Biobased rubber for hoses offers enhanced sustainability by reducing reliance on fossil fuels compared to traditional natural rubber. It provides comparable elasticity and durability while improving environmental impact through renewable sourcing.
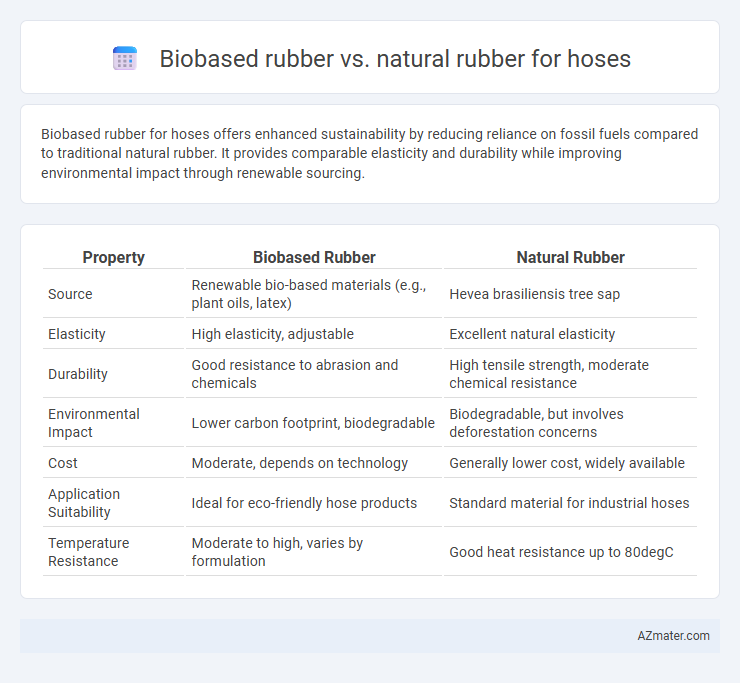
Table of Comparison
| Property | Biobased Rubber | Natural Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Renewable bio-based materials (e.g., plant oils, latex) | Hevea brasiliensis tree sap |
| Elasticity | High elasticity, adjustable | Excellent natural elasticity |
| Durability | Good resistance to abrasion and chemicals | High tensile strength, moderate chemical resistance |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, biodegradable | Biodegradable, but involves deforestation concerns |
| Cost | Moderate, depends on technology | Generally lower cost, widely available |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for eco-friendly hose products | Standard material for industrial hoses |
| Temperature Resistance | Moderate to high, varies by formulation | Good heat resistance up to 80degC |
Introduction: Biobased Rubber vs. Natural Rubber for Hoses
Biobased rubber, derived from renewable plant sources such as guayule and dandelion, offers a sustainable alternative to traditional natural rubber extracted from Hevea brasiliensis trees. This emerging material provides comparable elasticity and durability essential for hose manufacturing while reducing environmental impact through lower greenhouse gas emissions and less deforestation. Advances in biobased rubber processing enhance its chemical resistance and weatherability, making it increasingly viable for industrial hose applications.
Defining Biobased and Natural Rubber
Biobased rubber refers to elastomers derived from renewable plant sources, such as guayule or dandelion, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional materials. Natural rubber is primarily harvested from the latex sap of the Hevea brasiliensis tree and is valued for its high elasticity and resilience in hose applications. Both types of rubber provide essential mechanical properties but differ significantly in origin and environmental impact.
Raw Material Sources and Sustainability
Biobased rubber for hoses is derived from renewable plant sources such as guayule and dandelion, reducing reliance on traditional rubber tree plantations. Natural rubber, primarily harvested from Hevea brasiliensis trees, involves extensive land use and environmental impact due to deforestation and monoculture farming. Biobased alternatives offer enhanced sustainability by promoting biodiversity, lowering carbon footprints, and supporting circular economy principles compared to conventional natural rubber.
Manufacturing Processes: Key Differences
Biobased rubber for hoses is primarily produced from renewable biomass like plant oils and agricultural waste through chemical modification and polymerization, whereas natural rubber is harvested directly from Hevea brasiliensis trees by latex tapping. Manufacturing biobased rubber involves more complex synthetic routes, including esterification and cross-linking techniques, to achieve desired elasticity and durability. Natural rubber processing focuses on coagulation, drying, and vulcanization, offering simpler and more established manufacturing with consistent material properties for hose applications.
Physical and Mechanical Properties Comparison
Biobased rubber for hoses offers enhanced sustainability while maintaining comparable tensile strength and elongation to natural rubber, ensuring durability under pressure. Its abrasion resistance often matches or surpasses that of natural rubber, contributing to longer service life in demanding applications. Compression set and resilience values are closely aligned, indicating biobased rubber's suitability as a reliable alternative without compromising mechanical performance.
Environmental Impact and Carbon Footprint
Biobased rubber for hoses significantly reduces environmental impact by utilizing renewable resources, leading to lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to natural rubber derived from rubber trees. The carbon footprint of biobased rubber is minimized through sustainable agricultural practices and reduced reliance on synthetic additives, enhancing biodegradability and end-of-life disposal benefits. Lifecycle assessments reveal that biobased rubber production generates fewer pollutants and conserves biodiversity, positioning it as a more eco-friendly alternative in hose manufacturing.
Performance and Durability in Hose Applications
Biobased rubber offers enhanced environmental sustainability while delivering comparable tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and flexibility to natural rubber in hose applications. Its molecular structure can be engineered for improved resistance to oil, heat, and weathering, extending hose service life under harsh operating conditions. Durability tests show biobased rubber-based hoses maintain performance metrics such as elongation and pressure tolerance similarly or better than natural rubber counterparts, making them a viable alternative in industrial hose manufacturing.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Biobased rubber for hoses offers a competitive cost advantage due to lower raw material expenses derived from renewable resources compared to traditional natural rubber, which is subject to volatile commodity prices influenced by geopolitical and climatic factors. Market availability of biobased rubber is expanding rapidly as sustainable manufacturing practices gain traction, with increased production capacity from bio-based polymer companies driving accessibility. Natural rubber maintains strong market presence owing to established supply chains and its superior mechanical properties, but rising environmental regulations are encouraging a shift toward biobased alternatives.
Regulatory Standards and Certifications
Biobased rubber for hoses increasingly meets stringent regulatory standards such as REACH and FDA compliance, ensuring reduced environmental impact without compromising safety or performance. Natural rubber, subject to well-established certifications like ASTM D2000 and ISO 3801, is favored for its consistent quality and durability under these industry norms. Both materials require adherence to specific elastomer regulations, but biobased rubber offers enhanced sustainability credentials aligning with evolving global eco-certifications.
Future Trends and Innovations in Rubber Hoses
Biobased rubber in hose manufacturing is gaining traction due to its sustainable origins and lower environmental impact compared to traditional natural rubber, driving innovation in eco-friendly hose solutions. Advances in biopolymer technology enhance the durability and flexibility of biobased rubber hoses, making them increasingly competitive for industrial and agricultural applications. Future trends emphasize integrating smart sensing capabilities and improved biodegradability in rubber hoses, promoting a circular economy in the rubber industry.
Infographic: Biobased rubber vs Natural rubber for Hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com