Thin stone veneer offers a natural, durable, and aesthetically rich facade option with excellent weather resistance, while fiber cement siding provides a cost-effective, low-maintenance, and versatile alternative with high impact resistance and fireproof properties. Choosing between them depends on desired texture, budget, and long-term durability requirements for building exteriors.
Table of Comparison
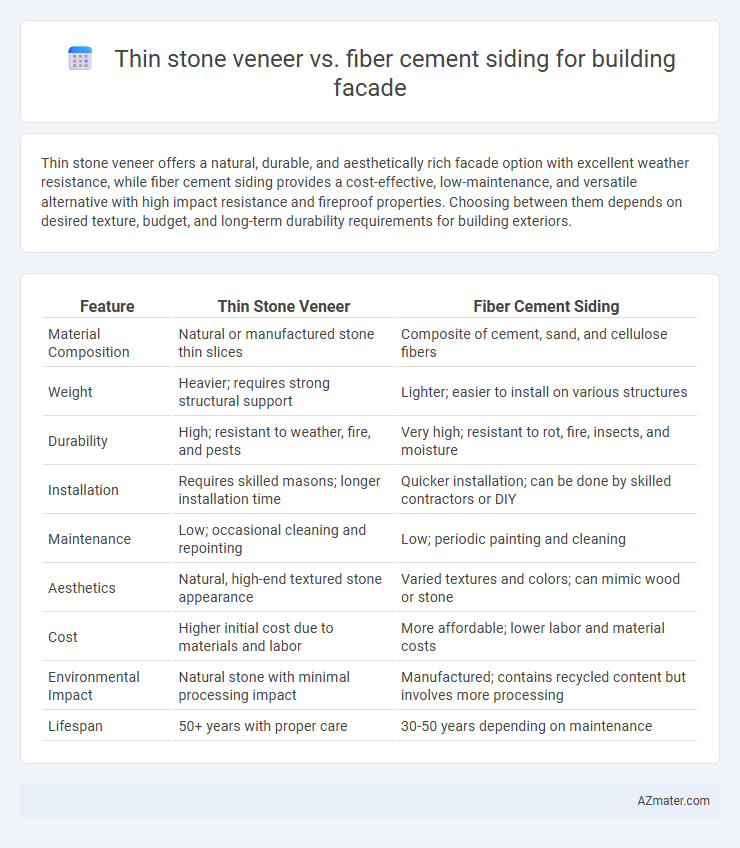
| Feature | Thin Stone Veneer | Fiber Cement Siding |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural or manufactured stone thin slices | Composite of cement, sand, and cellulose fibers |
| Weight | Heavier; requires strong structural support | Lighter; easier to install on various structures |
| Durability | High; resistant to weather, fire, and pests | Very high; resistant to rot, fire, insects, and moisture |
| Installation | Requires skilled masons; longer installation time | Quicker installation; can be done by skilled contractors or DIY |
| Maintenance | Low; occasional cleaning and repointing | Low; periodic painting and cleaning |
| Aesthetics | Natural, high-end textured stone appearance | Varied textures and colors; can mimic wood or stone |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to materials and labor | More affordable; lower labor and material costs |
| Environmental Impact | Natural stone with minimal processing impact | Manufactured; contains recycled content but involves more processing |
| Lifespan | 50+ years with proper care | 30-50 years depending on maintenance |
Introduction to Building Façade Cladding Options
Thin stone veneer offers a natural, textured appearance with durable and weather-resistant properties, making it an ideal choice for enhancing the aesthetic appeal of building facades. Fiber cement siding provides a versatile, low-maintenance solution that resists rot, fire, and pests, combining durability with cost-effectiveness for exterior cladding. Both materials cater to different architectural styles and performance needs, serving as popular facade cladding options for residential and commercial construction projects.
What is Thin Stone Veneer?
Thin stone veneer is a lightweight natural stone product made by slicing quarried stone into thin slabs, typically 1 inch or less, for use as a decorative facade material. It offers the authentic appearance and texture of natural stone while being easier to install and more cost-effective than full-thickness stone. This type of veneer provides excellent durability, weather resistance, and aesthetic appeal, making it a popular choice for both residential and commercial building exteriors.
Understanding Fiber Cement Siding
Fiber cement siding is a durable exterior cladding made from a blend of cement, sand, and cellulose fibers, offering resistance to fire, insects, and rot. It provides a versatile aesthetic that can mimic wood, stucco, or masonry, requiring low maintenance and enhancing building facade longevity. Compared to thin stone veneer, fiber cement siding is lighter, easier to install, and often more cost-effective while maintaining strong weather resistance.
Aesthetic Appeal: Comparing Visual Impact
Thin stone veneer offers a natural, textured appearance with depth and authenticity that enhances the architectural character of a building facade. Fiber cement siding delivers a smooth, uniform look with versatile color options but lacks the organic variation found in stone veneer. The choice between them depends on desired visual impact: stone veneer creates a luxurious, rugged aesthetic, while fiber cement provides a clean, contemporary style.
Durability and Longevity
Thin stone veneer offers superior durability and longevity due to its natural stone composition, resisting weathering and physical impacts more effectively than fiber cement siding. Fiber cement siding, while durable and resistant to rot, insects, and fire, generally has a shorter lifespan, typically lasting 20-40 years compared to stone veneer's potential 50+ years. Maintenance frequency is lower for thin stone veneer, making it a more long-term investment for building facades exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
Installation Process and Complexity
Thin stone veneer installation involves adhering lightweight stone panels to a properly prepared substrate using mortar or specialized adhesives, often requiring skilled labor to ensure proper alignment, joint spacing, and moisture barriers. Fiber cement siding installation is relatively straightforward, involving cutting panels to fit, fastening with corrosion-resistant nails or screws, and applying sealants or caulking to prevent water infiltration, making it a less labor-intensive option suitable for DIY projects. The complexity of thin stone veneer lies in its need for precise surface preparation and masonry skills, whereas fiber cement siding offers quicker installation with basic carpentry tools and techniques.
Cost Comparison: Initial and Long-Term
Thin stone veneer offers a higher initial cost, typically ranging from $6 to $12 per square foot, due to the natural stone materials and labor-intensive installation process, while fiber cement siding is more affordable, averaging $3 to $7 per square foot. In the long term, fiber cement siding generally provides better cost efficiency because of its durability, low maintenance requirements, and resistance to rot, insects, and fire, which reduces repair and replacement expenses. Thin stone veneer may incur higher maintenance and potential repair costs over time, especially in harsh climates, impacting overall lifecycle expenses.
Maintenance Requirements and Ease
Thin stone veneer requires minimal maintenance, primarily occasional cleaning and periodic sealing to prevent moisture infiltration, making it highly durable for building facades. Fiber cement siding demands routine inspections for cracks, repainting every 10-15 years, and prompt repairs to avoid water damage and mold growth. The ease of upkeep favors thin stone veneer due to its resistance to weathering and minimal need for regular maintenance compared to the more labor-intensive fiber cement siding.
Energy Efficiency and Insulation
Thin stone veneer offers superior thermal mass, enhancing energy efficiency by stabilizing indoor temperatures and reducing heating and cooling costs. Fiber cement siding provides moderate insulation but requires additional materials to achieve comparable energy performance. When prioritizing insulation and energy savings, combining thin stone veneer with proper insulation systems delivers optimal building facade efficiency.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Thin stone veneer offers natural durability and minimal resource extraction compared to fiber cement siding, which involves energy-intensive manufacturing and cement production with associated CO2 emissions. Fiber cement siding, while less energy-demanding than some synthetic alternatives, often incorporates recyclable materials and provides longer lifespan with reduced maintenance. Selecting between these options depends on prioritizing natural material extraction impacts versus manufacturing energy consumption and recyclability in sustainable facade design.
Infographic: Thin stone veneer vs Fiber cement siding for Building façade
 azmater.com
azmater.com