Tuff offers lightweight aggregate properties ideal for insulation and drainage, while andesite provides superior hardness and durability for high-strength construction applications. Choose tuff for projects requiring reduced weight and andesite for enhanced structural support.
Table of Comparison
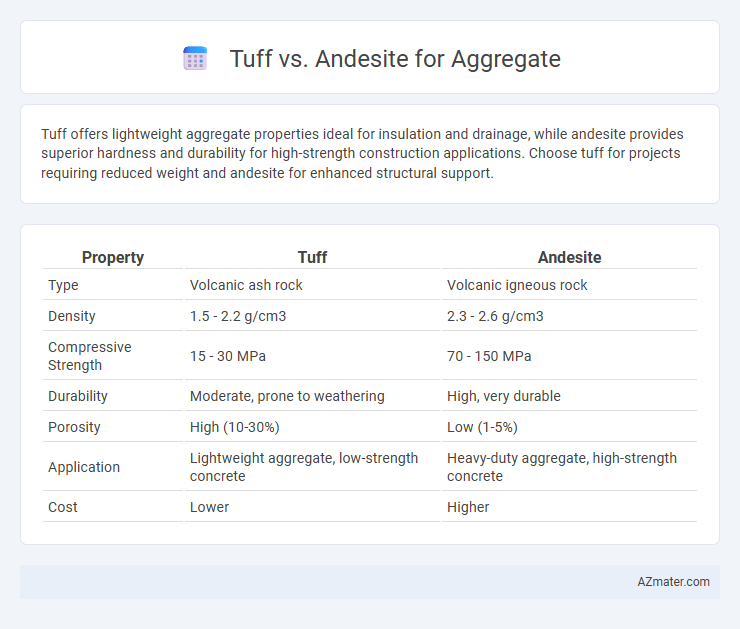
| Property | Tuff | Andesite |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Volcanic ash rock | Volcanic igneous rock |
| Density | 1.5 - 2.2 g/cm3 | 2.3 - 2.6 g/cm3 |
| Compressive Strength | 15 - 30 MPa | 70 - 150 MPa |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to weathering | High, very durable |
| Porosity | High (10-30%) | Low (1-5%) |
| Application | Lightweight aggregate, low-strength concrete | Heavy-duty aggregate, high-strength concrete |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Tuff and Andesite Aggregates
Tuff and andesite are volcanic rocks widely used as aggregates in construction due to their distinct properties. Tuff, formed from consolidated volcanic ash, is lightweight and porous, offering good thermal insulation and ease of handling. Andesite, a dense and durable extrusive igneous rock, provides high strength and resistance to weathering, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications like road base and concrete production.
Geological Formation and Composition
Tuff is a volcanic rock composed mainly of compacted volcanic ash and fragmented material formed from explosive volcanic eruptions, characterized by its relatively low density and high porosity. Andesite, an extrusive igneous rock formed through subduction zone volcanism, contains a balanced composition of plagioclase, pyroxene, and amphibole minerals, resulting in a denser and more durable aggregate. The geological formation influences their performance as aggregate: tuff's porous nature leads to lower strength and higher water absorption, while andesite's crystalline structure offers superior compressive strength and abrasion resistance.
Physical Properties Comparison
Tuff exhibits lower density and compressive strength compared to Andesite, making Andesite more suitable for heavy structural applications due to its higher durability and hardness. Andesite's superior abrasion resistance and lower porosity contribute to enhanced long-term performance in road construction and concrete aggregates. Tuff, being more porous and lightweight, is often preferred for landscaping and non-load-bearing projects where weight reduction is critical.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Andesite exhibits higher compressive strength and superior abrasion resistance compared to tuff, making it more suitable for high-load aggregate applications. Tuff's lower density and porosity result in reduced mechanical strength and increased susceptibility to weathering and chemical degradation over time. Durability tests show andesite aggregates maintain structural integrity longer in harsh environmental conditions, ensuring better long-term performance in construction projects.
Workability in Construction Projects
Tuff offers superior workability compared to andesite due to its lighter weight and softer texture, making it easier to cut and shape on construction sites. Andesite, while harder and more durable, requires more effort and specialized tools for processing, which can slow down project timelines. Choosing tuff as aggregate can enhance efficiency in mixing and handling, especially in large-scale infrastructure projects where ease of workability is critical.
Suitability for Road Base and Asphalt
Tuff exhibits lower density and higher porosity compared to Andesite, impacting its durability and load-bearing capacity for road base applications. Andesite's higher compressive strength and abrasion resistance make it more suitable for asphalt mixtures, ensuring better performance under heavy traffic conditions. The dense, fine-grained texture of Andesite contributes to improved interlock and stability in road construction, whereas Tuff may require stabilization for long-term durability.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
Tuff offers environmental advantages over andesite by typically requiring less energy-intensive quarrying due to its softer composition, resulting in lower carbon emissions during extraction and processing. Andesite, being denser and harder, demands more energy for crushing and grinding, affecting its sustainability profile negatively. Utilizing tuff as aggregate can contribute to reduced environmental impact in construction projects, especially in regions where sustainable sourcing and minimizing carbon footprint are prioritized.
Cost and Availability in the Market
Tuff offers a cost-effective option for aggregate due to its widespread availability and ease of extraction in volcanic regions, leading to lower transportation expenses. Andesite, while more expensive because of its denser composition and limited quarry sites, provides superior durability for heavy construction projects. Market availability of tuff is generally higher in areas with recent volcanic activity, whereas andesite aggregates dominate in regions with older volcanic rock formations, affecting overall project budgeting.
Performance in Concrete Applications
Tuff exhibits lower compressive strength and higher porosity compared to Andesite, making Andesite more suitable for high-performance concrete applications requiring durability and load-bearing capacity. Andesite's dense mineral composition contributes to better abrasion resistance and reduced water absorption, enhancing the longevity and structural integrity of concrete. Concrete mixes incorporating Andesite aggregates typically achieve superior strength and durability metrics relative to those with Tuff aggregates.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Tuff and Andesite
Tuff provides lightweight aggregate with good insulation properties, making it suitable for construction projects requiring thermal efficiency and ease of handling. Andesite offers higher strength and durability, ideal for heavy-duty applications such as road base and concrete structures. Selecting between Tuff and Andesite depends on the project's load requirements, environmental conditions, and specific performance needs.
Infographic: Tuff vs Andesite for Aggregate
 azmater.com
azmater.com