Ash plywood offers superior strength and durability with a coarse grain texture, ideal for heavy-duty applications. Birch plywood provides a smooth, fine grain surface and consistent density, making it preferred for cabinetry and furniture requiring a sleek finish.
Table of Comparison
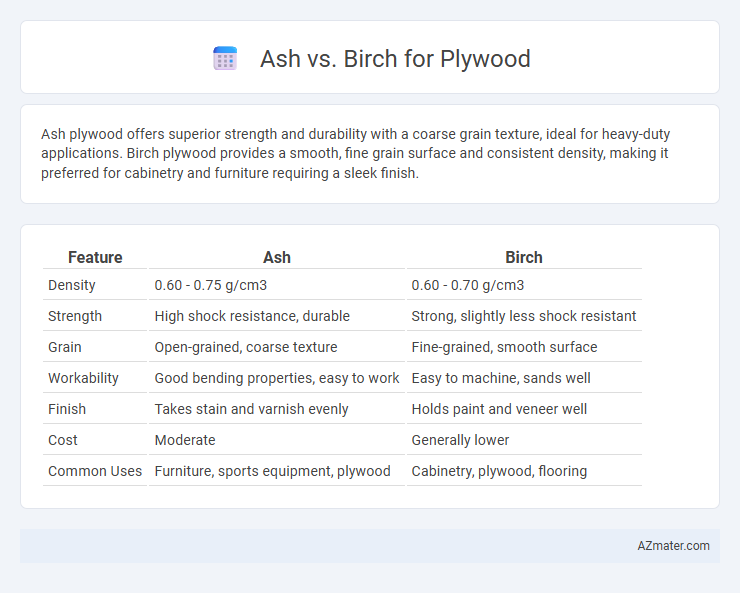
| Feature | Ash | Birch |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 0.60 - 0.75 g/cm3 | 0.60 - 0.70 g/cm3 |
| Strength | High shock resistance, durable | Strong, slightly less shock resistant |
| Grain | Open-grained, coarse texture | Fine-grained, smooth surface |
| Workability | Good bending properties, easy to work | Easy to machine, sands well |
| Finish | Takes stain and varnish evenly | Holds paint and veneer well |
| Cost | Moderate | Generally lower |
| Common Uses | Furniture, sports equipment, plywood | Cabinetry, plywood, flooring |
Introduction to Ash and Birch Plywood
Ash plywood features strong, flexible hardwood fibers known for excellent shock resistance and durability, making it ideal for structural applications and furniture production. Birch plywood offers a fine, uniform grain with a smooth surface, prized for its strength and resistance to warping, commonly used in cabinetry and interior design. Both types provide reliable performance, but ash plywood emphasizes toughness while birch plywood highlights aesthetic appeal and stability.
Botanical Differences: Ash vs. Birch
Ash wood, sourced from the Fraxinus genus, features a coarse texture with distinct open grain patterns, offering greater elasticity and shock resistance due to its dense ring-porous structure. Birch, derived from the Betula genus, exhibits a fine, even texture with closed grain patterns, providing a smooth surface ideal for veneers and finishing. Botanically, ash trees have compound leaves and produce samara fruits, while birch trees display simple serrated leaves and papery bark, influencing the aesthetic and mechanical properties of their plywood.
Visual Appearance and Grain Patterns
Ash plywood features a distinctive light color with pronounced, straight grain patterns that offer a clean and contemporary look, making it popular for modern furniture and cabinetry. Birch plywood presents a more uniform and pale surface with subtle grain variations, providing a smooth and consistent appearance ideal for veneer applications and painted finishes. Both woods deliver unique aesthetic qualities, with ash emphasizing bold texture and birch highlighting an even, refined visual appeal.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Ash plywood offers superior mechanical strength with high shock resistance and excellent load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. Birch plywood provides notable durability and stiffness, with a dense, fine grain that enhances resistance to wear and deformation. Both woods ensure reliable performance, but ash edges out in flexibility and impact strength, while birch excels in hardness and stability over time.
Workability and Machining Properties
Ash plywood offers excellent workability due to its coarse texture and open grain, allowing for easy cutting, shaping, and sanding. Birch plywood provides superior machining properties with a fine, even grain that reduces tool wear and delivers smooth, precise finishes. Both woods perform well in woodworking applications, but birch is favored for intricate detailing while ash excels in applications requiring durability combined with ease of handling.
Cost Comparison: Ash vs. Birch Plywood
Ash plywood tends to be more expensive than birch plywood due to its higher density and durability, making it a preferred choice for heavy-duty applications. Birch plywood offers a cost-effective alternative with good strength and a smooth surface, ideal for cabinetry and furniture. Choosing between ash and birch plywood depends on budget constraints and the intended use of the material.
Common Applications and Uses
Ash plywood is favored for applications requiring strength and shock resistance, such as furniture making, sports equipment, and cabinetry due to its dense grain and durability. Birch plywood is widely used in cabinetry, flooring, and interior paneling because of its smooth surface, fine grain, and excellent paint adhesion. Both types are popular in woodworking projects, though ash is preferred where structural integrity is critical, while birch excels in aesthetic and finish qualities.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ash plywood demonstrates moderate environmental impact due to its slower growth rate and limited availability, which affects renewable sourcing. Birch plywood is often considered more sustainable because birch trees grow faster, are widely cultivated, and contribute to more efficient carbon sequestration. Both woods' sustainability depends heavily on responsible forestry practices and certifications like FSC to ensure minimal ecological footprint.
Pros and Cons of Ash Plywood
Ash plywood offers superior strength and durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications and furniture requiring high impact resistance. Its pronounced grain pattern provides an attractive aesthetic but may limit design versatility compared to the lighter, more uniform appearance of birch plywood. However, ash plywood tends to be heavier and more expensive, which could impact project cost and ease of handling.
Pros and Cons of Birch Plywood
Birch plywood offers superior strength, smooth finish, and excellent resistance to warping, making it ideal for high-quality furniture and cabinetry. Its consistent grain and uniform color allow for a sleek, professional appearance, but it tends to be heavier and more expensive than ash plywood. While birch plywood is less flexible than ash, its durability and superior sanding qualities make it a preferred choice for surfaces that require a refined finish.
Infographic: Ash vs Birch for Plywood
 azmater.com
azmater.com