Engineered stone offers consistent durability and uniform appearance ideal for detailed sculptures, while serpentine provides natural veining and softer textures favored for intricate hand-carving. Sculptors choose engineered stone for precision and longevity, whereas serpentine is selected for its aesthetic depth and ease of manipulation.
Table of Comparison
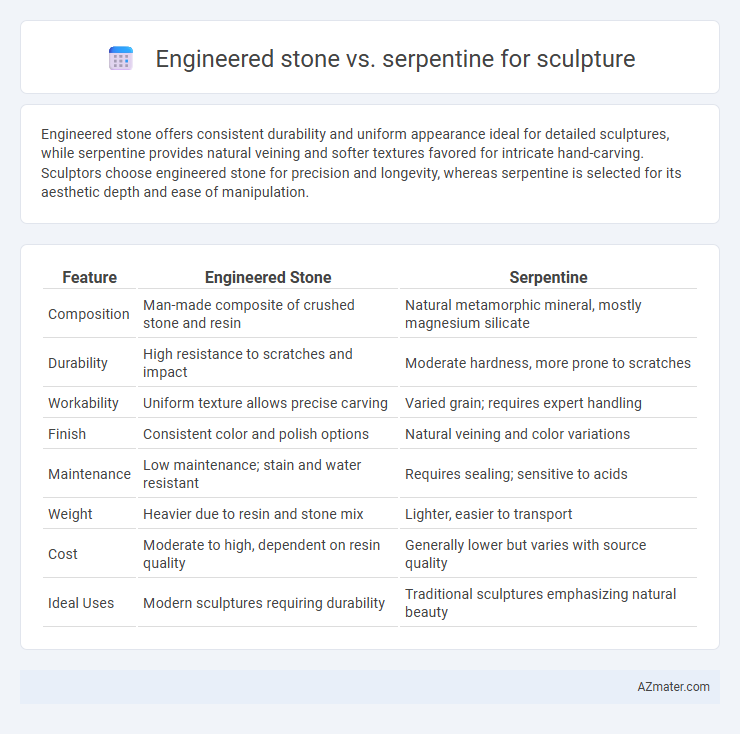
| Feature | Engineered Stone | Serpentine |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Man-made composite of crushed stone and resin | Natural metamorphic mineral, mostly magnesium silicate |
| Durability | High resistance to scratches and impact | Moderate hardness, more prone to scratches |
| Workability | Uniform texture allows precise carving | Varied grain; requires expert handling |
| Finish | Consistent color and polish options | Natural veining and color variations |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; stain and water resistant | Requires sealing; sensitive to acids |
| Weight | Heavier due to resin and stone mix | Lighter, easier to transport |
| Cost | Moderate to high, dependent on resin quality | Generally lower but varies with source quality |
| Ideal Uses | Modern sculptures requiring durability | Traditional sculptures emphasizing natural beauty |
Introduction to Engineered Stone and Serpentine
Engineered stone, composed of crushed quartz mixed with resins, offers durability and uniformity, making it ideal for intricate sculpting and contemporary designs. Serpentine, a natural metamorphic rock with rich green hues and subtle veining, has been favored by sculptors for centuries due to its softness and ease of carving. The choice between engineered stone and serpentine depends on the desired aesthetic, structural strength, and texture requirements in sculpture projects.
Composition and Structure Comparison
Engineered stone consists primarily of quartz crystals bound with polymer resins, creating a non-porous, highly durable surface ideal for detailed sculpting and minimal maintenance. Serpentine, a natural metamorphic rock composed mainly of magnesium silicate minerals, features a softer, more fibrous structure that offers unique textural qualities but is more susceptible to weathering and chemical degradation. The engineered stone's uniform consistency allows for precise carving and structural stability, whereas serpentine's variable grain and mineral inclusions provide distinct aesthetic patterns but challenge long-term durability in outdoor sculptures.
Visual Aesthetics: Color and Texture
Engineered stone offers a wide palette of consistent colors and uniform textures, allowing sculptors to achieve precise visual effects with smooth or patterned finishes. Serpentine features natural veining and a rich range of green, yellow, and black hues, providing unique, organic aesthetics that vary with each piece. The choice between engineered stone and serpentine hinges on the desired balance of predictability in color and texture versus the natural, variable beauty that serpentine imparts.
Workability and Sculpting Techniques
Engineered stone offers consistent hardness and uniform texture, making it highly versatile for intricate carving and fine detailing in sculpture. Serpentine, with its softer and more variable composition, allows for easier initial shaping and smoother finishing techniques but may require more attention to prevent cracking. Sculptors often select engineered stone for precision work, while serpentine is favored for organic forms and fluid sculpting styles due to its superior workability.
Durability and Longevity in Sculptures
Engineered stone offers superior durability for sculptures due to its consistent composition and resistance to chipping, cracking, and weathering, making it ideal for both indoor and outdoor installations. Serpentine, a natural metamorphic rock, has moderate durability but is more prone to chemical weathering and surface degradation over time, especially in harsh environmental conditions. Sculptors prioritizing longevity often choose engineered stone to ensure sustained structural integrity and minimal maintenance.
Cost Considerations for Artists
Engineered stone offers a cost-effective option for artists due to its lower price per square foot compared to serpentine, making it accessible for larger-scale sculptures or multiple projects. Serpentine, known for its unique veining and natural beauty, commands higher prices and may require more specialized tools and handling, increasing overall expenses. Budget-conscious artists often choose engineered stone to balance aesthetics and affordability without compromising on durability or ease of carving.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Engineered stone used in sculpture often incorporates recycled materials, reducing quarrying-related environmental degradation, while serpentine extraction involves significant habitat disruption and energy-intensive mining. Engineered stone's consistent composition allows for minimal waste during sculpting, promoting sustainability through efficient material use and reduced disposal. Serpentine, being a natural mineral, lacks recyclability and generates more dust and waste, contributing to higher environmental impact compared to engineered alternatives.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Engineered stone requires minimal maintenance due to its non-porous surface, resisting stains and scratches without frequent sealing or special treatments. Serpentine, a natural stone, demands regular sealing and careful cleaning with pH-neutral products to prevent etching and discoloration caused by acids or moisture. Both materials benefit from avoiding harsh chemicals and abrasives, but engineered stone offers greater durability and easier upkeep for sculptors prioritizing low-maintenance solutions.
Notable Examples in Modern Sculpture
Engineered stone, composed of crushed natural stones bonded with resin, is prized in modern sculpture for its durability and consistency, allowing artists like Anish Kapoor to create smooth, polished surfaces with vibrant colors. Serpentine, a natural mineral valued for its rich green hues and workability, has been favored by sculptors such as Henry Moore, who emphasized organic forms and textural contrasts in his pieces. While engineered stone offers uniformity and enhanced structural integrity, serpentine provides unique, variegated patterns that appeal to artists seeking natural imperfections and historic resonance.
Choosing the Best Material for Your Sculpture Project
Engineered stone offers uniformity, durability, and resistance to weathering, making it ideal for detailed or outdoor sculptures requiring longevity. Serpentine, known for its unique color variations and softer texture, enables intricate carving but may weather faster and require more maintenance. Selecting the best material depends on the sculpture's exposure environment, desired finish, and the artist's preference for workability or durability.
Infographic: Engineered stone vs Serpentine for Sculpture
 azmater.com
azmater.com