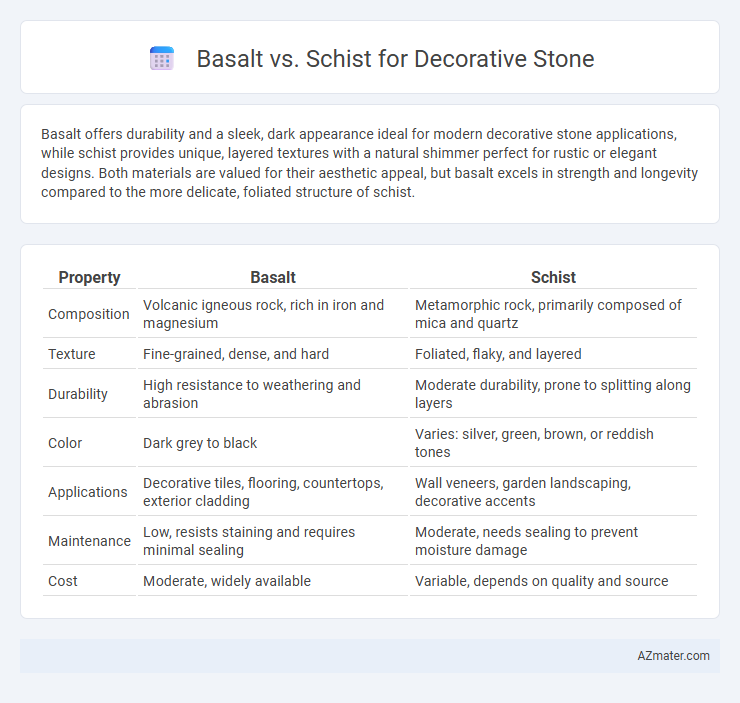
Basalt offers durability and a sleek, dark appearance ideal for modern decorative stone applications, while schist provides unique, layered textures with a natural shimmer perfect for rustic or elegant designs. Both materials are valued for their aesthetic appeal, but basalt excels in strength and longevity compared to the more delicate, foliated structure of schist.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Basalt | Schist |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Volcanic igneous rock, rich in iron and magnesium | Metamorphic rock, primarily composed of mica and quartz |
| Texture | Fine-grained, dense, and hard | Foliated, flaky, and layered |
| Durability | High resistance to weathering and abrasion | Moderate durability, prone to splitting along layers |
| Color | Dark grey to black | Varies: silver, green, brown, or reddish tones |
| Applications | Decorative tiles, flooring, countertops, exterior cladding | Wall veneers, garden landscaping, decorative accents |
| Maintenance | Low, resists staining and requires minimal sealing | Moderate, needs sealing to prevent moisture damage |
| Cost | Moderate, widely available | Variable, depends on quality and source |
Introduction to Basalt and Schist as Decorative Stones
Basalt is a dense, fine-grained volcanic rock prized for its durability and dark, uniform appearance, making it ideal for outdoor decorative stone applications such as paving and cladding. Schist, a metamorphic rock characterized by its foliated texture and shimmering mineral crystals, offers a unique aesthetic appeal with its layered patterns and varied colors, suitable for interior wall accents and landscaping features. Both stones provide distinctive textures and strength, with basalt favored for modern, sleek designs and schist chosen for natural, rustic elegance in decorative stone projects.
Geological Formation of Basalt vs Schist
Basalt forms from rapid cooling of basaltic lava at the Earth's surface, resulting in fine-grained, dense volcanic rock with a uniform texture ideal for decorative stone applications. Schist, on the other hand, originates from the metamorphism of mudstone or shale under high temperature and pressure, producing a foliated, crystalline texture characterized by visible mineral grains such as mica and quartz. The distinct geological formation processes of basalt and schist influence their durability, color variation, and aesthetic appeal in architectural and landscaping projects.
Visual and Textural Differences
Basalt features a fine-grained, uniform texture with a typically dark gray to black color, offering a sleek, modern aesthetic ideal for minimalist designs. Schist displays a visibly foliated, layered structure with shimmering mica crystals, providing a more complex and varied visual texture that highlights natural patterns and earthy tones. The contrast between basalt's smooth, consistent surface and schist's coarse, reflective layers makes each stone uniquely suited for different decorative stone applications.
Color Variations and Aesthetic Appeal
Basalt offers a consistent dark gray to black color palette with subtle texture, ideal for sleek, modern decorative stone applications, while Schist presents a wide range of colors including silver, green, brown, and purple due to its mica content, enhancing its aesthetic versatility. The reflective, layered structure of Schist creates a shimmering effect, making it popular for adding visual interest and depth in design projects. Basalt's uniform appearance provides a minimalist, contemporary look favored in both interior and exterior architectural elements.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Basalt and schist differ significantly in durability and weather resistance, making basalt a superior choice for decorative stone in exterior applications due to its dense, fine-grained structure and high resistance to abrasion and weathering. Schist, characterized by its foliated, layered texture, tends to be more susceptible to weather-induced cracking and erosion, limiting its longevity in outdoor environments. Basalt's exceptional durability and low porosity ensure minimal water absorption and excellent resilience against freeze-thaw cycles compared to schist's higher porosity and vulnerability in harsh climates.
Applications in Landscaping and Architecture
Basalt's dense, durable composition makes it ideal for heavy-traffic landscaping features such as pathways, retaining walls, and outdoor steps, offering a sleek, modern aesthetic with its dark, uniform color. Schist's foliated texture and natural shimmer provide distinctive visual appeal suited for decorative cladding, garden borders, and textured outdoor surfaces, enhancing architectural design with its varied mineral layers. Both stones are valued for weather resistance and versatility, but basalt better suits structural applications, while schist excels in ornamental detailing.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Basalt offers superior durability and low porosity, making it easier to maintain with minimal sealing and simple cleaning routines compared to schist, which requires regular sealing due to its foliated structure and increased porosity. Installation of basalt is generally more straightforward because of its consistent density and hardness, whereas schist's layered composition demands careful handling to prevent flaking and chipping during cutting and placement. Both materials require appropriate surface preparation, but basalt's resistance to wear makes it ideal for high-traffic decorative stone applications.
Cost Comparison: Basalt vs Schist
Basalt generally offers a lower cost per square foot compared to schist, making it a more budget-friendly option for decorative stone projects. Schist, known for its unique foliated texture and shimmering mineral content, commands higher prices due to its aesthetic appeal and limited availability. When choosing between basalt and schist, factors such as installation complexity and durability also influence overall project expenses beyond the initial material cost.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Basalt is a dense, volcanic rock with lower porosity and higher durability, resulting in less frequent replacement and reduced resource consumption compared to schist, a foliated metamorphic rock prone to weathering and erosion. The extraction of basalt typically involves less environmental disturbance due to its homogeneous structure, whereas schist quarrying can generate more waste and requires careful management to prevent habitat degradation. Basalt's longer lifespan and lower maintenance contribute to greater sustainability, making it a preferred choice for eco-conscious decorative stone projects.
Choosing the Right Stone for Your Project
Basalt offers a dense, durable surface ideal for high-traffic areas and modern designs, while schist provides a unique, textured appearance with shimmering mica flakes perfect for decorative accents and rustic aesthetics. Selecting the right stone depends on the project's functional requirements and visual goals, with basalt excelling in strength and weather resistance and schist delivering intricate visual patterns and natural luster. Consider factors such as durability, maintenance, and desired aesthetic impact to ensure the stone complements both the environment and the intended design style.
Infographic: Basalt vs Schist for Decorative Stone
 azmater.com
azmater.com