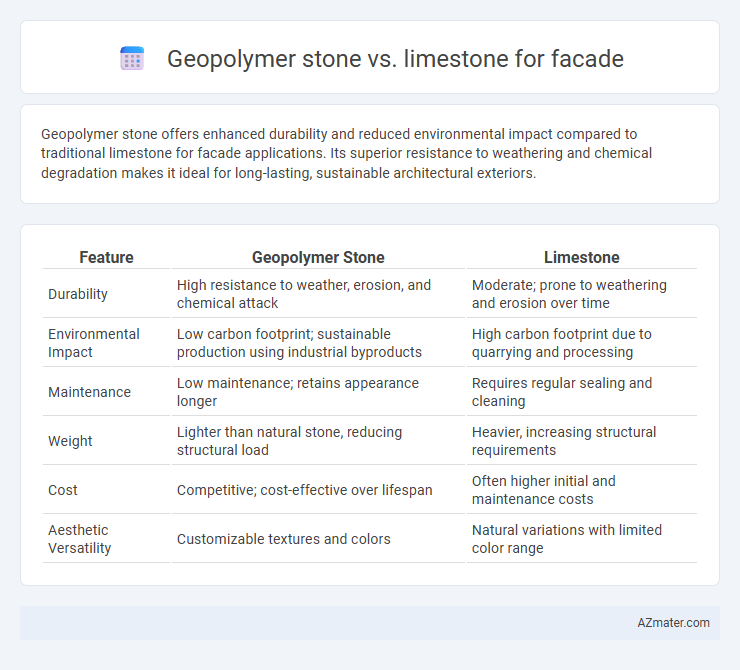
Geopolymer stone offers enhanced durability and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional limestone for facade applications. Its superior resistance to weathering and chemical degradation makes it ideal for long-lasting, sustainable architectural exteriors.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Geopolymer Stone | Limestone |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High resistance to weather, erosion, and chemical attack | Moderate; prone to weathering and erosion over time |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint; sustainable production using industrial byproducts | High carbon footprint due to quarrying and processing |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; retains appearance longer | Requires regular sealing and cleaning |
| Weight | Lighter than natural stone, reducing structural load | Heavier, increasing structural requirements |
| Cost | Competitive; cost-effective over lifespan | Often higher initial and maintenance costs |
| Aesthetic Versatility | Customizable textures and colors | Natural variations with limited color range |
Introduction to Geopolymer Stone and Limestone
Geopolymer stone is an innovative building material created from industrial byproducts like fly ash and slag, offering superior durability and resistance to environmental factors compared to traditional stones. Limestone, a natural sedimentary rock composed primarily of calcium carbonate, has long been favored for facades due to its classic aesthetic and ease of carving. While limestone provides a timeless appearance, geopolymer stone delivers enhanced sustainability and strength, making it a modern alternative for architectural exteriors.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Geopolymer stone is composed of aluminosilicate materials activated by alkaline solutions, creating a synthetic, eco-friendly material with superior durability and chemical resistance compared to natural limestone, which primarily consists of calcium carbonate formed from marine organisms over millions of years. The manufacturing process of geopolymer stone involves low-temperature curing, reducing carbon emissions and energy consumption, whereas limestone is extracted from quarries and processed through cutting and polishing. Geopolymer technology offers enhanced control over composition and physical properties, enabling customized facade solutions that outperform traditional limestone in sustainability and performance metrics.
Aesthetic Qualities and Design Flexibility
Geopolymer stone offers a contemporary aesthetic with customizable colors, textures, and finishes that can mimic natural stone or create unique, modern looks for facades. Limestone provides a classic, timeless appearance characterized by its natural veining and subtle color variations, enhancing traditional architectural designs. The design flexibility of geopolymer stone surpasses limestone due to its engineered composition, allowing for intricate shapes and sizes that limestone's natural formation cannot easily achieve.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Geopolymer stone exhibits superior durability and weather resistance compared to traditional limestone, as it is engineered to withstand extreme temperature fluctuations, moisture, and chemical exposure without significant degradation. Its enhanced resistance to acid rain and freeze-thaw cycles makes geopolymer stone an ideal choice for facades in harsh environmental conditions. Limestone, while aesthetically appealing, is more prone to erosion, staining, and weathering over time, reducing its longevity on exterior surfaces.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Geopolymer stone significantly reduces carbon emissions compared to traditional limestone by utilizing industrial byproducts like fly ash and slag, lowering the demand for quarrying and preserving natural landscapes. The production process of geopolymer stone consumes less energy and emits fewer greenhouse gases, enhancing its sustainability profile for facade applications. Limestone extraction often leads to habitat disruption and high CO2 emissions, making geopolymer stone an environmentally preferable choice for eco-conscious building projects.
Thermal and Acoustic Performance
Geopolymer stone offers superior thermal insulation and acoustic dampening compared to traditional limestone, reducing heat transfer and external noise infiltration. Its low thermal conductivity enhances energy efficiency in facades, while its dense microstructure improves sound absorption, making it ideal for urban environments. Limestone, although durable, generally exhibits higher thermal conductivity and less effective sound insulation, resulting in increased energy consumption and noise levels.
Weight and Structural Considerations
Geopolymer stone offers significantly lower weight compared to traditional limestone, reducing structural load and enabling easier installation on facades. Its high compressive strength and durability make it suitable for long-term exterior use, often outperforming limestone in resistance to weathering and environmental stress. The reduced weight of geopolymer stone decreases the need for heavy structural support, providing architects and engineers with greater design flexibility.
Installation and Maintenance Differences
Geopolymer stone offers easier installation due to its lightweight nature and consistent sizing, reducing labor time compared to traditional limestone, which is heavier and more variable in thickness. Maintenance of geopolymer stone is typically lower because it resists staining, weathering, and requires less frequent sealing, whereas limestone often demands regular cleaning and sealing to prevent erosion and discoloration. The durability of geopolymer stone in harsh environmental conditions makes it a cost-effective facade option when compared to limestone's susceptibility to acid rain and freeze-thaw damage.
Cost Comparison and Economic Factors
Geopolymer stone offers a competitive cost advantage over limestone for facades, primarily due to lower material and production expenses driven by the use of industrial byproducts like fly ash or slag. Limestone extraction and processing involve higher labor and transportation costs, which can increase overall project budgets significantly. Economic factors favor geopolymer stone as it reduces long-term maintenance and environmental compliance costs, enhancing its value for sustainable construction projects.
Suitability for Modern Facade Applications
Geopolymer stone offers superior durability and environmental benefits compared to traditional limestone, making it highly suitable for modern facade applications that demand sustainability and resilience. Its high compressive strength and resistance to weathering ensure long-lasting performance in harsh urban environments while providing a versatile aesthetic similar to natural stone. Limestone, though classic and visually appealing, is prone to acid rain damage and erosion, limiting its use in pollution-heavy areas and reducing its suitability for contemporary, eco-conscious construction projects.
Infographic: Geopolymer stone vs Limestone for Facade
 azmater.com
azmater.com