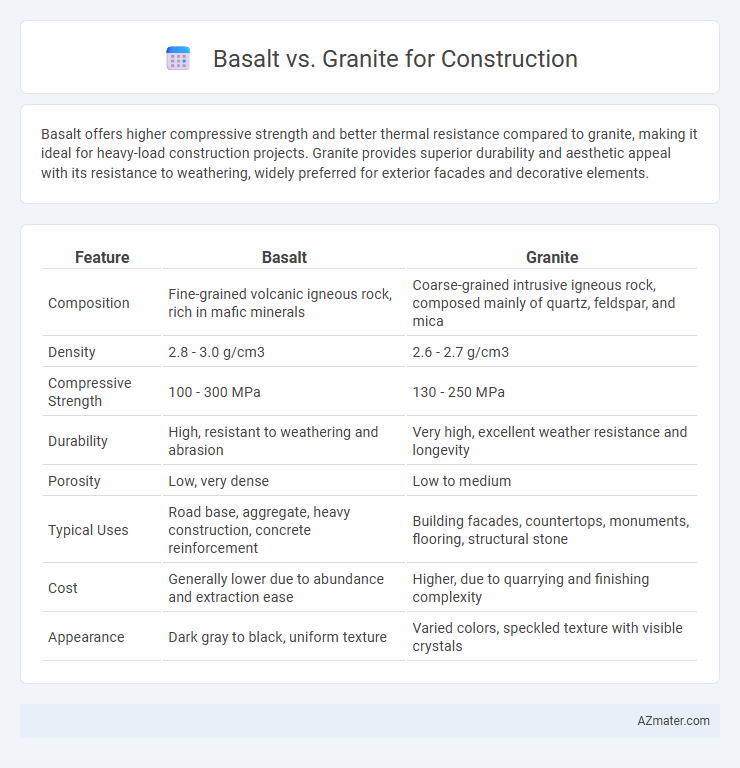
Basalt offers higher compressive strength and better thermal resistance compared to granite, making it ideal for heavy-load construction projects. Granite provides superior durability and aesthetic appeal with its resistance to weathering, widely preferred for exterior facades and decorative elements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Basalt | Granite |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Fine-grained volcanic igneous rock, rich in mafic minerals | Coarse-grained intrusive igneous rock, composed mainly of quartz, feldspar, and mica |
| Density | 2.8 - 3.0 g/cm3 | 2.6 - 2.7 g/cm3 |
| Compressive Strength | 100 - 300 MPa | 130 - 250 MPa |
| Durability | High, resistant to weathering and abrasion | Very high, excellent weather resistance and longevity |
| Porosity | Low, very dense | Low to medium |
| Typical Uses | Road base, aggregate, heavy construction, concrete reinforcement | Building facades, countertops, monuments, flooring, structural stone |
| Cost | Generally lower due to abundance and extraction ease | Higher, due to quarrying and finishing complexity |
| Appearance | Dark gray to black, uniform texture | Varied colors, speckled texture with visible crystals |
Introduction to Basalt and Granite in Construction
Basalt and granite are two of the most commonly used igneous rocks in construction, prized for their durability and aesthetic appeal. Basalt, formed from rapid cooling of lava, is dense, fine-grained, and exhibits excellent compressive strength, making it ideal for road base, concrete aggregate, and building facades. Granite, an intrusive igneous rock with a coarse-grained texture, offers exceptional hardness, resistance to abrasion, and a wide range of colors, often used in countertops, flooring, and monument construction.
Geological Formation and Characteristics
Basalt forms from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in iron and magnesium, resulting in a fine-grained, dense igneous rock ideal for high-strength construction projects and road base materials. Granite originates from the slow crystallization of magma beneath the Earth's surface, characterized by a coarse-grained texture with prominent quartz, feldspar, and mica, making it durable and aesthetically preferred for countertops and architectural facades. The contrasting geological formation processes influence their physical properties, with basalt exhibiting higher compressive strength and granite offering superior resistance to weathering and abrasion.
Physical Properties Comparison
Basalt exhibits higher compressive strength and greater density compared to granite, making it ideal for heavy load-bearing construction. Granite offers superior abrasion resistance and better aesthetic variety due to its coarse-grained texture and diverse mineral composition. Both stones demonstrate excellent durability and low porosity, yet basalt's finer grain size contributes to enhanced structural integrity in infrastructure projects.
Durability and Strength: Basalt vs Granite
Basalt exhibits exceptional durability and compressive strength, making it highly resistant to weathering and wear, ideal for heavy construction projects. Granite, known for its high tensile strength and hardness, provides superior resistance to abrasion and structural integrity in both residential and commercial buildings. Both materials offer excellent performance, but basalt's fine-grained texture enhances its toughness, while granite's crystalline structure contributes to its long-term stability.
Workability and Ease of Installation
Basalt offers superior workability in construction due to its fine-grained texture, allowing for easier cutting and shaping compared to granite's coarse grain. Granite's hardness provides excellent durability but can increase installation time and labor costs due to the difficulty in handling and precision cutting. Choosing basalt over granite can streamline project timelines and reduce labor expenses without compromising structural integrity.
Cost Analysis and Affordability
Basalt offers a cost-effective alternative to granite due to its abundant availability and lower quarrying expenses, making it suitable for budget-conscious construction projects. Granite, while generally more expensive because of its durability and aesthetic appeal, often justifies its higher price with longevity and lower maintenance costs. Choosing between basalt and granite requires balancing initial material cost against long-term value and project specifications.
Aesthetic Appeal and Color Variations
Basalt exhibits a sleek, dark gray to black color palette with subtle texture, offering a modern and minimalist aesthetic ideal for contemporary construction projects. Granite provides a broader spectrum of color variations, including whites, pinks, reds, and greens, which adds versatility and richness to design schemes. The natural veining and speckled patterns in granite enhance visual interest, making it a preferred choice for decorative facades and countertops where color diversity is desired.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Basalt demonstrates a lower environmental impact in construction due to its abundant availability and lower energy consumption during extraction and processing compared to granite. Granite mining involves intensive quarrying practices, leading to greater habitat disruption and higher carbon emissions. Utilizing basalt promotes sustainability by reducing resource depletion and enabling longer lifecycle applications in infrastructure projects.
Ideal Applications in Construction Projects
Basalt is ideal for heavy-load bearing applications such as road base layers and bridge abutments due to its high compressive strength and durability. Granite is preferred for architectural elements, countertops, and decorative facades because of its aesthetic appeal and resistance to weathering. Both materials offer excellent hardness, but basalt excels in industrial construction projects while granite is favored in both structural and ornamental uses.
Final Verdict: Choosing Between Basalt and Granite
Basalt offers superior durability and strength, making it ideal for heavy-load construction and outdoor applications, while granite provides exceptional aesthetic appeal with its wide variety of colors and patterns suitable for decorative purposes. Both materials exhibit excellent resistance to weathering and abrasion, but basalt's finer grain structure often results in higher compressive strength. Selecting between basalt and granite depends on whether structural performance or visual impact is the primary construction requirement.
Infographic: Basalt vs Granite for Construction
 azmater.com
azmater.com