Thin stone veneer offers a lightweight, natural stone appearance with easier installation and greater design flexibility, while precast concrete panels provide high durability, thermal insulation, and faster on-site assembly for building envelopes. Selecting between the two depends on project priorities such as aesthetic preference, structural requirements, and budget constraints.
Table of Comparison
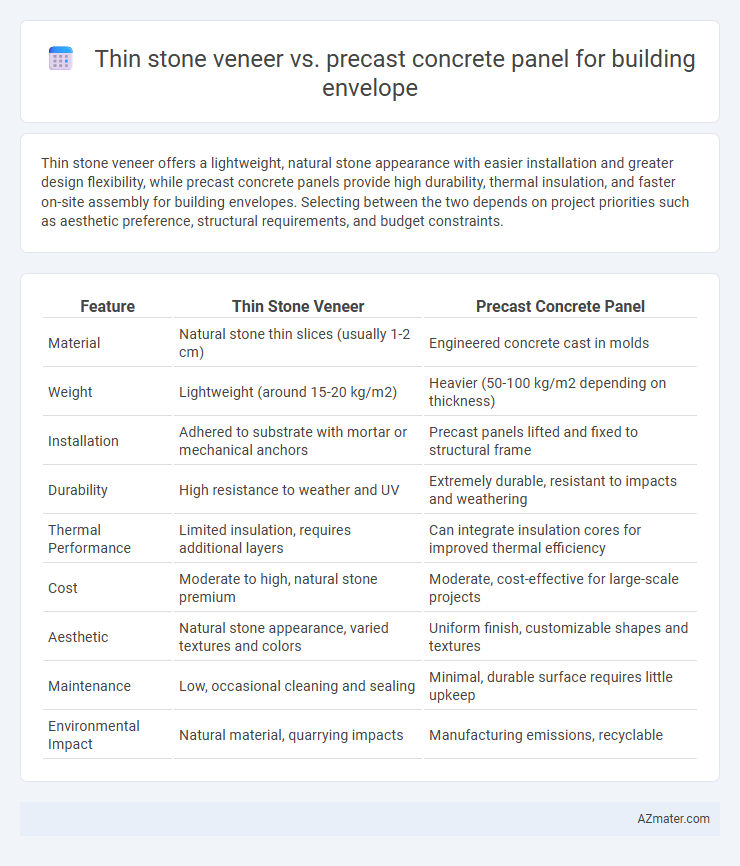
| Feature | Thin Stone Veneer | Precast Concrete Panel |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Natural stone thin slices (usually 1-2 cm) | Engineered concrete cast in molds |
| Weight | Lightweight (around 15-20 kg/m2) | Heavier (50-100 kg/m2 depending on thickness) |
| Installation | Adhered to substrate with mortar or mechanical anchors | Precast panels lifted and fixed to structural frame |
| Durability | High resistance to weather and UV | Extremely durable, resistant to impacts and weathering |
| Thermal Performance | Limited insulation, requires additional layers | Can integrate insulation cores for improved thermal efficiency |
| Cost | Moderate to high, natural stone premium | Moderate, cost-effective for large-scale projects |
| Aesthetic | Natural stone appearance, varied textures and colors | Uniform finish, customizable shapes and textures |
| Maintenance | Low, occasional cleaning and sealing | Minimal, durable surface requires little upkeep |
| Environmental Impact | Natural material, quarrying impacts | Manufacturing emissions, recyclable |
Introduction to Building Envelope Materials
Thin stone veneer offers a natural aesthetic with lightweight durability, ideal for exterior cladding that enhances architectural appeal while providing weather resistance. Precast concrete panels deliver high structural strength and thermal performance, enabling quick installation and superior longevity for building envelopes. Both materials contribute to energy efficiency and protection, but selection depends on design goals, cost considerations, and local climate demands.
Overview of Thin Stone Veneer
Thin stone veneer offers a lightweight, natural stone appearance that enhances the aesthetic appeal of building envelopes while providing durability and resistance to weathering. It typically consists of a thin slice of natural stone bonded to a backup substrate, allowing for easier installation and reduced structural load compared to traditional full-thickness stone. This material is favored for its versatility, cost-effectiveness, and ability to mimic the look of solid stone without the associated weight and expense.
Understanding Precast Concrete Panels
Precast concrete panels offer superior durability, thermal insulation, and structural strength compared to thin stone veneer, making them ideal for building envelopes requiring enhanced weather resistance and load-bearing capacity. These panels are manufactured off-site under controlled conditions, ensuring consistent quality, precise dimensions, and faster installation times that reduce construction delays. Their ability to integrate insulation and achieve various architectural finishes provides a versatile solution for energy-efficient, long-lasting facades in commercial and residential buildings.
Aesthetic Appeal: Natural vs. Manufactured
Thin stone veneer offers a rich, natural aesthetic with unique textures and color variations that enhance building envelopes by providing an authentic, timeless appearance. Precast concrete panels deliver a more uniform, manufactured look with customizable finishes that can mimic natural materials but lack the organic complexity of real stone. Designers often choose thin stone veneer for projects valuing natural beauty and historical character, while precast panels suit modern, streamlined designs emphasizing precision and consistency.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Thin stone veneer offers exceptional durability with natural resistance to weathering, erosion, and UV exposure, ensuring a long-lasting building envelope. Precast concrete panels provide superior strength and impact resistance, along with excellent performance against freeze-thaw cycles and moisture infiltration. Both materials deliver robust weather resistance, but thin stone veneer emphasizes aesthetic appeal and natural texture while precast concrete panels prioritize structural integrity and uniformity.
Installation Process and Complexity
Thin stone veneer installation involves adhering lightweight natural stone panels to a substrate using mortar or mechanical fasteners, requiring precise alignment and waterproofing measures to prevent moisture intrusion; skilled labor familiar with stone masonry is essential. Precast concrete panels are manufactured off-site under controlled conditions and installed by lifting heavy, large panels into place using cranes, demanding careful coordination, structural anchoring, and connection to ensure watertight seals and load transfer. Installation complexity of thin stone veneer is generally higher due to intricate detailing and finishing, while precast concrete panels require heavy equipment handling and precise structural integration but allow faster on-site assembly.
Structural Support Requirements
Thin stone veneer requires a strong structural framework or substrate, such as steel or masonry, to support its weight and prevent detachment, often necessitating additional reinforcement and anchoring systems. Precast concrete panels offer inherent structural support, acting as both cladding and load-bearing elements, reducing the need for secondary support structures in the building envelope. Selection between these materials depends on the building's load capacity, design specifications, and the integration of structural systems to ensure safety and durability.
Cost Comparison and Value
Thin stone veneer offers a cost-effective solution for building envelopes with lower material and installation expenses compared to precast concrete panels, which typically require higher upfront investment due to manufacturing and transportation costs. The value of thin stone veneer lies in its natural aesthetic and ease of application on various substrates, while precast concrete panels provide superior durability, thermal performance, and faster installation timelines that can reduce long-term maintenance costs. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals that thin stone veneers optimize budget constraints without compromising design quality, whereas precast concrete panels deliver enhanced structural integrity and energy efficiency, justifying their higher initial price for long-term value.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Thin stone veneer offers a sustainable building envelope option with natural material extraction and minimal processing, resulting in lower embodied energy compared to precast concrete panels. Precast concrete panels, while durable and energy-efficient due to thermal mass properties, often involve higher carbon emissions during cement production and transportation. Lifecycle assessments indicate that thin stone veneer typically has a smaller environmental footprint, making it a greener choice for sustainable construction.
Maintenance and Long-term Performance
Thin stone veneer offers a durable, low-maintenance facade with natural weather resistance and easy repairs, ideal for preserving aesthetic appeal over time. Precast concrete panels provide superior structural strength, enhanced resistance to impact and environmental degradation, and require minimal maintenance, making them suitable for long-term building envelope performance. Both materials deliver longevity, but precast concrete panels often outperform thin stone veneer in resisting moisture intrusion and thermal cycling effects.
Infographic: Thin stone veneer vs Precast concrete panel for Building envelope
 azmater.com
azmater.com