Chestnut plywood offers superior durability and a rich, warm aesthetic compared to birch plywood, which is known for its smooth finish and lighter color. Birch plywood provides excellent strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for cabinetry and furniture, while chestnut excels in applications requiring enhanced hardness and wear resistance.
Table of Comparison
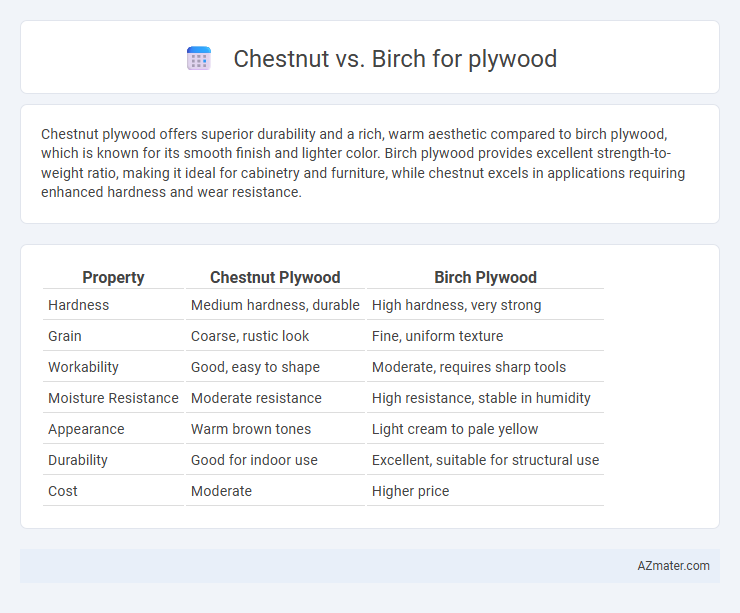
| Property | Chestnut Plywood | Birch Plywood |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | Medium hardness, durable | High hardness, very strong |
| Grain | Coarse, rustic look | Fine, uniform texture |
| Workability | Good, easy to shape | Moderate, requires sharp tools |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate resistance | High resistance, stable in humidity |
| Appearance | Warm brown tones | Light cream to pale yellow |
| Durability | Good for indoor use | Excellent, suitable for structural use |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher price |
Overview: Chestnut vs Birch for Plywood
Chestnut plywood offers a warm, reddish-brown hue with moderate hardness and durability, making it suitable for decorative interior applications. Birch plywood is known for its pale color, fine grain, and superior strength, often preferred in furniture and structural projects requiring high stability. Both woods provide good dimensional stability, but birch plywood generally delivers better performance in strength and smooth finish.
Wood Characteristics: Grain and Texture Comparison
Chestnut plywood exhibits a coarse, open grain with a rustic texture that lends a rich, natural appearance ideal for decorative applications. Birch plywood features a fine, uniform grain and smooth texture, providing a clean and consistent surface favored for cabinetry and furniture making. The distinct grain patterns of chestnut offer visual warmth, while birch's subtle texture enhances versatility in various design styles.
Strength and Durability Differences
Chestnut plywood exhibits higher strength due to its dense grain structure, making it more resistant to bending and mechanical stress compared to birch plywood. Birch plywood offers moderate durability but excels in stability and smooth surface finish, which provides advantages for interior applications. The superior hardness of chestnut results in better impact resistance, while birch plywood's consistent layer bonding ensures dimensional stability under varying humidity conditions.
Workability and Ease of Machining
Chestnut plywood offers moderate workability with a fine, straight grain that machines smoothly but may require sharper tools to avoid splintering. Birch plywood is highly regarded for its excellent workability, featuring a uniform texture that allows for clean cutting, sanding, and shaping with minimal effort. The dense, consistent fibers in birch make it preferred in applications demanding precision and ease of machining.
Resistance to Moisture and Decay
Chestnut plywood offers superior resistance to moisture and decay compared to birch plywood due to its denser grain structure and natural oils that inhibit fungal growth. Birch plywood, while strong and flexible, tends to absorb more moisture, making it more susceptible to swelling and decay in damp conditions. For applications requiring enhanced durability in wet environments, chestnut plywood provides a more reliable choice.
Aesthetic Appeal: Color and Finish Options
Chestnut plywood offers a warm, rich tone with reddish-brown hues that enhance natural grain patterns, making it ideal for rustic and classic interiors. Birch plywood provides a lighter, creamy color with a smooth, uniform texture that suits modern, minimalist aesthetics and accepts a wide range of finishes easily. Both woods deliver excellent veneer options, but chestnut's deep warmth contrasts with birch's clean brightness, influencing design choices based on desired ambiance and finish versatility.
Environmental Sustainability and Sourcing
Chestnut plywood offers greater environmental sustainability due to its fast growth rate and ability to thrive in diverse climates, resulting in a more renewable and eco-friendly source compared to birch. Birch plywood, while durable and strong, often requires harvesting from slower-growing forests, leading to higher ecological impact and more challenging sustainable sourcing. Choosing chestnut plywood supports reduced deforestation and promotes responsible forestry management, making it a preferred option for environmentally conscious construction and manufacturing.
Cost Comparison and Market Availability
Chestnut plywood generally costs more than birch plywood due to the chestnut wood's limited availability and slower growth rate, making it a premium choice for specialty projects. Birch plywood is widely available in global markets, benefiting from faster-growing birch trees and mature supply chains, which results in more competitive pricing and easier procurement. The cost difference between chestnut and birch plywood can be significant, with chestnut often priced 20-30% higher depending on grade and thickness, reflecting its niche status and market scarcity.
Common Applications in Plywood Manufacturing
Chestnut plywood is favored for decorative interior paneling and furniture due to its attractive grain and moderate hardness, offering good durability for cabinetry and shelving. Birch plywood is widely used in structural applications like flooring, cabinetry, and plywood for boats because of its high strength, smooth surface, and superior resistance to warping. Both woods provide versatility in plywood manufacturing, but birch's robust mechanical properties make it a preferred choice for load-bearing and exterior-grade plywood.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Wood for Your Plywood
Chestnut plywood offers durability and a rich aesthetic, making it ideal for decorative applications and furniture requiring a warm, classic look. Birch plywood provides superior strength and smoothness, suitable for structural uses and projects needing a consistent finish. Selecting between chestnut and birch depends on prioritizing either aesthetic appeal or structural reliability for the intended plywood use.
Infographic: Chestnut vs Birch for Plywood
 azmater.com
azmater.com