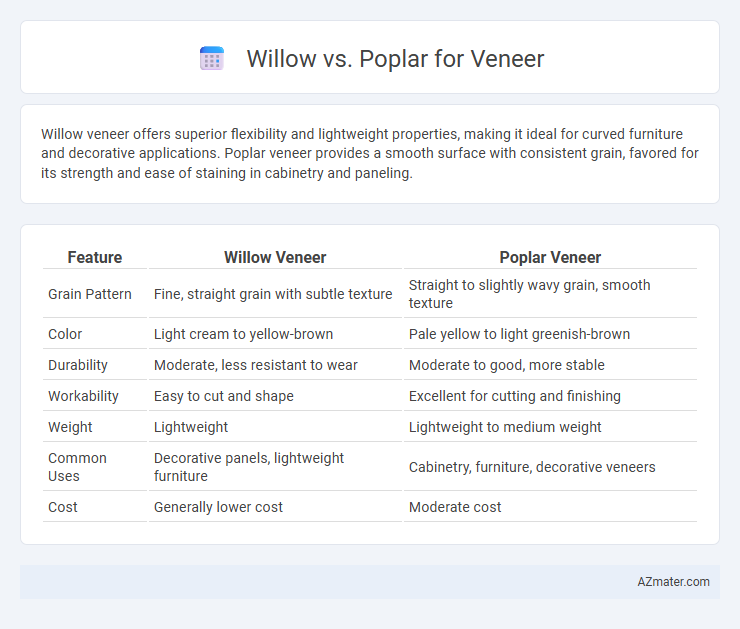
Willow veneer offers superior flexibility and lightweight properties, making it ideal for curved furniture and decorative applications. Poplar veneer provides a smooth surface with consistent grain, favored for its strength and ease of staining in cabinetry and paneling.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Willow Veneer | Poplar Veneer |
|---|---|---|
| Grain Pattern | Fine, straight grain with subtle texture | Straight to slightly wavy grain, smooth texture |
| Color | Light cream to yellow-brown | Pale yellow to light greenish-brown |
| Durability | Moderate, less resistant to wear | Moderate to good, more stable |
| Workability | Easy to cut and shape | Excellent for cutting and finishing |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight to medium weight |
| Common Uses | Decorative panels, lightweight furniture | Cabinetry, furniture, decorative veneers |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Moderate cost |
Introduction to Willow and Poplar Veneer
Willow veneer, known for its lightweight and flexible fibers, offers a smooth texture suitable for intricate woodwork and artistic applications. Poplar veneer features a fine, even grain with a light cream to greenish hue, providing a stable and easily paintable surface preferred in cabinetry and furniture making. Both veneers serve distinct aesthetic and functional purposes, with willow prized for its pliability and poplar valued for its uniformity and smooth finish.
Botanical Overview: Willow vs Poplar
Willow (Salix spp.) and Poplar (Populus spp.) are both fast-growing hardwood trees commonly used for veneer, but they differ botanically in leaf shape and growth environments; willow trees feature slender, lance-shaped leaves, often favoring moist or riparian habitats, while poplar trees exhibit broader, ovate leaves and thrive in a wider range of climates and soils. Willow belongs to the Salicaceae family and is known for its flexible, fine-grained wood ideal for intricate veneer patterns, whereas poplar, also part of the Salicaceae family, offers a lighter, more uniform texture with a pale color that is easier to stain and finish. These botanical distinctions influence veneer characteristics, with willow veneers typically preferred for decorative applications requiring intricate grain, and poplar veneers favored for their consistency and adaptability in commercial wood products.
Physical Appearance and Grain Patterns
Willow veneer exhibits a fine, smooth texture with a pale creamy to light brown color, featuring subtle, wavy grain patterns that offer a soft, natural aesthetic ideal for contemporary designs. Poplar veneer presents a more varied palette with shades ranging from light greenish to yellowish-brown, highlighted by straighter, more uniform grain patterns that provide a consistent and clean look. The contrast between Willow's delicate, flowing grains and Poplar's structured, linear arrangement makes each suitable for distinct stylistic applications in veneer woodworking.
Color Differences in Veneer Sheets
Willow veneer sheets typically showcase a pale, creamy hue with subtle green undertones that lend a soft, natural appearance, while poplar veneers exhibit a wider color range including light yellow, olive green, and occasional pinkish streaks. The color stability of poplar veneer tends to be higher, maintaining its vibrancy over time compared to willow, which may darken slightly with exposure. Designers often prefer poplar veneer for projects requiring richer tonal variation and durable color retention in fine woodworking and cabinetry.
Workability and Machining Properties
Willow veneer offers exceptional workability due to its fine, even texture and low density, allowing for smooth cutting and minimal tool wear during machining. Poplar veneer, while slightly denser, provides consistent machining properties with good dimensional stability and resistance to warping, making it ideal for intricate woodworking tasks. Both veneers respond well to adhesives and finishes, but willow's softer nature facilitates easier shaping and sanding in detailed applications.
Durability and Resistance to Damage
Willow veneer offers moderate durability but is generally softer and more prone to dents and scratches compared to poplar veneer. Poplar veneer ranks higher in resistance to damage due to its denser grain structure, making it suitable for applications requiring longevity and wear resistance. Selecting poplar veneer enhances the durability of furniture and paneling where strength and surface resilience are critical.
Cost Comparison: Willow vs Poplar Veneer
Willow veneer typically costs less than poplar veneer due to its faster growth rate and more abundant availability. Poplar veneer tends to be pricier because of its finer grain and smoother finish, which are highly valued in furniture making and cabinetry. Choosing between willow and poplar veneer ultimately depends on budget constraints and desired aesthetic qualities.
Common Uses in Furniture and Interiors
Willow veneer is prized for its flexible grain and warm, light tones, making it ideal for crafting curved furniture, decorative panels, and rustic interior accents. Poplar veneer features a fine, uniform texture with subtle greenish or creamy hues, commonly used in contemporary cabinetry, drawer fronts, and painted furniture finishes. Both woods offer cost-effective solutions with distinct aesthetic qualities, suitable for varied design styles in furniture and interior applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Willow veneer offers a faster growth cycle, enabling more sustainable harvesting with lower environmental impact compared to poplar, which requires longer growth periods and intensive resource inputs. Poplar trees, while popular for their uniform grain and strength, typically involve higher water consumption and chemical treatments that can affect ecosystem health. Choosing willow supports carbon sequestration through rapid biomass turnover and reduces deforestation pressures on slower-growing hardwood species.
Choosing the Right Veneer: Key Considerations
Willow veneer offers a lightweight, flexible option with a fine grain ideal for decorative applications, while poplar veneer provides a more durable surface with a consistent texture suited for furniture and cabinetry. Key considerations include the desired aesthetic, durability requirements, and surface finish compatibility, as poplar absorbs stains evenly and willow provides a unique, natural pattern. Budget constraints and sourcing availability also influence the choice, with poplar generally more affordable and widely available in veneer form.
Infographic: Willow vs Poplar for Veneer
 azmater.com
azmater.com