Thin stone veneer offers lightweight, easy-to-install roofing with a natural stone appearance, while slate provides exceptional durability, fire resistance, and a lifespan exceeding 100 years but requires professional installation due to its weight. Choosing between thin stone veneer and slate depends on balancing budget, structural capacity, and desired roofing longevity.
Table of Comparison
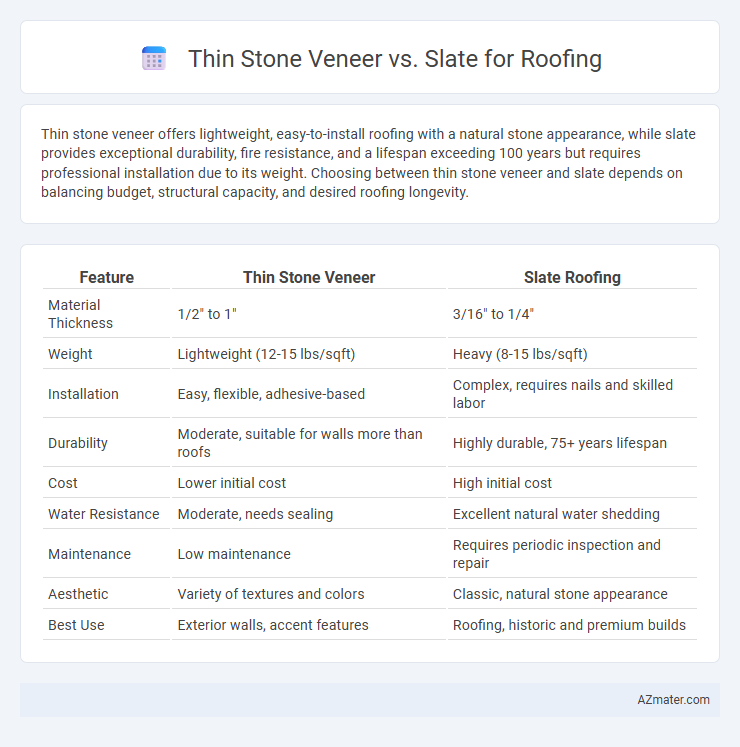
| Feature | Thin Stone Veneer | Slate Roofing |
|---|---|---|
| Material Thickness | 1/2" to 1" | 3/16" to 1/4" |
| Weight | Lightweight (12-15 lbs/sqft) | Heavy (8-15 lbs/sqft) |
| Installation | Easy, flexible, adhesive-based | Complex, requires nails and skilled labor |
| Durability | Moderate, suitable for walls more than roofs | Highly durable, 75+ years lifespan |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | High initial cost |
| Water Resistance | Moderate, needs sealing | Excellent natural water shedding |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance | Requires periodic inspection and repair |
| Aesthetic | Variety of textures and colors | Classic, natural stone appearance |
| Best Use | Exterior walls, accent features | Roofing, historic and premium builds |
Introduction to Roofing Materials: Thin Stone Veneer vs Slate
Thin stone veneer offers a lightweight, cost-effective alternative to traditional slate for roofing, providing natural stone aesthetics without the heavy structural demands. Slate roofing is renowned for its durability, longevity exceeding 100 years, and natural resistance to weather elements. Choosing between thin stone veneer and slate depends on factors such as budget, structural support capacity, and desired roofing lifespan.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Thin stone veneer is typically composed of natural stone that has been cut into thin, lightweight slices, retaining the stone's natural texture and color, while slate roofing consists of fine-grained metamorphic rock formed through the compression of clay and volcanic ash. Manufacturing of thin stone veneer involves slicing large blocks of stone with advanced saws and sometimes applying a backing for added strength, whereas slate roofing tiles are split along natural cleavage planes to create durable, flat sheets ideal for waterproof roofing. The inherent differences in material composition and manufacturing processes impact the weight, durability, installation techniques, and aesthetic appeal of each roofing option.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Flexibility
Thin stone veneer offers a lightweight, natural stone look that enhances aesthetic appeal with a wide range of textures and colors, allowing for versatile design options in roofing projects. Slate provides a classic, elegant appearance with deep, rich hues and a distinctive cleavage pattern, known for its timeless beauty and durability. Both materials enable creative architectural expressions, but thin stone veneer allows for easier installation on complex roof shapes, expanding design flexibility beyond the rigid form of traditional slate tiles.
Installation Process and Labor Requirements
Thin stone veneer offers a lightweight and easier installation process compared to natural slate, requiring fewer labor hours due to its manageable size and compatibility with standard framing. Slate roofing demands skilled labor specializing in precise handling and alignment to ensure durability, often increasing both time and cost due to its heavy weight and fragility. Homeowners opting for thin stone veneer can expect reduced labor expenses and quicker project completion, while slate requires experienced roofers to maintain its long-term performance.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Thin stone veneer offers moderate durability with a lifespan of 20-30 years, benefiting from lightweight installation and resistance to weathering but less impact resistance compared to natural stone. Slate roofing, known for exceptional durability, can last 75-100 years or more due to its dense, non-porous composition that withstands extreme weather, fire, and freeze-thaw cycles. While slate demands higher initial investment and structural support, its longevity and minimal maintenance make it a superior choice for long-term roofing solutions.
Weight and Structural Considerations
Thin stone veneer offers a lightweight alternative to traditional slate roofing, significantly reducing the load on the roof structure. Slate, known for its durability and natural beauty, is much heavier, often requiring reinforced roof framing to support its substantial weight. Selecting thin stone veneer can minimize structural modifications and lower installation costs while maintaining aesthetic appeal.
Maintenance Needs and Weather Resistance
Thin stone veneer requires minimal maintenance with occasional cleaning to prevent dirt buildup, offering durable weather resistance against rain, wind, and UV rays. Slate roofing boasts superior weather resistance, naturally resisting moisture, freeze-thaw cycles, and fire, yet demands periodic inspections to address potential cracks or chips. Both materials provide long-lasting performance, but slate's dense composition generally ensures greater longevity in harsh climates compared to thin stone veneer.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Thin stone veneer roofing offers a lighter weight solution with reduced resource extraction compared to traditional slate, lowering transportation emissions and overall carbon footprint. Slate roofing, known for its natural durability and longevity, minimizes waste through its ability to last over a century, reducing the need for frequent replacements. Sustainable roofing choices include considering the life cycle, with thin stone veneer benefiting from efficient manufacturing processes while slate's natural composition remains fully recyclable and environmentally inert.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-Term Expenses
Thin stone veneer offers a lower upfront cost compared to natural slate, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious roofing projects. Slate, although more expensive initially, provides superior durability and longevity, resulting in reduced maintenance and replacement expenses over time. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including installation, repair, and lifespan, reveals that slate may offer greater value despite its higher initial price point.
Choosing the Right Roofing Material for Your Project
Thin stone veneer offers a lightweight, cost-effective solution that mimics natural stone aesthetics, making it ideal for residential roofing projects seeking durability and visual appeal. Slate roofing provides unmatched longevity, fire resistance, and a distinctive natural appearance, though it requires professional installation and higher upfront costs. Evaluating factors such as budget, roof weight capacity, climate, and long-term maintenance needs will guide the optimal material choice for your roofing project.
Infographic: Thin stone veneer vs Slate for Roofing
 azmater.com
azmater.com