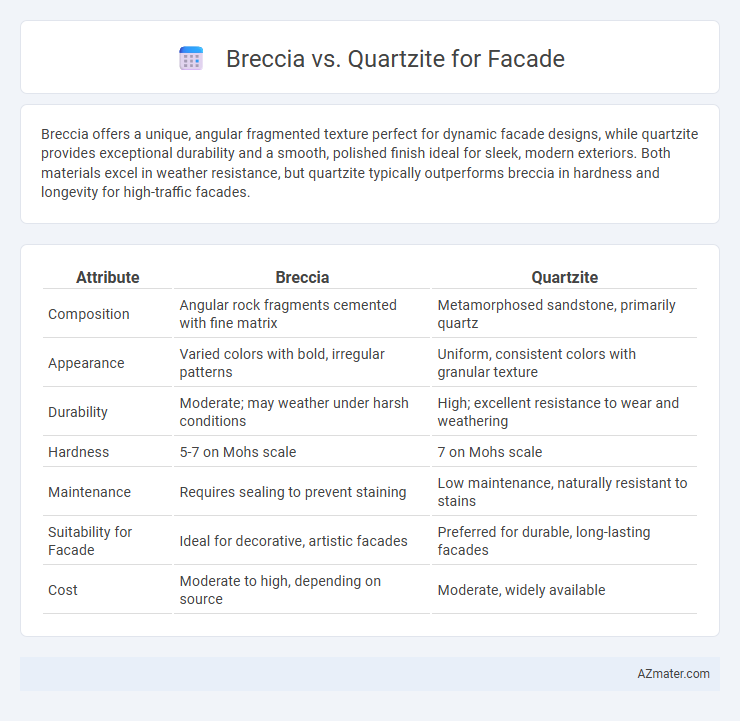
Breccia offers a unique, angular fragmented texture perfect for dynamic facade designs, while quartzite provides exceptional durability and a smooth, polished finish ideal for sleek, modern exteriors. Both materials excel in weather resistance, but quartzite typically outperforms breccia in hardness and longevity for high-traffic facades.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Breccia | Quartzite |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Angular rock fragments cemented with fine matrix | Metamorphosed sandstone, primarily quartz |
| Appearance | Varied colors with bold, irregular patterns | Uniform, consistent colors with granular texture |
| Durability | Moderate; may weather under harsh conditions | High; excellent resistance to wear and weathering |
| Hardness | 5-7 on Mohs scale | 7 on Mohs scale |
| Maintenance | Requires sealing to prevent staining | Low maintenance, naturally resistant to stains |
| Suitability for Facade | Ideal for decorative, artistic facades | Preferred for durable, long-lasting facades |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on source | Moderate, widely available |
Introduction to Breccia and Quartzite
Breccia is a clastic sedimentary rock composed of angular fragments cemented together, prized for its bold, irregular patterns and natural color variations that create a dramatic facade appearance. Quartzite, a metamorphic rock formed from sandstone, offers exceptional durability and a smooth, glassy surface with consistent texture and color, ideal for sleek and modern building exteriors. Both materials provide distinctive aesthetic and structural benefits, making them popular choices for high-end architectural facades.
Geological Formation and Characteristics
Breccia is a clastic sedimentary rock composed of angular, fragmented rock pieces cemented by finer material, formed through processes like tectonic activity or volcanic eruptions. Quartzite originates from the metamorphism of pure quartz sandstone, resulting in a dense, hard, and highly durable rock with interlocking quartz grains. For facade applications, breccia offers distinctive, varied textures and color patterns due to its heterogeneous composition, while quartzite provides superior weather resistance and a uniform, crystalline appearance.
Aesthetic Differences in Facade Applications
Breccia displays a striking, fragmented texture with angular, multicolored rock pieces set in a contrasting matrix, creating a dynamic and visually complex facade that emphasizes natural patterns and irregularity. Quartzite offers a more uniform, crystalline appearance with subtle veining and a smooth surface, delivering a sleek and elegant facade aesthetic that highlights durability and refined stone character. For facade applications, breccia's bold, mosaic-like visuals suit statement architectural designs, while quartzite's consistent texture complements minimalist and contemporary styles.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Breccia offers a unique aesthetic but is generally less durable than quartzite due to its composition of cemented rock fragments, making it more susceptible to weathering and erosion on facades exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Quartzite, a metamorphic rock primarily composed of fused quartz grains, provides superior hardness and resistance to abrasion, ensuring longer-lasting facade performance with minimal maintenance. For facade applications demanding long-term durability, quartzite is preferred over breccia, especially in climates with fluctuating temperatures and moisture exposure.
Weather Resistance and Maintenance
Breccia offers unique aesthetic appeal with its angular fragments but tends to be less weather resistant than quartzite, as its natural porosity can lead to water absorption and surface erosion over time. Quartzite, formed from high-grade metamorphism, exhibits superior weather resistance due to its dense, non-porous structure, making it ideal for facades exposed to harsh climatic conditions. Maintenance for breccia often requires regular sealing to prevent staining and weather damage, whereas quartzite demands minimal upkeep, retaining its durability and appearance with simple cleaning.
Color and Texture Variations
Breccia offers a striking facade option with its angular fragments and diverse color palette ranging from deep reds and browns to soft creams, creating a dynamic, textured surface. Quartzite provides a more uniform appearance with subtle color variations in whites, grays, and earthy tones, coupled with a smooth, glassy texture that enhances natural light reflection. Selecting Breccia emphasizes bold, contrasting patterns, while Quartzite ensures elegant consistency and durability for exterior cladding.
Installation Methods and Challenges
Breccia and quartzite each require distinct installation methods tailored to their physical properties; breccia's varied texture demands precise cutting and specialized adhesives to prevent fracturing, while quartzite's hardness necessitates diamond-tipped tools and anchors for secure mounting. Challenges with breccia include managing its natural fissures and ensuring structural integrity during handling, whereas quartzite poses difficulties due to its density and weight, often requiring reinforced support systems. Selecting appropriate installation techniques and addressing these material-specific challenges ensures durability and aesthetic appeal for facades using breccia or quartzite.
Cost Analysis: Breccia vs Quartzite
Breccia typically costs less than quartzite due to its more abundant availability and easier quarrying processes, making it a budget-friendly choice for facades. Quartzite, known for its hardness and durability, commands a higher price, reflecting its superior resistance to weathering and longer lifespan. When analyzing facade material costs, consider both initial purchase price and long-term maintenance expenses, where quartzite often offers better value despite its higher upfront investment.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Breccia and quartzite differ significantly in sustainability and environmental impact when used for facades. Quartzite, a naturally durable and dense metamorphic rock, requires less maintenance and has a longer lifespan, reducing the frequency of replacement and associated resource extraction. Breccia, composed of various rock fragments cemented together, often requires more processing and sealing, leading to higher environmental costs and less longevity compared to quartzite.
Choosing the Best Stone for Facades
Breccia offers a unique, angular pattern with vibrant colors, making it ideal for striking, decorative facades, while quartzite provides exceptional hardness and weather resistance, ensuring long-lasting durability in exterior applications. Choosing the best stone for facades depends on balancing aesthetic preferences with structural requirements, as quartzite's superior strength withstands harsh environments better than breccia's more porous composition. For facade projects where longevity and minimal maintenance are priorities, quartzite remains the preferred choice, whereas breccia suits designs emphasizing visual impact and distinctive texture.
Infographic: Breccia vs Quartzite for Facade
 azmater.com
azmater.com