Reconstituted stone offers enhanced durability and consistent texture compared to natural sandstone, making it ideal for pavement applications. Sandstone provides natural aesthetic appeal but is more prone to weathering and erosion over time.
Table of Comparison
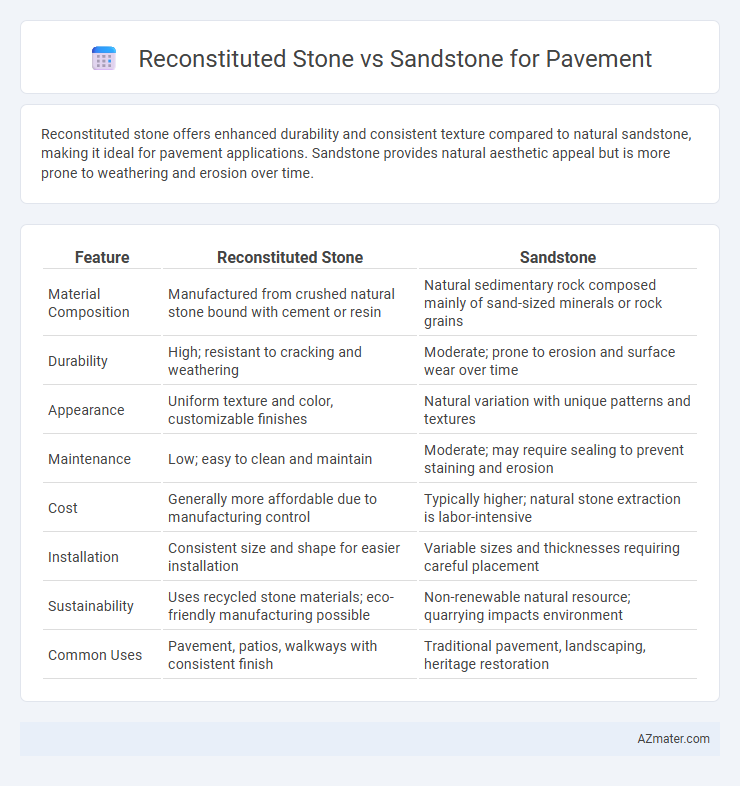
| Feature | Reconstituted Stone | Sandstone |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Manufactured from crushed natural stone bound with cement or resin | Natural sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized minerals or rock grains |
| Durability | High; resistant to cracking and weathering | Moderate; prone to erosion and surface wear over time |
| Appearance | Uniform texture and color, customizable finishes | Natural variation with unique patterns and textures |
| Maintenance | Low; easy to clean and maintain | Moderate; may require sealing to prevent staining and erosion |
| Cost | Generally more affordable due to manufacturing control | Typically higher; natural stone extraction is labor-intensive |
| Installation | Consistent size and shape for easier installation | Variable sizes and thicknesses requiring careful placement |
| Sustainability | Uses recycled stone materials; eco-friendly manufacturing possible | Non-renewable natural resource; quarrying impacts environment |
| Common Uses | Pavement, patios, walkways with consistent finish | Traditional pavement, landscaping, heritage restoration |
Introduction to Reconstituted Stone and Sandstone
Reconstituted stone is a manufactured material composed of crushed natural stone bound together with resin or cement, offering enhanced durability and design flexibility for pavement applications. Sandstone, a natural sedimentary rock formed from compacted sand grains, features a distinctive grainy texture and varies widely in color and hardness, influencing its suitability for outdoor pavements. Both materials provide aesthetic appeal and functional benefits, with reconstituted stone offering more uniformity and sandstone delivering authentic natural patterns.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Reconstituted stone for pavement is composed of crushed natural stone fragments bound together with cement or resin, allowing for consistent texture and color, while sandstone is a naturally occurring sedimentary rock primarily made of quartz and feldspar grains cemented by silica or calcium carbonate. The manufacturing process of reconstituted stone involves mixing raw aggregates with binders, molding, and curing under controlled conditions to achieve desired strength and durability, whereas sandstone is quarried directly from the earth and requires minimal processing beyond cutting and finishing. The controlled production of reconstituted stone offers greater uniformity and design flexibility compared to the natural variability inherent in sandstone.
Visual Appearance and Aesthetic Differences
Reconstituted stone offers a uniform texture and consistent color palette, allowing for customizable designs that mimic natural sandstone while providing enhanced pattern flexibility. Sandstone exhibits unique, naturally occurring color variations and grain patterns that create an organic, rustic aesthetic, often preferred for traditional pavement applications. The choice between reconstituted stone and sandstone impacts the visual appeal, with reconstituted stone enabling more controlled aesthetics and sandstone emphasizing natural irregularity.
Durability and Longevity
Reconstituted stone offers enhanced durability for pavement applications due to its engineered composition, which includes crushed natural stone bonded with resin or cement, making it highly resistant to wear, weathering, and freeze-thaw cycles. Sandstone, a natural sedimentary rock, provides a timeless aesthetic but can be more susceptible to erosion, chipping, and moisture absorption, potentially reducing its longevity in high-traffic or harsh climate areas. For long-lasting pavements, reconstituted stone typically outperforms sandstone by maintaining structural integrity and appearance over extended periods under variable environmental conditions.
Slip Resistance and Safety
Reconstituted stone offers enhanced slip resistance for pavements due to its uniform texture and ability to incorporate anti-slip aggregates during manufacturing, making it safer in wet or icy conditions compared to natural sandstone, which can become smooth and slippery over time. Sandstone's porous surface can retain moisture, increasing slip hazards, especially when worn or polished. Choosing reconstituted stone for high-traffic or safety-critical pavement areas significantly reduces slip risk and improves overall pedestrian safety.
Maintenance Requirements
Reconstituted stone pavement requires significantly less maintenance than natural sandstone due to its uniform composition and enhanced durability against weathering and wear. Sandstone pavements often need frequent sealing and repairs because of their porous nature, which makes them susceptible to erosion, staining, and cracking over time. Choosing reconstituted stone can reduce long-term maintenance costs and extend pavement lifespan in high-traffic outdoor environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Reconstituted stone for pavement often demonstrates a lower environmental impact due to its use of recycled materials and reduced quarrying requirements compared to natural sandstone. Sandstone extraction involves significant land disruption, higher carbon emissions, and habitat disturbance, whereas reconstituted stone production can integrate industrial by-products, promoting circular economy principles. Choosing reconstituted stone aligns with sustainability goals by minimizing resource depletion and lowering overall ecological footprint in pavement construction.
Cost Comparison and Value
Reconstituted stone offers a cost-effective alternative to natural sandstone for pavements, typically reducing material expenses by up to 30% due to its engineered manufacturing process. While natural sandstone provides unique aesthetic and textural qualities, reconstituted stone delivers consistent quality and enhanced durability, minimizing long-term maintenance costs. Investing in reconstituted stone maximizes value by combining affordability with performance, making it an efficient choice for large-scale paving projects.
Installation Process and Flexibility
Reconstituted stone offers a more streamlined installation process compared to natural sandstone due to its uniform size and shape, allowing for faster laying with minimal cutting or adjustment. Its engineered composition provides superior flexibility in design, enabling the creation of intricate patterns and curves that are more challenging with the irregularity of natural sandstone slabs. Sandstone pavement requires careful fitting and may demand additional labor to accommodate its variations, reducing installation efficiency and limiting design adaptability.
Best Applications and Use Cases
Reconstituted stone offers superior uniformity, durability, and a broader range of colors and textures, making it ideal for high-traffic urban pavements, commercial plazas, and contemporary landscaping projects. Sandstone, prized for its natural aesthetic and weathering properties, is best suited for traditional, low-traffic pathways, garden features, and historical restoration projects where authenticity is a priority. Selecting reconstituted stone enhances long-term performance and design flexibility, whereas sandstone delivers a classic, organic look with natural slip resistance.
Infographic: Reconstituted stone vs Sandstone for Pavement
 azmater.com
azmater.com