Diorite offers durability and a coarse-grained texture ideal for rugged landscape decoration, while Schist provides a layered, foliated appearance with excellent split surfaces perfect for decorative walls and pathways. Choosing between Diorite and Schist depends on the desired aesthetic and functional requirements of the landscape design.
Table of Comparison
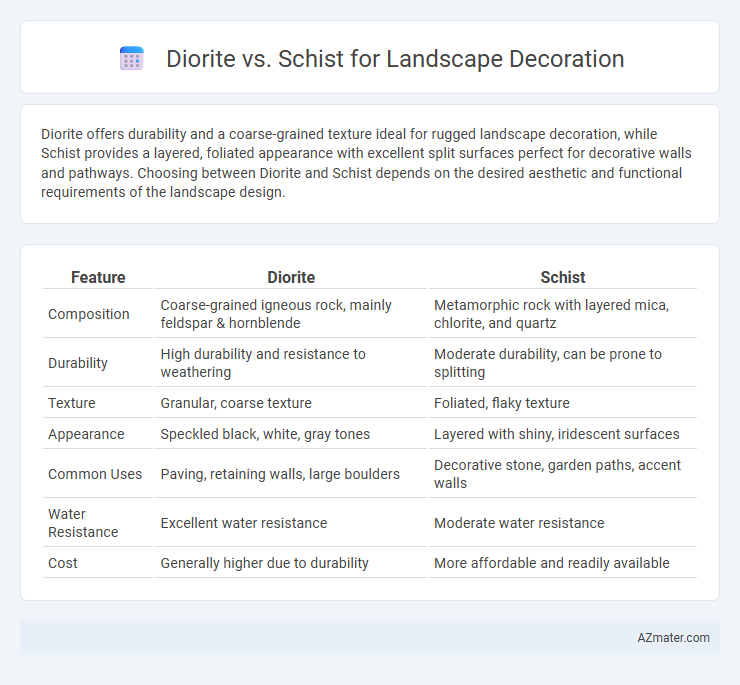
| Feature | Diorite | Schist |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Coarse-grained igneous rock, mainly feldspar & hornblende | Metamorphic rock with layered mica, chlorite, and quartz |
| Durability | High durability and resistance to weathering | Moderate durability, can be prone to splitting |
| Texture | Granular, coarse texture | Foliated, flaky texture |
| Appearance | Speckled black, white, gray tones | Layered with shiny, iridescent surfaces |
| Common Uses | Paving, retaining walls, large boulders | Decorative stone, garden paths, accent walls |
| Water Resistance | Excellent water resistance | Moderate water resistance |
| Cost | Generally higher due to durability | More affordable and readily available |
Introduction to Diorite and Schist in Landscape Design
Diorite, an intrusive igneous rock characterized by its coarse-grained texture and durable nature, offers a striking combination of gray, black, and white minerals ideal for rugged landscape accents. Schist, a metamorphic rock known for its foliated texture and shimmering mica content, provides versatile, layered surfaces that enhance aesthetic depth and natural elegance in garden paths and retaining walls. Both materials contribute unique textures and colors, with diorite's strength suited for structural features and schist's foliated nature lending itself to decorative applications in landscape design.
Geological Origins: Diorite vs Schist
Diorite is an intrusive igneous rock formed from the slow cooling of magma beneath the Earth's surface, characterized by a coarse-grained texture composed primarily of plagioclase feldspar and biotite or hornblende minerals. Schist is a metamorphic rock originating from the transformation of shale or mudstone under high temperature and pressure conditions, exhibiting a foliated structure with abundant mica minerals that give it a shiny appearance. The contrasting geological origins influence their durability and aesthetic appeal, making diorite more resistant to weathering and schist favored for its layered textures in landscape decoration.
Physical Characteristics: Texture and Appearance
Diorite features a coarse-grained texture with interlocking crystals of feldspar and dark minerals, creating a speckled, salt-and-pepper appearance ideal for bold landscape accents. Schist exhibits a foliated texture with visible layers of mica and quartz, offering a shiny, flaky surface that adds a natural, rustic charm to garden pathways and decorative rock formations. Both stones provide durability, but Diorite's granular surface resists weathering better, while Schist's layered structure enhances organic aesthetic appeal in landscape design.
Color Variations and Aesthetic Appeal
Diorite offers a striking, speckled appearance with black, white, and gray tones that create a sleek, modern aesthetic ideal for contemporary landscapes. Schist features layered textures with earthy hues like green, brown, and silver, providing a rustic, natural appeal perfect for garden paths and rock walls. Both stones enhance landscape decoration, but diorite's polished look contrasts with schist's textured, shimmering surface, influencing design choices based on desired visual effects.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Diorite offers exceptional durability and superior weather resistance due to its coarse-grained, igneous composition, making it ideal for long-lasting landscape decoration in harsh climates. Schist, a metamorphic rock with pronounced foliation, is less durable and more prone to weathering and erosion, especially in freeze-thaw cycles or heavy moisture exposure. Choosing diorite ensures minimal maintenance and sustained aesthetic appeal, while schist provides a more textured look but requires protection from weathering elements.
Installation Techniques for Each Stone
Diorite requires mechanical cutting and precise drilling due to its hardness, making installation labor-intensive but durable for landscape edging and retaining walls. Schist's foliated texture allows for easier splitting and shaping using hand tools, facilitating faster installation for decorative pathways and garden accents. Both stones need proper sub-base preparation and drainage to ensure long-lasting stability in outdoor settings.
Maintenance Requirements: Diorite vs Schist
Diorite requires minimal maintenance due to its dense, hard composition that resists weathering, making it ideal for long-lasting landscape features. Schist, characterized by its foliated texture, demands more frequent upkeep as it is prone to flaking and erosion under harsh environmental conditions. Choosing diorite over schist reduces the need for sealing, cleaning, and repairs, ensuring a more durable and low-maintenance decorative landscape element.
Cost Comparison and Budget Considerations
Diorite typically costs more than schist due to its durability and aesthetic appeal, making it a premium choice for landscape decoration projects. Schist offers a more budget-friendly option with its unique layered texture, appealing to those prioritizing cost-efficiency. When budgeting for landscape decoration, considering material price per square foot and installation expenses is essential to balance durability with financial constraints.
Best Landscaping Applications for Diorite and Schist
Diorite's coarse-grained texture and durability make it ideal for high-traffic landscape features such as pathways, retaining walls, and decorative boulders, providing long-lasting structural integrity. Schist, characterized by its foliated layers and natural cleavage, excels in garden accents, water features, and rockeries where its shimmering mineral composition adds aesthetic appeal and natural drainage benefits. Both stones enhance outdoor spaces, but diorite suits structural applications, while schist is preferred for ornamental landscaping elements.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Diorite and schist differ notably in environmental impact and sustainability for landscape decoration; diorite's durability and resistance reduce the need for frequent replacement, minimizing resource consumption and waste. Schist, being more easily quarried and lightweight, often results in lower transportation emissions, but its susceptibility to weathering may lead to higher maintenance demands. Selecting diorite supports long-term sustainability through extended lifespan, whereas schist's lower extraction impact suits projects prioritizing minimal initial environmental disruption.
Infographic: Diorite vs Schist for Landscape Decoration
 azmater.com
azmater.com