Tuff is a softer, porous volcanic rock unsuitable for cutting tools, while obsidian is a natural volcanic glass with exceptional sharpness and edge retention, making it ideal for precision cutting. Obsidian's fine-grained structure allows for extremely sharp blades commonly used in surgical instruments.
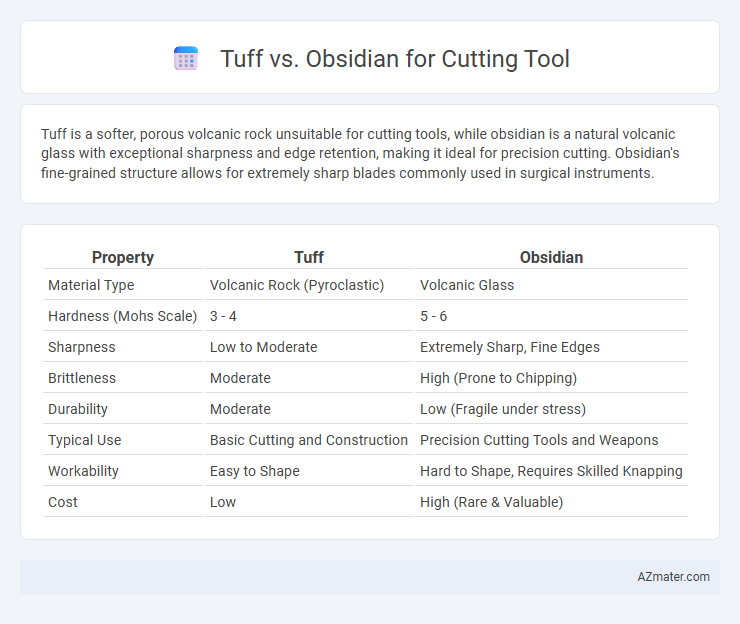
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tuff | Obsidian |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Volcanic Rock (Pyroclastic) | Volcanic Glass |
| Hardness (Mohs Scale) | 3 - 4 | 5 - 6 |
| Sharpness | Low to Moderate | Extremely Sharp, Fine Edges |
| Brittleness | Moderate | High (Prone to Chipping) |
| Durability | Moderate | Low (Fragile under stress) |
| Typical Use | Basic Cutting and Construction | Precision Cutting Tools and Weapons |
| Workability | Easy to Shape | Hard to Shape, Requires Skilled Knapping |
| Cost | Low | High (Rare & Valuable) |
Introduction to Tuff and Obsidian as Cutting Tools
Tuff and obsidian are both volcanic materials used as cutting tools, with obsidian being a naturally occurring volcanic glass known for its sharp edges and high precision in cutting applications. Tuff, a porous and softer volcanic rock, is less commonly used for cutting due to its lower hardness and brittleness compared to obsidian. Obsidian's superior hardness and fracture patterns make it ideal for knives and surgical blades, while tuff's abrasive properties limit its application primarily to grinding or crude cutting tasks.
Geological Formation and Composition
Tuff and obsidian differ significantly in geological formation and composition, influencing their suitability for cutting tools. Tuff is a porous, volcanic rock formed from consolidated ash and fragmented volcanic debris, primarily composed of volcanic glass, crystalline minerals, and rock fragments, resulting in a relatively softer and more brittle material. Obsidian is an extrusive igneous rock formed from rapidly cooled felsic lava, characterized by its high silica content (around 70-75%) and glassy texture, offering superior sharpness and fracture properties ideal for precise and durable cutting edges.
Physical Properties: Hardness and Durability
Tuff exhibits moderate hardness ranging between 5 and 6 on the Mohs scale, making it relatively soft compared to obsidian, which rates around 5 to 6 but offers superior edge sharpness due to its glassy volcanic origin. Obsidian's amorphous structure grants exceptional durability for cutting tools, allowing for extremely fine, sharp edges that maintain integrity despite use. Tuff's porous and sedimentary nature limits its durability and makes it less suitable for precision cutting applications compared to obsidian's superior hardness and fracture resistance.
Sharpness and Edge Retention
Tuff exhibits exceptional sharpness due to its fine-grained microstructure, enabling precise and clean cuts in various materials. Obsidian stands out for its superior edge retention, maintaining a sharper edge longer because of its natural glass-like composition that resists dulling. In cutting tool applications, choosing between Tuff and Obsidian depends on the balance between initial sharpness and long-term edge durability.
Historical and Archaeological Significance
Obsidian has been historically prized for its sharpness and precision in cutting tools, evidenced by its widespread use in prehistoric cultures for making arrowheads and surgical instruments due to its conchoidal fracture yielding extremely fine edges. Tuff, a volcanic ash rock, held more regional significance, often utilized for grinding tools and less frequently for cutting edges due to its softer composition. Archaeological findings reveal that obsidian artifacts provide crucial insights into ancient trade networks and craftsmanship, while tuff artifacts help understand local resource utilization and technological diversity.
Availability and Sourcing
Tuff and Obsidian differ significantly in availability and sourcing for cutting tools, with Tuff being more widely accessible due to its abundant natural deposits and simpler extraction processes. Obsidian, while prized for its sharpness and durability, is rarer and often sourced from specific volcanic regions, leading to limited commercial availability. The sourcing constraints of Obsidian result in higher costs and longer lead times compared to the more readily obtainable Tuff materials.
Performance in Tool Making
Tuff, a volcanic rock, has lower hardness and fracture toughness compared to obsidian, impacting its durability in cutting tool applications. Obsidian's natural glass structure offers superior sharpness and edge retention, making it preferred for precision cutting tools. Performance in tool making heavily favors obsidian due to its brittleness that allows for finer, more consistent flaking and sharper blade edges.
Suitability for Various Cutting Applications
Tuff exhibits superior toughness and impact resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty cutting applications such as metalworking and construction. Obsidian offers exceptional sharpness at the microscopic edge, suited for precision cutting tasks like surgical instruments and fine craftsmanship. Both materials excel in different cutting environments, with Tuff favoring durability and Obsidian prioritizing edge sharpness for delicate operations.
Cost and Sustainability
Tuff cutting tools typically offer a lower initial cost compared to Obsidian, making them more budget-friendly for large-scale industrial applications. Obsidian, however, excels in sustainability due to its natural volcanic glass composition, which reduces the need for synthetic materials and lowers environmental impact during production. Choosing Obsidian enhances tool longevity and reduces waste, supporting eco-friendly manufacturing processes despite a higher upfront investment.
Conclusion: Comparing Tuff and Obsidian Effectiveness
Tuff and obsidian differ significantly in their effectiveness as cutting tools due to their material properties; obsidian exhibits a glass-like structure that allows for extremely sharp edges, making it ideal for precision cutting. Tuff, a porous volcanic rock, lacks the durability and sharpness of obsidian, resulting in less efficient cutting capability. For applications requiring fine, clean cuts, obsidian is the superior choice, while tuff's rougher texture limits its use in cutting tool effectiveness.
Infographic: Tuff vs Obsidian for Cutting Tool
 azmater.com
azmater.com