Alder wood offers a softer texture and natural antibacterial properties, making it ideal for gentle cutting tasks, while Maple wood provides a harder, more durable surface that resists knife marks and warping, ensuring long-lasting performance for heavy chopping. Choosing between Alder and Maple depends on the balance between softness for blade preservation and hardness for durability in cutting boards.
Table of Comparison
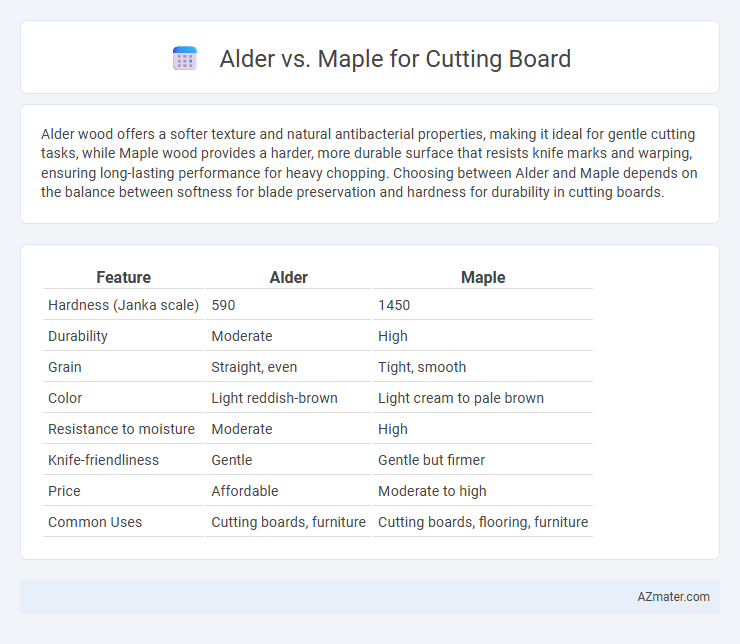
| Feature | Alder | Maple |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Janka scale) | 590 | 1450 |
| Durability | Moderate | High |
| Grain | Straight, even | Tight, smooth |
| Color | Light reddish-brown | Light cream to pale brown |
| Resistance to moisture | Moderate | High |
| Knife-friendliness | Gentle | Gentle but firmer |
| Price | Affordable | Moderate to high |
| Common Uses | Cutting boards, furniture | Cutting boards, flooring, furniture |
Introduction to Alder and Maple Cutting Boards
Alder cutting boards are valued for their smooth texture and gentle hardness, making them less likely to dull knives, while offering natural antimicrobial properties. Maple cutting boards provide exceptional durability and are highly resistant to knife marks, thanks to their dense, hard grain structure. Both woods are popular choices for kitchen use, with alder known for its lighter weight and maple favored for its longevity and ease of maintenance.
Wood Hardness: Alder vs Maple
Maple wood, with a Janka hardness rating of approximately 1450, is significantly harder than Alder, which rates around 590, making Maple more resistant to cuts, dents, and scratches for cutting boards. Alder's softness can lead to faster wear and deeper knife marks, but it is easier on knife blades and offers a smoother surface for food preparation. The choice between Alder and Maple for cutting boards balances durability against gentleness on knives, with Maple being preferred for heavy-duty use and Alder for lighter, more delicate tasks.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Alder wood offers moderate durability with a softer texture that may show knife marks more easily, while maple is known for its exceptional hardness and resistance to wear, making it a preferred choice for cutting boards. Maple's dense grain structure enhances longevity by preventing deep cuts and bacteria accumulation, ensuring a hygienic surface over time. Choosing maple over alder can significantly extend the lifespan of a cutting board due to its superior strength and ability to withstand heavy daily use.
Grain Pattern and Aesthetics
Alder cutting boards feature a fine, consistent grain pattern that provides a smooth surface ideal for precise cutting and an understated, warm reddish-brown hue enhancing kitchen aesthetics. Maple cutting boards boast a tight, uniform grain with light cream to golden tones, offering exceptional durability and a classic, clean look favored by chefs. Both woods resist knife marks well, but maple's harder texture and brighter appearance make it the preferred choice for long-lasting visual appeal and resilience.
How Each Wood Affects Knife Edges
Alder wood features a softer grain that is gentle on knife edges, reducing dulling and helping maintain sharpness over time, making it ideal for frequent kitchen use. Maple, renowned for its hardness and dense grain, offers superior durability but can cause knives to dull faster due to its firmness. Choosing between alder and maple cutting boards depends on balancing durability with the preservation of knife edge sharpness.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Alder cutting boards require less maintenance due to their softer wood grain, which is less prone to deep scratches but may show wear over time. Maple cutting boards are more durable and resistant to knife marks, demanding regular oiling to prevent drying and cracking while offering superior longevity with proper care. Both woods benefit from hand washing and frequent application of food-safe mineral oil to maintain their finish and hygiene.
Cost Differences: Alder vs Maple
Alder cutting boards are generally more affordable than maple due to the wood's faster growth rate and wider availability. Maple, particularly hard maple, tends to be pricier because of its density, durability, and popularity among chefs for cutting surfaces. Choosing alder offers a cost-effective option without compromising moderate durability, while maple provides a longer-lasting investment at a higher upfront price.
Food Safety and Porosity
Alder wood offers moderate porosity with tight grain structure, making it less prone to bacterial retention and easier to sanitize compared to highly porous woods. Maple is renowned for its dense, fine grain that significantly resists moisture absorption and inhibits bacterial growth, making it a top choice for cutting boards prioritizing food safety. Both woods provide natural antimicrobial properties, but maple's lower porosity and durability provide superior protection against contaminants and knife marks.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Alder wood is often considered more sustainable than maple due to its faster growth rate and lower demand in commercial timber markets, reducing pressure on forest ecosystems. Maple, particularly hard maple, is denser and more durable but typically grows slower, which can lead to increased environmental impact from longer harvesting cycles. Choosing alder for cutting boards supports sustainable forestry by promoting renewable resources with a smaller ecological footprint and faster replenishment times.
Which Wood is Right for Your Kitchen?
Alder wood, known for its fine grain and moderate hardness, offers a smooth surface ideal for gentle knife use, making it a great choice for cutting boards in kitchens prioritizing blade preservation. Maple, with its denser, tight grain and superior durability, is favored for heavy daily chopping and resists deep cuts or scratches, providing a longer-lasting, hygienic cutting surface. Choosing between alder and maple depends on kitchen workflow intensity and maintenance willingness--alder suits light to moderate use, while maple excels in high-traffic culinary environments.
Infographic: Alder vs Maple for Cutting Board
 azmater.com
azmater.com