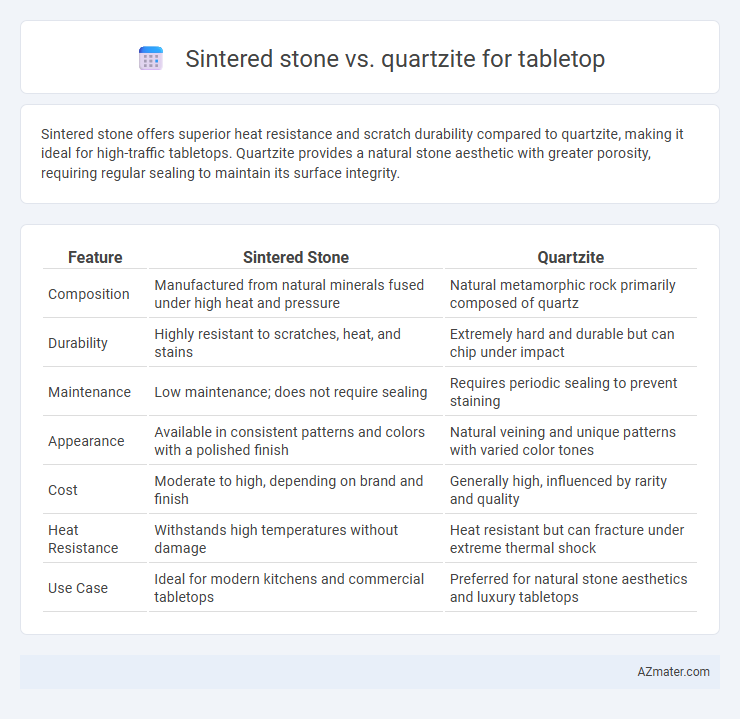
Sintered stone offers superior heat resistance and scratch durability compared to quartzite, making it ideal for high-traffic tabletops. Quartzite provides a natural stone aesthetic with greater porosity, requiring regular sealing to maintain its surface integrity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sintered Stone | Quartzite |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Manufactured from natural minerals fused under high heat and pressure | Natural metamorphic rock primarily composed of quartz |
| Durability | Highly resistant to scratches, heat, and stains | Extremely hard and durable but can chip under impact |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; does not require sealing | Requires periodic sealing to prevent staining |
| Appearance | Available in consistent patterns and colors with a polished finish | Natural veining and unique patterns with varied color tones |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on brand and finish | Generally high, influenced by rarity and quality |
| Heat Resistance | Withstands high temperatures without damage | Heat resistant but can fracture under extreme thermal shock |
| Use Case | Ideal for modern kitchens and commercial tabletops | Preferred for natural stone aesthetics and luxury tabletops |
Introduction to Sintered Stone and Quartzite
Sintered stone is a highly durable, engineered material composed of natural minerals fused under extreme heat and pressure, offering superior resistance to scratches, stains, and heat, making it ideal for tabletops. Quartzite is a natural metamorphic rock renowned for its hardness and unique veining, providing an elegant aesthetic with excellent durability but requiring regular sealing to maintain its resistance to stains. Both materials serve as premium choices for tabletops, balancing strength and beauty, with sintered stone offering enhanced maintenance ease and quartzite delivering natural stone authenticity.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Sintered stone is made from a blend of natural minerals that are compacted and fused under extreme heat and pressure through a process called sintering, resulting in a highly durable and non-porous surface. Quartzite is a natural metamorphic rock primarily composed of quartz grains that have been subjected to intense heat and pressure, creating a hard and dense material ideal for tabletops. Unlike quartzite, which is quarried and cut, sintered stone is engineered using advanced technology to control thickness, color, and texture, offering more versatility in design and consistency.
Physical Appearance and Aesthetics
Sintered stone offers a wide range of colors and patterns with a matte or textured finish that mimics natural surfaces, providing a modern and uniform aesthetic for tabletops. Quartzite features natural veining and a glossy finish with a more organic, unique look that adds elegance and timeless beauty. Both materials enhance the visual appeal of tabletops, but sintered stone is ideal for consistent design while quartzite stands out with its natural stone character.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Sintered stone exhibits exceptional durability for tabletops due to its resistance to scratches, heat, and UV rays, making it ideal for high-traffic or outdoor use. Quartzite offers impressive strength and hardness, often surpassing granite, but it requires sealing to prevent staining and can be more prone to chipping under heavy impact. Both materials provide robust surfaces, with sintered stone generally outperforming quartzite in overall resistance to wear and environmental factors.
Resistance to Heat and Scratches
Sintered stone offers superior resistance to heat and scratches compared to quartzite, making it ideal for durable tabletops in both residential and commercial settings. Its manufacturing process fuses natural minerals at extremely high temperatures, resulting in a dense surface that withstands hot pots and sharp objects without damage. Quartzite, while naturally hard and scratch-resistant, is more susceptible to thermal shock and can develop cracks under sudden heat exposure.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Sintered stone tabletops require minimal maintenance due to their non-porous surface, making them resistant to stains, scratches, and heat, and they can be cleaned easily with mild soap and water. Quartzite, while naturally durable and scratch-resistant, is more porous and may require periodic sealing to prevent staining and moisture absorption. Regular cleaning of quartzite involves using pH-balanced cleaners to maintain its integrity, avoiding harsh chemicals that can damage the surface.
Cost Differences and Value
Sintered stone generally offers a higher initial cost compared to quartzite due to its advanced manufacturing process and enhanced durability features. However, its resistance to scratches, heat, and stains provides long-term value by reducing maintenance and replacement expenses. Quartzite remains a cost-effective choice with natural aesthetics and reasonable durability, but it may require more frequent sealing and care, impacting overall lifetime value.
Installation Considerations
Sintered stone offers superior ease of installation for tabletops due to its lighter weight and uniform thickness, reducing labor and structural support requirements compared to natural quartzite. Quartzite's variability in density and veining requires skilled handling and specialized cutting tools to prevent cracking during installation. Proper surface preparation and adhesive compatibility are critical for both materials to ensure long-term durability and seamless integration.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Sintered stone tables offer superior environmental benefits due to their manufacturing process, which uses abundant natural minerals subjected to high pressure and temperature without resins or chemicals, resulting in a non-toxic, highly durable surface with low emissions. Quartzite, a natural stone quarried from the earth, has a higher environmental footprint due to mining activities, energy-intensive extraction, and transportation, although it remains an inert, long-lasting material. Both materials promote sustainability through durability, but sintered stone's eco-friendly production and recyclability make it a more environmentally responsible choice for tabletops.
Choosing the Best Material for Your Tabletop
Sintered stone offers exceptional durability, heat resistance, and low porosity, making it ideal for tabletops that endure heavy use. Quartzite provides a natural stone aesthetic with superior hardness and resistance to scratches, though it requires periodic sealing to maintain its stain resistance. Choosing between sintered stone and quartzite depends on your preference for maintenance, design, and long-term durability in tabletop surfaces.
Infographic: Sintered stone vs Quartzite for Tabletop
 azmater.com
azmater.com