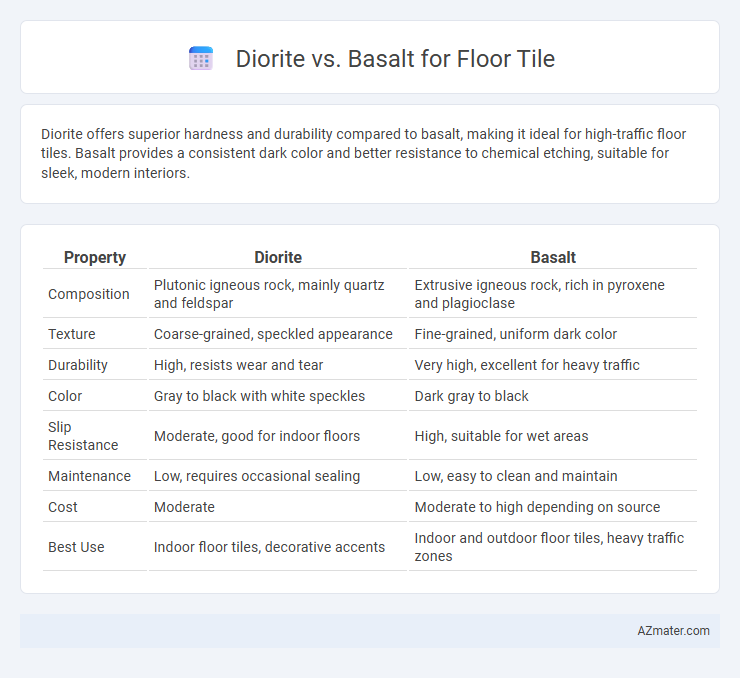
Diorite offers superior hardness and durability compared to basalt, making it ideal for high-traffic floor tiles. Basalt provides a consistent dark color and better resistance to chemical etching, suitable for sleek, modern interiors.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Diorite | Basalt |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Plutonic igneous rock, mainly quartz and feldspar | Extrusive igneous rock, rich in pyroxene and plagioclase |
| Texture | Coarse-grained, speckled appearance | Fine-grained, uniform dark color |
| Durability | High, resists wear and tear | Very high, excellent for heavy traffic |
| Color | Gray to black with white speckles | Dark gray to black |
| Slip Resistance | Moderate, good for indoor floors | High, suitable for wet areas |
| Maintenance | Low, requires occasional sealing | Low, easy to clean and maintain |
| Cost | Moderate | Moderate to high depending on source |
| Best Use | Indoor floor tiles, decorative accents | Indoor and outdoor floor tiles, heavy traffic zones |
Introduction to Diorite and Basalt Floor Tiles
Diorite floor tiles are known for their coarse-grained texture and striking salt-and-pepper appearance, offering durability and a unique aesthetic for indoor and outdoor flooring. Basalt floor tiles feature a fine-grained, dense composition with a naturally dark, consistent color, providing excellent resistance to wear and slip, making them ideal for high-traffic areas. Both materials, formed from different types of volcanic activity, combine natural strength with distinctive visual appeal, enhancing various architectural styles.
Geological Formation and Composition
Diorite, an intrusive igneous rock formed from slow crystallization of magma beneath the Earth's surface, is composed mainly of plagioclase feldspar and hornblende, providing a coarse-grained texture ideal for durable floor tiles. Basalt, an extrusive igneous rock resulting from rapid cooling of lava at the surface, features a fine-grained structure predominantly made of pyroxene and plagioclase, offering a dense, hard surface suitable for heavy-use flooring. The differing geological formations influence their porosity and wear resistance, with diorite's coarse crystals enhancing slip resistance, while basalt's fine grains contribute to superior compressive strength.
Appearance and Color Variations
Diorite floor tiles showcase a striking speckled appearance with interlocking crystals of black, white, and gray, creating a naturally variegated surface that enhances modern and rustic interiors. Basalt tiles typically feature a more uniform and matte texture with dark gray to black tones, offering a sleek and consistent look ideal for minimalist and contemporary designs. The varied coloration in diorite lends a dynamic and vibrant feel, while basalt provides subtle elegance through its monochromatic palette.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Diorite offers exceptional durability and hardness, making it highly resistant to wear, scratches, and impacts, which is ideal for high-traffic floor tile applications. Basalt, while also strong and dense, tends to be slightly less hard than diorite but provides excellent resistance to weathering and chemical exposure. Both stones possess impressive compressive strength, with diorite often exceeding 7,000 psi and basalt up to 6,500 psi, ensuring long-lasting performance in flooring installations.
Slip Resistance and Safety
Diorite offers a naturally textured surface, providing moderate slip resistance suitable for residential flooring, while basalt tends to be denser and smoother, potentially increasing the risk of slipping, especially in wet areas. Both stones can be treated with anti-slip finishes, but untreated diorite generally outperforms basalt in safety-related slip resistance. Choosing diorite for floor tiles in high-traffic or moisture-prone zones enhances safety by reducing slip hazards.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Diorite floor tiles demand minimal maintenance, requiring only regular sweeping and occasional mopping with a pH-neutral cleaner to preserve their polished finish and prevent surface damage. Basalt tiles, characterized by their dense volcanic origin, are highly resistant to stains and moisture but may need periodic sealing to maintain their natural texture and protect against dirt infiltration. Both materials offer durable, low-maintenance options for flooring, with Diorite's smooth surface facilitating easier cleaning compared to the slightly rougher, porous nature of Basalt tiles.
Cost and Budget Considerations
Diorite floor tiles typically cost more than basalt due to their rarity and unique speckled appearance, making them a premium choice for high-budget projects. Basalt tiles are generally more affordable and offer excellent durability, providing a cost-effective option for large-scale or budget-conscious flooring. Both materials require sealing and maintenance, but basalt's lower initial investment often suits practical flooring budgets without compromising on quality.
Installation Process Differences
Diorite floor tiles require specialized cutting tools due to their coarse-grained texture, making the installation process more labor-intensive compared to basalt tiles, which are finer-grained and easier to cut. Basalt tiles typically have a smoother surface, allowing for simpler leveling and adhesion during installation, whereas diorite tiles may need extra grinding to achieve a uniform finish. The curing time for adhesives on basalt tiles tends to be shorter, reducing overall installation time relative to the slower-setting adhesives used with diorite.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Diorite and basalt floor tiles differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability, with basalt offering a more eco-friendly option due to its abundant natural availability and lower carbon footprint during extraction and processing. Diorite, being less common and typically quarried with more energy-intensive methods, results in higher emissions and environmental disturbance. Basalt's durability and natural resistance to weathering also contribute to its sustainability by extending tile lifespan and reducing the need for frequent replacement.
Best Applications and Design Uses
Diorite floor tiles offer a unique speckled texture and high durability, making them ideal for high-traffic areas such as entrance halls and commercial spaces where a luxurious, natural stone aesthetic is desired. Basalt tiles are favored for outdoor and wet areas due to their slip-resistant surface and excellent weather resistance, often used in patios, pool surrounds, and modern minimalist interiors. Both stones provide robust performance with Diorite adding visual complexity and Basalt delivering sleek uniformity, enhancing diverse design schemes from contemporary to rustic.
Infographic: Diorite vs Basalt for Floor Tile
 azmater.com
azmater.com