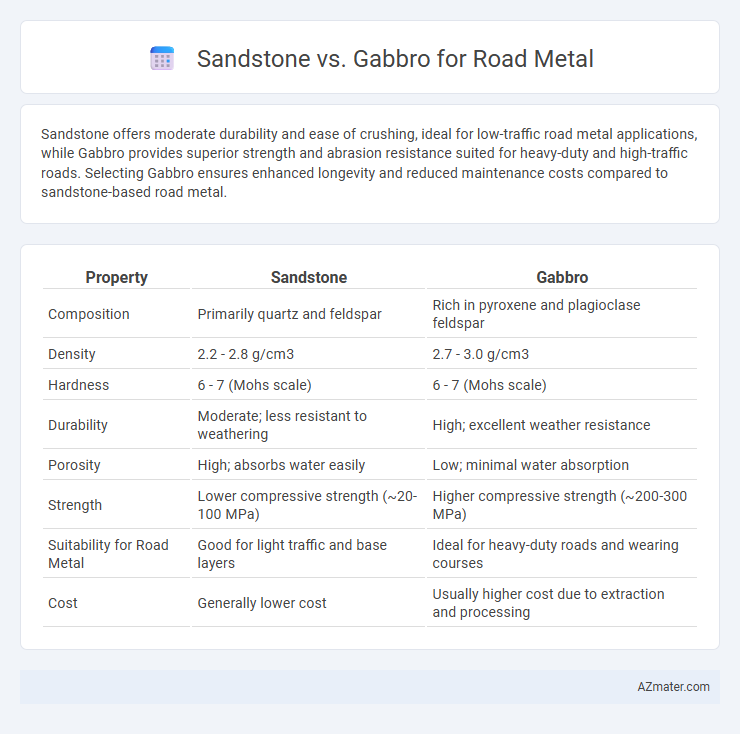
Sandstone offers moderate durability and ease of crushing, ideal for low-traffic road metal applications, while Gabbro provides superior strength and abrasion resistance suited for heavy-duty and high-traffic roads. Selecting Gabbro ensures enhanced longevity and reduced maintenance costs compared to sandstone-based road metal.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Sandstone | Gabbro |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Primarily quartz and feldspar | Rich in pyroxene and plagioclase feldspar |
| Density | 2.2 - 2.8 g/cm3 | 2.7 - 3.0 g/cm3 |
| Hardness | 6 - 7 (Mohs scale) | 6 - 7 (Mohs scale) |
| Durability | Moderate; less resistant to weathering | High; excellent weather resistance |
| Porosity | High; absorbs water easily | Low; minimal water absorption |
| Strength | Lower compressive strength (~20-100 MPa) | Higher compressive strength (~200-300 MPa) |
| Suitability for Road Metal | Good for light traffic and base layers | Ideal for heavy-duty roads and wearing courses |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Usually higher cost due to extraction and processing |
Introduction to Road Metal: Sandstone vs Gabbro
Road metal selection significantly impacts pavement durability and load-bearing capacity, with sandstone and gabbro being common choices. Sandstone, a sedimentary rock, offers good abrasion resistance but tends to be softer and more porous, affecting longevity in high-traffic conditions. Gabbro, an igneous rock, features higher density and superior compressive strength, making it ideal for heavy-duty road construction and enhanced skid resistance.
Geological Formation and Composition
Sandstone is a sedimentary rock formed from compacted sand grains, primarily composed of quartz and feldspar, making it relatively porous and softer compared to igneous rocks. Gabbro, an intrusive igneous rock, forms from slow-cooling magma beneath the Earth's surface, consisting mainly of plagioclase feldspar and pyroxene, resulting in a dense, coarse-grained texture. For road metal, gabbro's hardness and durability provide superior load-bearing capacity and resistance to wear, while sandstone's lower strength limits its usage to less demanding applications.
Physical Properties Comparison
Sandstone is a sedimentary rock with moderate hardness and lower compressive strength, typically ranging between 30-120 MPa, making it less durable for heavy road traffic. Gabbro, an intrusive igneous rock, exhibits higher density and compressive strength often exceeding 200 MPa, providing superior load-bearing capacity and resistance to abrasion. The coarse-grained texture and interlocking mineral crystals in gabbro contribute to its enhanced durability compared to the softer, more porous nature of sandstone.
Durability and Strength for Road Construction
Gabbro exhibits superior durability and strength compared to sandstone, making it more suitable for road metal in heavy traffic and load-bearing applications. The coarse-grained igneous texture of gabbro provides high compressive strength and resistance to abrasion, essential for long-lasting road surfaces. Sandstone, while easier to quarry and cost-effective, generally offers lower compressive strength and can degrade faster under intense mechanical stress and weather conditions.
Aggregate Size and Shape in Road Metal
Sandstone aggregates for road metal typically feature a more angular and coarse texture, enhancing interlock and traction but may vary in size distribution due to natural sediment layering. Gabbro aggregates tend to have a more uniform grain size and a denser, blocky shape, contributing to higher strength and durability in load-bearing road surfaces. The choice between sandstone and gabbro in road metal depends on specific aggregate size requirements and shape characteristics essential for optimal road stability and longevity.
Wear Resistance and Longevity
Sandstone's moderate wear resistance and porosity reduce its longevity under heavy traffic, making it less ideal for road metal where durability is critical. Gabbro, an igneous rock with high hardness and density, offers superior wear resistance and significantly longer lifespan in road construction. Its interlocking crystal structure withstands abrasive forces and weight, ensuring enhanced stability and reduced maintenance costs over time.
Water Absorption and Weathering Effects
Sandstone exhibits higher water absorption rates compared to gabbro, making it more susceptible to freeze-thaw cycles and accelerated weathering in road metal applications. Gabbro's low porosity and superior water resistance contribute to enhanced durability and reduced surface degradation under harsh weather conditions. These properties make gabbro a more reliable choice for road metal, ensuring longevity and structural integrity.
Cost and Availability in Construction Markets
Sandstone is generally more affordable and widely available in regional construction markets, making it a cost-effective choice for road metal. Gabbro, being denser and harder, often comes at a higher price due to quarrying complexity and limited local deposits. Availability of sandstone ensures quicker procurement and lower transportation costs, while gabbro's scarcity can lead to delays and increased expenses.
Environmental Impact of Sandstone vs Gabbro
Sandstone and gabbro differ significantly in environmental impact when used as road metal due to their geological and extraction characteristics. Sandstone quarrying leads to higher dust emissions and habitat disruption because it is softer and more porous, increasing erosion and sediment runoff risks. Gabbro, being denser and more durable, generates less fine particulate matter during crushing and offers longer-lasting road surfaces, reducing the frequency of material replacement and associated environmental disturbances.
Conclusion: Best Choice for Road Metal Applications
Gabbro is the best choice for road metal applications due to its superior hardness, durability, and resistance to weathering compared to sandstone. Its coarse-grained texture provides excellent load-bearing capacity and stability under heavy traffic conditions. Sandstone, being softer and more porous, is less suitable for high-traffic roads where longevity and strength are critical.
Infographic: Sandstone vs Gabbro for Road Metal
 azmater.com
azmater.com