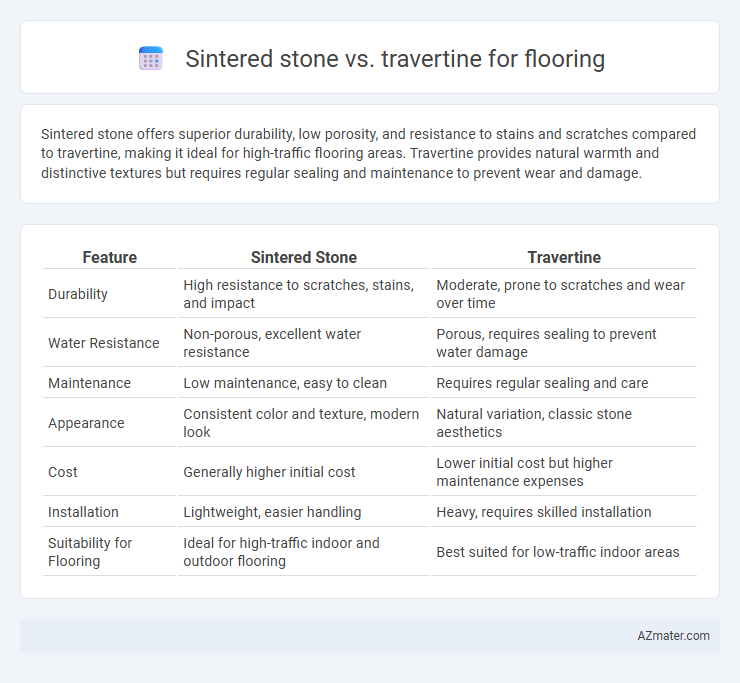
Sintered stone offers superior durability, low porosity, and resistance to stains and scratches compared to travertine, making it ideal for high-traffic flooring areas. Travertine provides natural warmth and distinctive textures but requires regular sealing and maintenance to prevent wear and damage.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sintered Stone | Travertine |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High resistance to scratches, stains, and impact | Moderate, prone to scratches and wear over time |
| Water Resistance | Non-porous, excellent water resistance | Porous, requires sealing to prevent water damage |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, easy to clean | Requires regular sealing and care |
| Appearance | Consistent color and texture, modern look | Natural variation, classic stone aesthetics |
| Cost | Generally higher initial cost | Lower initial cost but higher maintenance expenses |
| Installation | Lightweight, easier handling | Heavy, requires skilled installation |
| Suitability for Flooring | Ideal for high-traffic indoor and outdoor flooring | Best suited for low-traffic indoor areas |
Introduction to Sintered Stone and Travertine Flooring
Sintered stone is a highly durable, engineered material made by compacting natural minerals under extreme heat and pressure, offering superior resistance to scratches, stains, and heat compared to natural stones. Travertine, a natural limestone formed by mineral deposits from hot springs, provides a classic, warm aesthetic with distinctive porous textures that require sealing to prevent staining and moisture damage. Both materials are popular flooring options, with sintered stone excelling in modern high-traffic areas and travertine favored for traditional and rustic interior designs.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Sintered stone is engineered through a high-pressure, high-temperature process that fuses natural materials like quartz, feldspar, and porcelain, resulting in a dense, non-porous slab with enhanced durability and stain resistance. Travertine, a natural sedimentary limestone formed by mineral deposits from hot springs, undergoes minimal processing beyond cutting and polishing, making it more porous and susceptible to wear and staining. The manufacturing process of sintered stone creates a consistent, uniform surface ideal for high-traffic flooring, whereas travertine's organic composition and formation yield unique textures but require sealing to maintain longevity.
Aesthetic Appeal: Colors and Patterns
Sintered stone offers a vast palette of colors and intricate patterns with consistent, engineered designs that mimic natural stones or bold abstract styles, making it highly versatile for modern flooring aesthetics. Travertine showcases warm, earthy tones with natural veins and pores that provide a timeless, rustic charm and organic texture unique to each slab. While sintered stone patterns remain uniform across tiles, travertine's natural variations enhance visual depth and character, appealing to those seeking authentic stone flooring.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Sintered stone exhibits exceptional durability and strength, being highly resistant to scratches, stains, and heat, making it ideal for heavy-traffic flooring areas. Travertine, a natural limestone, is softer and more porous, requiring regular sealing to prevent damage and wear over time. Sintered stone outperforms travertine in longevity and maintenance, offering a more robust solution for durable flooring.
Water and Stain Resistance
Sintered stone offers superior water and stain resistance compared to travertine, making it ideal for high-moisture areas and heavy-traffic floors. Unlike travertine, which is porous and requires regular sealing to prevent staining and water damage, sintered stone features a non-porous surface that resists absorption and maintains its appearance over time. This durability ensures low maintenance and long-lasting aesthetics in residential and commercial flooring applications.
Maintenance Requirements
Sintered stone flooring offers exceptional resistance to stains, scratches, and moisture, requiring minimal maintenance such as regular sweeping and occasional damp mopping with neutral cleaners. Travertine flooring demands more intensive upkeep, including frequent sealing to protect against water absorption and staining, as well as careful cleaning to avoid damage from acidic or abrasive substances. Choosing sintered stone significantly reduces long-term maintenance efforts while maintaining durability and aesthetic appeal in high-traffic areas.
Installation Process and Considerations
Sintered stone flooring requires a precise installation process involving specialized adhesives and tools due to its dense, non-porous surface, which ensures durability and resistance to stains and scratches. Travertine installation demands careful sealing and grout application because its porous nature makes it more susceptible to moisture and staining, requiring ongoing maintenance to preserve its appearance. Both materials benefit from skilled installers, but sintered stone typically offers a quicker, lower-maintenance installation with higher durability, while travertine requires more detailed preparation and upkeep to maintain longevity.
Cost Analysis
Sintered stone flooring generally incurs higher upfront costs compared to travertine due to advanced manufacturing processes and superior durability. Travertine offers a more budget-friendly option with lower material prices but may require additional maintenance and sealing over time, increasing long-term expenses. When evaluating total cost of ownership, sintered stone's resistance to scratches, stains, and weathering often leads to reduced replacement and repair costs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Sintered stone flooring offers superior sustainability due to its use of natural minerals fused at high temperatures, resulting in a highly durable, non-porous surface with minimal maintenance and longer lifespan compared to travertine. Travertine, a natural sedimentary rock, involves extensive quarrying processes that contribute to habitat disruption and higher carbon emissions, alongside requiring frequent sealing and care to prevent damage. Choosing sintered stone minimizes environmental footprint by combining eco-friendly production methods with enhanced durability, making it a more sustainable flooring solution.
Best Use Cases and Final Recommendations
Sintered stone offers superior durability, resistance to scratches, stains, and UV rays, making it ideal for high-traffic and outdoor flooring applications where longevity and low maintenance are crucial. Travertine, with its natural porous texture and warm aesthetic, excels in indoor spaces such as living rooms, bathrooms, and patios, providing a classic and elegant look but requires regular sealing and care to prevent damage. For commercial or heavy-use settings, sintered stone is recommended, while travertine suits residential areas prioritizing natural beauty and traditional appeal.
Infographic: Sintered stone vs Travertine for Flooring
 azmater.com
azmater.com