
Basswood offers a lightweight yet stable option for doors, featuring moderate durability ideal for interior use but less resistance to dents and scratches compared to hardwoods. Alder provides superior strength and durability, making it better suited for doors subjected to frequent use or external elements, with higher resistance to wear and impact. Overall, alder's denser grain structure enhances door longevity, while basswood remains favored for ease of carving and smoother finishes in decorative applications.
Workability and Machining Properties
Basswood offers exceptional workability and machining properties due to its fine, even texture and softness, allowing for smooth cuts and detailed carvings without splintering. Alder, while slightly harder than basswood, still provides good machinability with minimal wear on tools and holds nails and screws securely, making it suitable for durable door construction. Both woods respond well to sanding and finishing, but basswood's softness favors intricate designs, whereas alder's strength supports structural integrity.
Weight and Density Considerations
Basswood is significantly lighter than alder, with a density of approximately 410 kg/m3 compared to alder's 590 kg/m3, making basswood easier to handle and ideal for lightweight door applications. Alder offers greater durability due to its higher density, providing enhanced strength and resistance to dents and impacts. Choosing between basswood and alder for doors depends on balancing the need for a lightweight material with the desire for a sturdier, more resilient door surface.
Cost and Availability
Basswood doors typically cost more than alder doors due to the wood's fine grain and smooth finish, making it favored for detailed carving and painting. Alder is more readily available and affordable, offering a budget-friendly option with a warm, natural appearance that suits staining and clear finishes. The widespread availability of alder makes it a practical choice for large projects, while basswood is preferred for higher-end doors where precision and paint adherence are critical.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Basswood, known for its rapid growth and regrowth capabilities, offers a more sustainable option for door manufacturing due to its lower environmental impact and efficient carbon sequestration. Alder, while also renewable, generally grows slower than basswood, resulting in a higher carbon footprint over the lifecycle of the material. The lightweight nature of basswood reduces transportation emissions, further enhancing its eco-friendly profile compared to alder in door applications.
Basswood vs Alder: Which is Best for Doors?
Basswood offers a fine, even texture and excellent workability, making it ideal for intricate door designs that require smooth finishes and detailed carvings. Alder, known for its consistent grain and warm reddish-brown hue, provides durability and a natural aesthetic suited for rustic or traditional doors. Choosing between basswood and alder depends on the balance of desired visual appeal and functional strength, with basswood favored for painted doors and alder preferred for stained finishes.
Infographic: Basswood vs Alder for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com