Gneiss offers superior strength and durability for construction blocks due to its high density and resistance to weathering, making it ideal for structural applications. Tuff, being lightweight and porous, provides excellent insulation but has lower compressive strength, limiting its use mainly to non-load-bearing elements.
Table of Comparison
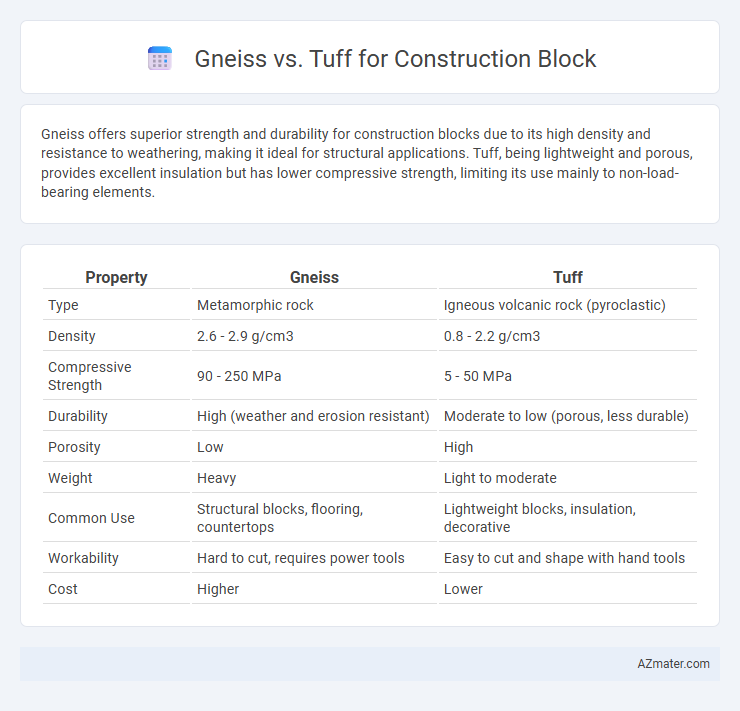
| Property | Gneiss | Tuff |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Metamorphic rock | Igneous volcanic rock (pyroclastic) |
| Density | 2.6 - 2.9 g/cm3 | 0.8 - 2.2 g/cm3 |
| Compressive Strength | 90 - 250 MPa | 5 - 50 MPa |
| Durability | High (weather and erosion resistant) | Moderate to low (porous, less durable) |
| Porosity | Low | High |
| Weight | Heavy | Light to moderate |
| Common Use | Structural blocks, flooring, countertops | Lightweight blocks, insulation, decorative |
| Workability | Hard to cut, requires power tools | Easy to cut and shape with hand tools |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Overview: Gneiss vs Tuff as Construction Block Materials
Gneiss is a metamorphic rock known for its high durability, strength, and resistance to weathering, making it an excellent choice for construction blocks in structural applications. Tuff, a volcanic ash-based rock, offers lightweight properties and ease of cutting but generally has lower compressive strength and durability compared to gneiss. The choice between gneiss and tuff depends on specific construction needs, with gneiss preferred for load-bearing structures and tuff favored for non-structural, insulating, or decorative blocks.
Geological Formation of Gneiss and Tuff
Gneiss forms through high-grade regional metamorphism of pre-existing igneous or sedimentary rocks, characterized by foliation and banding due to intense heat and pressure deep within the Earth's crust. Tuff is a volcanic rock formed by the consolidation of volcanic ash ejected during explosive eruptions, resulting in a porous and lightweight structure. The dense, durable texture of gneiss contrasts with the softer, more porous nature of tuff, influencing their suitability and performance as construction blocks.
Physical Properties Comparison
Gneiss exhibits high compressive strength, low porosity, and excellent durability, making it ideal for load-bearing construction blocks. Tuff, characterized by its lighter weight and higher porosity, offers better thermal insulation but lower strength and weather resistance compared to Gneiss. The physical properties of Gneiss support long-term structural integrity, while Tuff is advantageous for non-load-bearing applications requiring insulation.
Strength and Durability Analysis
Gneiss exhibits high compressive strength, typically between 150-250 MPa, making it highly suitable for load-bearing construction blocks due to its dense, interlocking mineral grains. Tuff, a volcanic rock, has significantly lower strength, often ranging from 10-50 MPa, and tends to be more porous and less durable under weathering conditions. The durability of gneiss surpasses tuff because of its resistance to abrasion, chemical weathering, and freeze-thaw cycles, ensuring longer-lasting structural integrity in construction applications.
Workability and Ease of Shaping
Gneiss offers moderate workability with a coarse-grained, foliated texture that requires robust cutting tools but provides excellent durability for construction blocks. Tuff, a volcanic ash rock, is highly favored for ease of shaping due to its lightweight and relatively soft nature, allowing for efficient masonry work and faster construction. When choosing between the two, tuff enhances workability and reduces labor time, whereas gneiss ensures long-term structural strength despite more challenging shaping processes.
Weather Resistance and Longevity
Gneiss exhibits superior weather resistance due to its dense, foliated structure, making it highly durable against freeze-thaw cycles and chemical erosion, which extends its longevity in construction applications. Tuff, being a volcanic rock with a porous composition, tends to absorb moisture and deteriorate faster under harsh weather conditions, limiting its lifespan as a construction block. For projects demanding long-term stability and low maintenance, gneiss is generally the preferred material over tuff.
Aesthetic Differences in Construction
Gneiss offers a visually striking appearance with its banded texture and varied mineral composition, creating a natural, elegant aesthetic ideal for upscale construction projects. In contrast, tuff presents a more uniform, porous texture with earthy tones, lending a rustic and warm charm suited for traditional or Mediterranean-style buildings. The choice between gneiss and tuff significantly impacts the overall architectural style, with gneiss emphasizing sophistication and tuff highlighting natural simplicity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Gneiss offers superior durability and lower porosity, resulting in longer lifespan and reduced need for frequent replacement, which minimizes environmental resource consumption. Tuff is a lightweight volcanic rock with good insulation properties, reducing energy use in buildings, but its softness can lead to faster degradation and increased maintenance, impacting sustainability negatively. The choice between gneiss and tuff depends on balancing durability with insulation benefits to optimize the environmental footprint in construction projects.
Cost and Availability Factors
Gneiss is generally more expensive than tuff due to its higher strength and durability, making it suitable for long-lasting construction blocks. Tuff is cost-effective and widely available in volcanic regions, offering easier quarrying but lower durability compared to gneiss. Availability of tuff often reduces transportation costs, whereas gneiss may incur higher expenses if sourced from distant quarries.
Best Applications: Where to Use Gneiss or Tuff
Gneiss offers high durability and resistance to weathering, making it ideal for outdoor structural elements, retaining walls, and load-bearing foundations in construction. Tuff, being lighter and easier to cut, is best suited for interior walls, insulation blocks, and decorative facades where weight reduction and thermal properties are prioritized. Selecting between gneiss and tuff depends on load requirements and environmental exposure, with gneiss preferred for strength and longevity and tuff for lightweight, thermal efficiency.
Infographic: Gneiss vs Tuff for Construction Block
 azmater.com
azmater.com