Granite gravel offers superior durability and resistance to weathering compared to schist, which tends to be softer and more prone to breaking down over time. For long-lasting gravel applications, granite provides better structural stability and lower maintenance costs than schist.
Table of Comparison
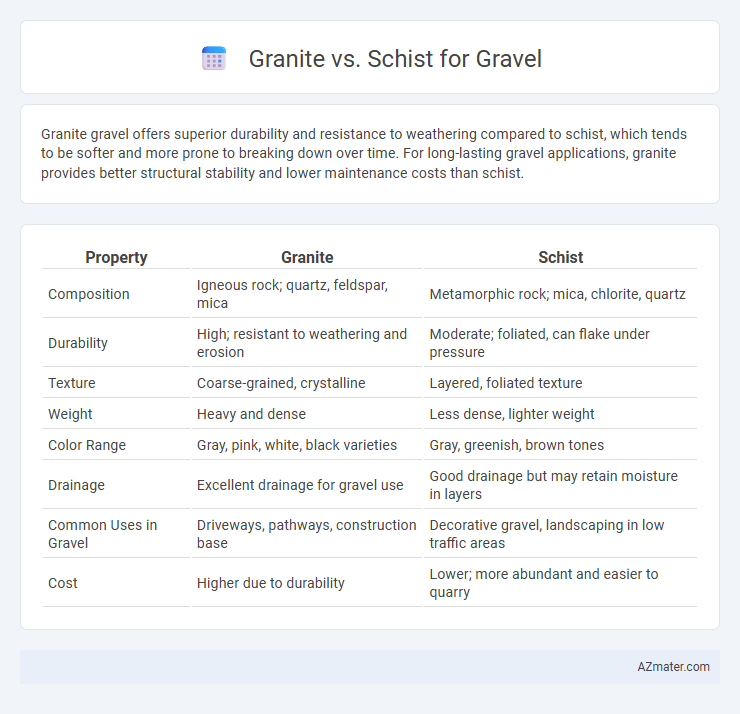
| Property | Granite | Schist |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Igneous rock; quartz, feldspar, mica | Metamorphic rock; mica, chlorite, quartz |
| Durability | High; resistant to weathering and erosion | Moderate; foliated, can flake under pressure |
| Texture | Coarse-grained, crystalline | Layered, foliated texture |
| Weight | Heavy and dense | Less dense, lighter weight |
| Color Range | Gray, pink, white, black varieties | Gray, greenish, brown tones |
| Drainage | Excellent drainage for gravel use | Good drainage but may retain moisture in layers |
| Common Uses in Gravel | Driveways, pathways, construction base | Decorative gravel, landscaping in low traffic areas |
| Cost | Higher due to durability | Lower; more abundant and easier to quarry |
Introduction to Granite and Schist Gravel
Granite gravel is composed of durable, coarse-grained igneous rock primarily made of quartz, feldspar, and mica, offering excellent strength and stability for construction and landscaping projects. Schist gravel originates from metamorphic rock characterized by its foliated texture and mineral composition, providing a unique aesthetic with varied colors and greater flexibility under pressure. Both granite and schist gravel serve different purposes based on their hardness, weather resistance, and visual appeal, making them suitable for specific gravel applications.
Geological Differences: Granite vs Schist
Granite is an igneous rock composed mainly of quartz, feldspar, and mica, characterized by its coarse-grained texture formed from slow cooling of magma deep within the Earth's crust. Schist is a metamorphic rock exhibiting a foliated texture due to the alignment of platy minerals like mica, formed under high pressure and temperature conditions altering pre-existing rocks. The fundamental geological difference lies in granite's crystalline, intrusive igneous origin versus schist's foliated, metamorphic formation, influencing their durability, mineral composition, and suitability for gravel applications.
Physical Properties Comparison
Granite gravel is characterized by high durability, hardness, and resistance to weathering, making it ideal for heavy-duty construction and landscaping applications. Schist gravel has a foliated texture and lower hardness, which results in less resistance to abrasion and greater susceptibility to fragmentation under pressure. The physical properties of granite, including higher compressive strength and abrasion resistance, generally outperform schist in gravel uses requiring longevity and structural stability.
Aesthetic Appeal and Color Variations
Granite gravel features a wide range of color variations, including shades of white, pink, gray, and black, providing a versatile and aesthetically appealing choice for landscaping projects. Schist gravel is known for its shimmering, layered texture and rich earthy tones such as browns, greens, and golds, adding a natural, dynamic visual interest. Both stones offer unique aesthetic qualities, with granite providing durability and classic elegance, while schist contributes a rustic, textured look that enhances garden pathways and decorative features.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Granite gravel offers superior durability and weather resistance due to its dense, hard mineral composition, making it ideal for high-traffic and outdoor applications. Schist gravel, while attractive with its layered texture, is more prone to weathering and erosion because of its foliated structure and weaker mineral bonds. Choosing granite ensures longer-lasting performance in harsh weather conditions compared to schist gravel.
Cost and Availability of Granite and Schist Gravel
Granite gravel is widely available and often more affordable due to the abundance of granite quarries, making it a cost-effective choice for construction and landscaping. Schist gravel tends to be less common and more expensive because schist formations are less prevalent and typically require specialized extraction methods. The cost difference between granite and schist gravel also reflects their varying durability and intended usage in outdoor projects.
Performance in Driveways and Paths
Granite gravel offers exceptional durability and resistance to weathering, making it ideal for driveways and paths with heavy traffic due to its hardness and angular texture that provides excellent compaction and stability. Schist gravel, while visually appealing with its shiny, flaky texture, is softer and more prone to break down under pressure, which can lead to faster erosion and increased maintenance in high-traffic areas. For long-lasting performance in driveways and paths, granite gravel is preferred for its strength and low wear rate, whereas schist is better suited for decorative, low-traffic applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Granite gravel is widely used due to its durability and minimal chemical weathering, resulting in low environmental contamination during extraction and use. Schist gravel, while attractive for landscaping, requires more energy-intensive processing because of its foliated structure, leading to higher carbon emissions. Both materials can be sourced responsibly, but granite's abundance and stability make it a more sustainable choice for large-scale applications with reduced ecological disruption.
Best Uses: Landscaping, Construction, and Beyond
Granite gravel excels in construction projects due to its durability, strength, and resistance to weathering, making it ideal for driveways, foundations, and pathways. Schist gravel, with its layered texture and aesthetic appeal, is preferred in landscaping to enhance garden beds, walkways, and decorative features. Both materials offer unique benefits; granite is favored for heavy-duty applications, while schist adds natural beauty and drainage advantages in outdoor spaces.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Gravel for Your Project
Granite gravel offers exceptional durability and resistance to weathering, making it ideal for high-traffic areas and structural applications. Schist gravel provides unique aesthetic appeal with its layered texture and mineral composition, suitable for decorative landscaping and garden pathways. Selecting the right gravel depends on project requirements: prioritize granite for strength and longevity, or schist for visual impact and natural beauty.
Infographic: Granite vs Schist for Gravel
 azmater.com
azmater.com