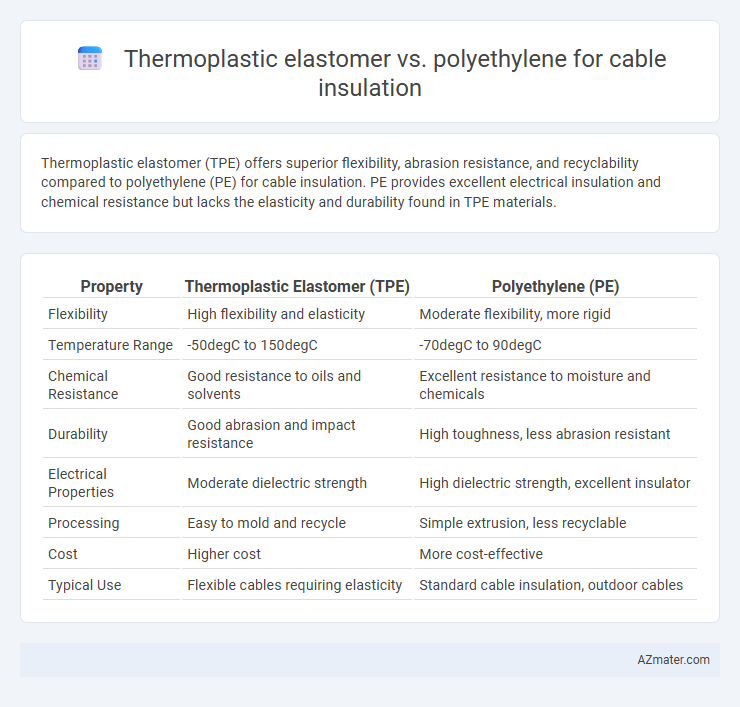
Thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) offers superior flexibility, abrasion resistance, and recyclability compared to polyethylene (PE) for cable insulation. PE provides excellent electrical insulation and chemical resistance but lacks the elasticity and durability found in TPE materials.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) | Polyethylene (PE) |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | High flexibility and elasticity | Moderate flexibility, more rigid |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 150degC | -70degC to 90degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils and solvents | Excellent resistance to moisture and chemicals |
| Durability | Good abrasion and impact resistance | High toughness, less abrasion resistant |
| Electrical Properties | Moderate dielectric strength | High dielectric strength, excellent insulator |
| Processing | Easy to mold and recycle | Simple extrusion, less recyclable |
| Cost | Higher cost | More cost-effective |
| Typical Use | Flexible cables requiring elasticity | Standard cable insulation, outdoor cables |
Introduction to Cable Insulation Materials
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) and polyethylene (PE) are widely used materials for cable insulation due to their excellent electrical properties and flexibility. TPE offers superior elasticity, impact resistance, and ease of processing, making it ideal for dynamic applications requiring frequent bending and mechanical stress. Polyethylene, especially cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE), provides outstanding dielectric strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, making it a preferred choice for high-voltage power cables and long-term outdoor installations.
Overview of Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE)
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) combine the elasticity of rubber with the processability of plastics, making them ideal for cable insulation due to their flexibility, durability, and resistance to environmental stress. TPE materials provide excellent chemical resistance, high impact strength, and superior thermal stability compared to polyethylene, which can improve cable lifespan and performance in demanding applications. Their recyclability and ease of extrusion further enhance manufacturing efficiency, distinguishing TPE as a versatile choice in modern cable insulation technologies.
Overview of Polyethylene (PE)
Polyethylene (PE) is a widely used thermoplastic polymer known for its excellent electrical insulation properties, low dielectric constant, and high resistance to moisture and chemicals, making it ideal for cable insulation. It offers outstanding mechanical strength and durability, ensuring long service life in harsh environments and minimizing signal loss. PE's thermal stability and cost-effectiveness contribute to its popularity in medium and high-voltage power cables as well as telecommunications wiring.
Key Properties of TPE for Cable Insulation
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer superior flexibility, excellent abrasion resistance, and enhanced thermal stability compared to polyethylene (PE), making them ideal for dynamic cable insulation applications. TPE's ability to maintain elasticity over a wide temperature range, typically -40degC to 120degC, ensures reliable performance in varying environmental conditions. High dielectric strength and resistance to chemicals and UV radiation further optimize TPE as a durable and long-lasting material choice for cable insulation.
Key Properties of Polyethylene for Cable Insulation
Polyethylene exhibits excellent dielectric strength and low moisture absorption, making it ideal for cable insulation applications requiring reliable electrical performance. Its outstanding chemical resistance and high tensile strength enhance durability and longevity in harsh environments. The material's low density contributes to lightweight cables without compromising mechanical properties, ensuring efficient installation and flexibility.
Performance Comparison: TPE vs Polyethylene
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer superior flexibility and impact resistance compared to polyethylene, making them ideal for applications requiring frequent bending and movement in cable insulation. Polyethylene excels in electrical insulation properties and moisture resistance, contributing to enhanced dielectric strength and long-term durability in harsh environments. TPE provides better thermal stability and chemical resistance but may have slightly lower voltage ratings than high-density polyethylene (HDPE) used in high-voltage cables.
Flexibility and Mechanical Strength
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer superior flexibility compared to polyethylene (PE), allowing cables to withstand repeated bending and flexing without cracking. PE exhibits higher mechanical strength and excellent resistance to abrasion and impact, making it ideal for applications requiring durable insulation. The choice between TPE and PE depends on the balance needed between flexibility for dynamic use and mechanical robustness for protective insulation.
Chemical and Thermal Resistance
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) offer superior chemical resistance against oils, solvents, and many acids compared to polyethylene (PE), making them ideal for harsh industrial environments. TPEs maintain flexibility and performance at higher temperatures, often withstanding continuous use up to 125degC, whereas polyethylene typically has a lower thermal limit around 90degC. The enhanced thermal stability and chemical inertness of TPEs contribute to longer cable lifespan and improved safety in demanding applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer enhanced recyclability and lower environmental impact compared to polyethylene (PE), as TPEs can be repeatedly melted and reshaped, reducing waste and energy consumption in manufacturing. Polyethylene, while widely used for cable insulation due to its excellent electrical properties and chemical resistance, poses challenges in sustainability owing to its non-biodegradable nature and difficulties in recycling. Choosing TPE for cable insulation supports circular economy goals and reduces long-term ecological footprint by enabling material recovery and limiting plastic pollution.
Application Suitability and Market Trends
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer superior flexibility, abrasion resistance, and thermal stability, making them highly suitable for dynamic cable insulation applications such as robotics and automotive wiring. Polyethylene (PE) excels in electrical insulation properties, chemical resistance, and cost efficiency, driving its dominance in power distribution and communication cables. Market trends show increasing adoption of TPE in specialized, high-performance sectors, while PE maintains a strong presence in large-scale infrastructure due to its established reliability and lower price point.
Infographic: Thermoplastic elastomer vs Polyethylene for Cable insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com