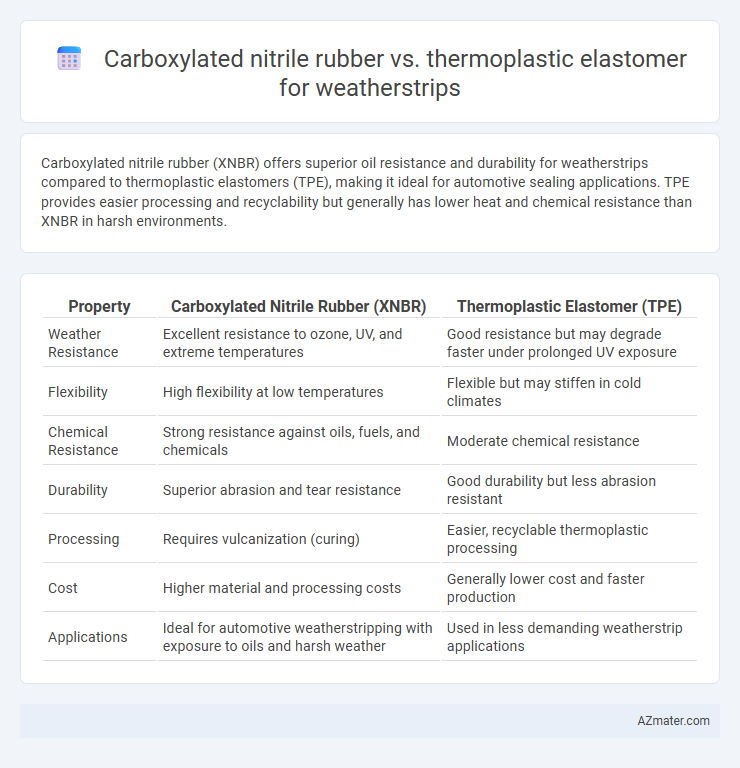
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior oil resistance and durability for weatherstrips compared to thermoplastic elastomers (TPE), making it ideal for automotive sealing applications. TPE provides easier processing and recyclability but generally has lower heat and chemical resistance than XNBR in harsh environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR) | Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) |
|---|---|---|
| Weather Resistance | Excellent resistance to ozone, UV, and extreme temperatures | Good resistance but may degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure |
| Flexibility | High flexibility at low temperatures | Flexible but may stiffen in cold climates |
| Chemical Resistance | Strong resistance against oils, fuels, and chemicals | Moderate chemical resistance |
| Durability | Superior abrasion and tear resistance | Good durability but less abrasion resistant |
| Processing | Requires vulcanization (curing) | Easier, recyclable thermoplastic processing |
| Cost | Higher material and processing costs | Generally lower cost and faster production |
| Applications | Ideal for automotive weatherstripping with exposure to oils and harsh weather | Used in less demanding weatherstrip applications |
Introduction to Weatherstrip Materials
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers excellent resistance to oil, ozone, and weathering, making it a durable choice for weatherstrip applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) provide flexibility and ease of processing, with good resistance to UV and cold temperatures, which suits weatherstripping requiring frequent deformation and installation adaptability. Selecting between XNBR and TPE depends on specific weatherstrip performance needs, such as chemical resistance, elasticity, and exposure to varying climates.
Overview of Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber (XNBR)
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) is a synthetic elastomer known for its enhanced abrasion resistance, high tensile strength, and excellent chemical resistance, particularly against oils and fuels, making it ideal for weatherstrip applications exposed to harsh environments. The presence of carboxyl groups in XNBR increases cross-link density, resulting in superior mechanical properties and improved aging resistance compared to standard nitrile rubber. In contrast, thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) offer easier processing and recyclability but generally lack the durability and chemical resistance required for long-lasting weatherstrips in automotive and industrial settings.
Overview of Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE)
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) combine the elasticity of rubber with the processability of plastics, making them ideal for weatherstrip applications requiring flexibility, durability, and ease of manufacturing. Compared to carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR), TPEs offer superior resistance to UV radiation, ozone, and extreme temperatures, extending weatherstrip lifespan in harsh outdoor environments. Their recyclability and ability to be molded into complex shapes without vulcanization also reduce production costs and environmental impact.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to thermoplastic elastomers (TPE), making it more durable under mechanical stress in weatherstrip applications. XNBR typically exhibits higher tear strength and better compression set resistance, ensuring longer lifespan in seals exposed to frequent deformation. In contrast, TPE provides greater flexibility and processability but generally falls short in maintaining mechanical integrity under extreme temperatures and prolonged mechanical stress.
Weather Resistance and Durability
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) exhibits superior weather resistance compared to thermoplastic elastomers (TPE), maintaining flexibility and tensile strength under prolonged exposure to UV radiation, ozone, and extreme temperatures. XNBR's enhanced crosslinking chemistry provides exceptional durability by resisting cracking and degradation in harsh environmental conditions critical for weatherstrip applications. Although TPE offers good resilience and ease of processing, it typically falls short in long-term weather resistance and mechanical stability relative to carboxylated nitrile rubber.
Cost Efficiency and Manufacturing Process
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior chemical resistance and durability, making it cost-efficient for weatherstrips that require long-term performance and minimal maintenance. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) provide faster manufacturing through injection molding and recycling advantages, leading to reduced production costs and increased design flexibility. Choosing between XNBR and TPE for weatherstrips depends on balancing initial material costs with long-term performance demands and production volume.
Flexibility and Compression Set
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) exhibits superior flexibility and lower compression set compared to thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) in weatherstrip applications, ensuring better seal resilience and durability under continuous compression. The enhanced cross-linking in XNBR provides greater elasticity and resistance to permanent deformation, crucial for maintaining airtight and watertight seals. TPEs offer ease of processing but generally show higher compression set values, leading to potential seal failures in long-term exposure to varying temperatures and mechanical stress.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers enhanced chemical resistance and durability for weatherstrips but poses challenges in recyclability due to its crosslinked structure, leading to complex disposal and environmental concerns. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) provide superior recyclability through remelting and reshaping, reducing landfill waste and lowering the carbon footprint associated with weatherstrip production. Environmental impact assessments favor TPEs for their lower emissions and improved sustainability in comparison to the more pollutant-intensive lifecycle of carboxylated nitrile rubber materials.
Typical Applications in Automotive Weatherstripping
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers excellent oil resistance and durability, making it ideal for automotive weatherstripping applications exposed to engine oils and harsh environmental conditions. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) provide superior flexibility and ease of processing, which suits exterior door seals and window trims requiring frequent compression and rebound. Both materials enhance vehicle durability, but XNBR is preferred in high-performance sealing contexts, while TPE is favored for cost-effective, lightweight weatherstrip components.
Summary: Choosing the Right Material for Weatherstrips
Carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) offers superior oil resistance, abrasion durability, and weathering performance, making it ideal for automotive weatherstrips exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) provide excellent flexibility, ease of processing, and recyclability, suitable for applications requiring cost-effective manufacturing and lighter weight. Selecting the right material depends on specific requirements such as chemical exposure, mechanical stress, and environmental durability.
Infographic: Carboxylated nitrile rubber vs Thermoplastic elastomer for Weatherstrip
 azmater.com
azmater.com