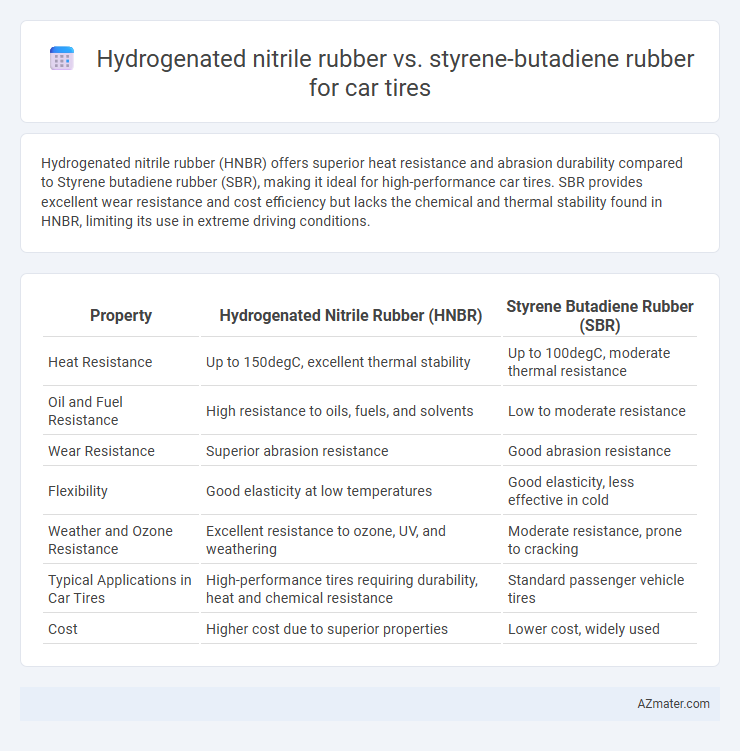
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior heat resistance and abrasion durability compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), making it ideal for high-performance car tires. SBR provides excellent wear resistance and cost efficiency but lacks the chemical and thermal stability found in HNBR, limiting its use in extreme driving conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) | Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Up to 150degC, excellent thermal stability | Up to 100degC, moderate thermal resistance |
| Oil and Fuel Resistance | High resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents | Low to moderate resistance |
| Wear Resistance | Superior abrasion resistance | Good abrasion resistance |
| Flexibility | Good elasticity at low temperatures | Good elasticity, less effective in cold |
| Weather and Ozone Resistance | Excellent resistance to ozone, UV, and weathering | Moderate resistance, prone to cracking |
| Typical Applications in Car Tires | High-performance tires requiring durability, heat and chemical resistance | Standard passenger vehicle tires |
| Cost | Higher cost due to superior properties | Lower cost, widely used |
Introduction to Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) and Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR)
Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior resistance to heat, oil, and abrasion, making it an ideal material for high-performance car tires requiring durability in extreme conditions. Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) offers excellent wear resistance and cost-effectiveness, widely used in standard car tire production for enhanced traction and longevity. Both polymers provide distinct advantages, with HNBR favored for specialty tires and SBR dominating mass-market automotive applications.
Chemical Structure and Composition Comparison
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) features a saturated polymer backbone with high hydrogenation levels, enhancing its resistance to heat, oil, and oxidative degradation, whereas styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) has an unsaturated backbone with alternating styrene and butadiene units, making it more prone to weathering and ozone attack. HNBR's nitrile groups provide superior oil and chemical resistance, while SBR lacks polar functional groups, resulting in lower chemical robustness but better flexibility at low temperatures. The chemical composition difference, with HNBR's hydrogenated nitrile units versus SBR's styrene-butadiene copolymer, directly influences tire performance in terms of durability, aging resistance, and mechanical properties.
Key Physical Properties: HNBR vs SBR
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior heat resistance, tensile strength, and abrasion resistance compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), making it highly suitable for high-performance car tires exposed to extreme temperatures. HNBR's enhanced chemical stability and resistance to oil, ozone, and weathering outperform SBR, which typically offers good wear resistance and flexibility but degrades faster under harsh environmental conditions. The improved mechanical properties of HNBR contribute to longer tire life and reliability in demanding automotive applications.
Durability and Wear Resistance in Tire Applications
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior durability and wear resistance compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) in car tire applications due to its enhanced resistance to heat, abrasion, and ozone degradation. HNBR maintains performance under high temperatures and harsh environmental conditions, resulting in extended tire lifespan and improved tread stability. SBR, while cost-effective and flexible, tends to exhibit faster wear and lower resistance to oxidative aging, making HNBR a preferred choice for premium, long-lasting tires.
Performance in Extreme Temperatures
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to extreme temperatures compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), maintaining flexibility and mechanical properties in conditions as low as -40degC and as high as 150degC. SBR typically performs well up to around 100degC but becomes rigid and brittle under severe cold, reducing tire traction and durability. For car tires exposed to fluctuating or harsh thermal environments, HNBR provides enhanced performance, longevity, and safety due to its resilience against thermal aging and oxidation.
Oil and Chemical Resistance: HNBR vs SBR
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior oil and chemical resistance compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), making it ideal for car tire applications exposed to harsh automotive fluids and fuels. HNBR's enhanced molecular structure provides excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils, hydraulic fluids, and ozone, extending tire durability and performance in aggressive environments. In contrast, SBR exhibits lower resistance to oils and chemicals, leading to faster degradation and reduced lifespan when exposed to similar conditions.
Rolling Resistance and Fuel Efficiency
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior rolling resistance compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) due to its enhanced abrasion resistance and thermal stability, which reduce energy loss during tire rotation. Tires incorporating HNBR compounds demonstrate improved fuel efficiency by maintaining lower hysteresis under varying temperature conditions, thereby decreasing fuel consumption. In contrast, SBR tires typically show higher rolling resistance, resulting in increased energy dissipation and reduced fuel economy over long-term vehicle operation.
Cost Analysis and Manufacturing Considerations
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior heat, oil, and abrasion resistance compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), but its higher raw material costs and more complex processing increase overall tire production expenses. SBR remains a cost-effective option for car tires due to lower material costs and simpler manufacturing methods, making it widely used in standard tire treads. Manufacturing considerations include HNBR's need for controlled curing conditions and specialized compounding, which can raise capital and operational costs, whereas SBR benefits from established production infrastructure and faster curing cycles.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers enhanced resistance to heat, ozone, and chemicals compared to styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), leading to longer tire life and reduced material consumption, thus lowering environmental impact. SBR, derived from petrochemicals, has higher rolling resistance, which increases fuel consumption and carbon emissions during tire use. The greater durability and fuel efficiency provided by HNBR contribute to improved sustainability in automotive tires by decreasing the frequency of replacements and reducing greenhouse gas emissions over the tire lifecycle.
Final Verdict: Best Rubber for Car Tire Applications
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) outperforms Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) in car tire applications due to its superior abrasion resistance, heat aging stability, and oil resistance, directly translating to extended tire lifespan and enhanced safety. While SBR is cost-effective and provides good abrasion resistance and aging properties, HNBR's resilience to extreme temperatures and chemical exposure makes it the preferred choice for high-performance and long-lasting tires. For optimized durability and performance under demanding driving conditions, HNBR stands as the best rubber material for car tires.
Infographic: Hydrogenated nitrile rubber vs Styrene butadiene rubber for Car tire
 azmater.com
azmater.com