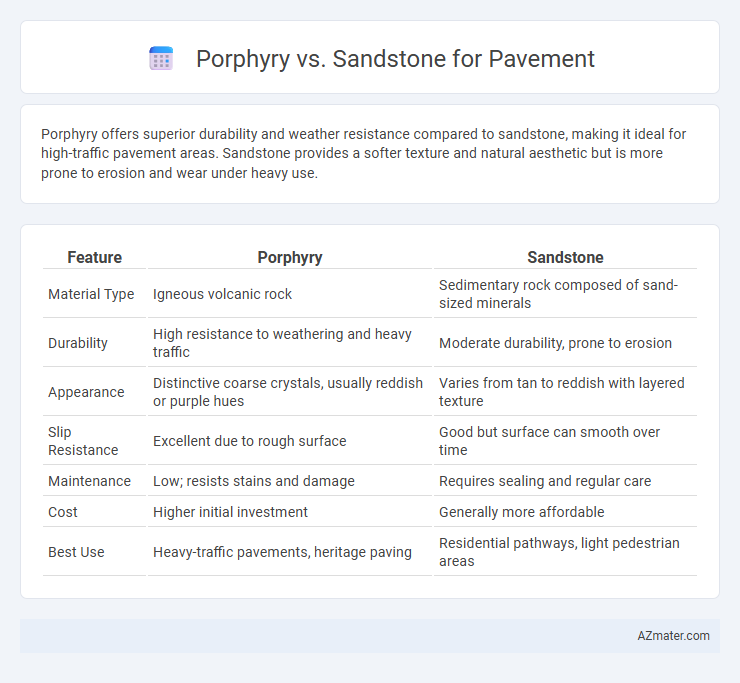
Porphyry offers superior durability and weather resistance compared to sandstone, making it ideal for high-traffic pavement areas. Sandstone provides a softer texture and natural aesthetic but is more prone to erosion and wear under heavy use.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Porphyry | Sandstone |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Igneous volcanic rock | Sedimentary rock composed of sand-sized minerals |
| Durability | High resistance to weathering and heavy traffic | Moderate durability, prone to erosion |
| Appearance | Distinctive coarse crystals, usually reddish or purple hues | Varies from tan to reddish with layered texture |
| Slip Resistance | Excellent due to rough surface | Good but surface can smooth over time |
| Maintenance | Low; resists stains and damage | Requires sealing and regular care |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Generally more affordable |
| Best Use | Heavy-traffic pavements, heritage paving | Residential pathways, light pedestrian areas |
Introduction to Porphyry and Sandstone Pavements
Porphyry pavements are known for their high durability and distinctive coarse-grained texture, making them ideal for heavy traffic areas and urban environments. Sandstone pavements offer a natural aesthetic with a softer, fine-grained surface that provides moderate durability suitable for pedestrian pathways and landscaping projects. Both materials vary in porosity and wear resistance, influencing maintenance requirements and longevity in pavement applications.
Geological Origins of Porphyry and Sandstone
Porphyry is an igneous rock characterized by large crystals embedded in a fine-grained matrix, formed from the slow cooling of magma deep within the Earth's crust, resulting in its durability and hardness ideal for pavement. Sandstone is a sedimentary rock composed primarily of sand-sized mineral particles or rock fragments, deposited over time by water or wind and cemented together, offering a softer and more porous pavement material. The distinct geological origins of porphyry's magmatic crystallization and sandstone's sedimentary deposition influence their performance and aesthetic qualities in pavement applications.
Physical Properties Comparison
Porphyry exhibits superior hardness and abrasion resistance compared to sandstone, making it ideal for high-traffic pavements. Its dense, fine-grained texture provides excellent durability and load-bearing capacity, while sandstone's softer, porous structure leads to faster wear and potential water absorption issues. Porphyry's low porosity and high compressive strength enhance pavement longevity, contrasting with sandstone's susceptibility to weathering and erosion under heavy use.
Durability in Different Climates
Porphyry offers superior durability for pavement in various climates due to its dense, igneous composition that resists weathering, freeze-thaw cycles, and abrasion. Sandstone, being sedimentary and more porous, tends to absorb water, making it more susceptible to cracking and erosion in harsh or wet environments. In regions with extreme temperature fluctuations or heavy rainfall, porphyry maintains its structural integrity longer than sandstone, ensuring lower long-term maintenance costs.
Aesthetic Appeal and Color Variations
Porphyry offers a rich, deep color palette with hues ranging from reddish-brown to purple, creating a striking and elegant aesthetic for pavements. Sandstone provides earthy, warm tones such as beige, tan, and rust, contributing to a natural and rustic appearance ideal for outdoor spaces. The vivid and varied texture of porphyry contrasts with sandstone's softer, grainy look, allowing designers to choose based on the desired visual impact and surrounding environment.
Installation Methods and Ease
Porphyry pavement installation involves precise cutting and fitting due to its hardness and irregular shape, requiring skilled labor and specialized tools which can increase project time and cost. Sandstone pavements, being softer and more uniform, allow easier cutting and shaping, facilitating quicker installation with standard tools and less labor intensity. Porphyry's durability justifies its complex installation, while sandstone offers more flexibility and ease for faster pavement projects.
Maintenance Requirements
Porphyry pavements require minimal maintenance due to their high durability and resistance to weathering and heavy traffic, making them ideal for long-term use in urban environments. Sandstone pavements need more frequent sealing and cleaning to prevent surface erosion and staining, as their softer composition is more vulnerable to wear and environmental damage. Regular maintenance of sandstone includes replenishing joint materials and addressing surface cracks, whereas porphyry's dense structure reduces the necessity for such interventions.
Cost Analysis: Porphyry vs Sandstone
Porphyry pavement typically incurs higher initial costs due to its dense, durable nature and complex extraction process, making it a premium choice for long-term use. Sandstone offers a more budget-friendly option with lower upfront expenses, but it generally requires more frequent maintenance and replacement, increasing overall lifecycle costs. When comparing total cost of ownership, porphyry's longevity and resistance to wear often justify the higher investment over sandstone's lower purchase price.
Eco-Friendliness and Sustainability
Porphyry offers superior eco-friendliness due to its natural durability and low maintenance requirements, reducing resource consumption over time. Sandstone, while biodegradable and sourced naturally, may require more frequent replacement and chemical treatments, impacting sustainability negatively. Porphyry's long lifespan and minimal environmental impact make it a more sustainable choice for pavement projects.
Best Applications and Use Cases
Porphyry's durability, high compressive strength, and resistance to weathering make it ideal for heavy-traffic urban pavements, plazas, and historic preservation projects where aesthetics and longevity are crucial. Sandstone offers excellent thermal insulation and slip resistance, making it well-suited for pedestrian walkways, park pathways, and residential landscaping with moderate foot traffic. Porphyry's dense structure supports vehicular loads, while sandstone's porous nature provides natural drainage and comfort in warmer climates.
Infographic: Porphyry vs Sandstone for Pavement
 azmater.com
azmater.com