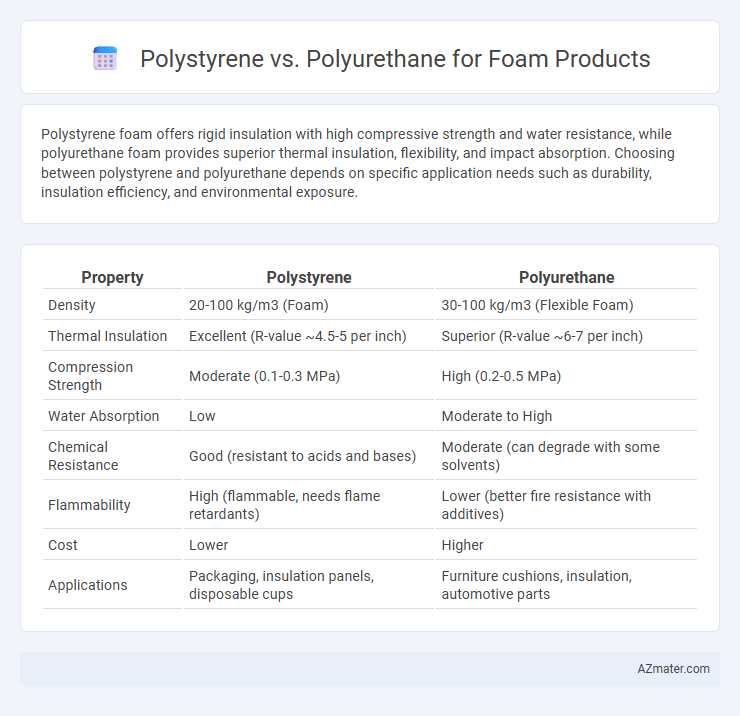
Polystyrene foam offers rigid insulation with high compressive strength and water resistance, while polyurethane foam provides superior thermal insulation, flexibility, and impact absorption. Choosing between polystyrene and polyurethane depends on specific application needs such as durability, insulation efficiency, and environmental exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polystyrene | Polyurethane |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 20-100 kg/m3 (Foam) | 30-100 kg/m3 (Flexible Foam) |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent (R-value ~4.5-5 per inch) | Superior (R-value ~6-7 per inch) |
| Compression Strength | Moderate (0.1-0.3 MPa) | High (0.2-0.5 MPa) |
| Water Absorption | Low | Moderate to High |
| Chemical Resistance | Good (resistant to acids and bases) | Moderate (can degrade with some solvents) |
| Flammability | High (flammable, needs flame retardants) | Lower (better fire resistance with additives) |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Applications | Packaging, insulation panels, disposable cups | Furniture cushions, insulation, automotive parts |
Introduction to Foam Materials: Polystyrene vs. Polyurethane
Polystyrene and polyurethane are two widely used foam materials, each offering distinct properties that influence their applications. Polystyrene is a rigid, lightweight foam known for its excellent thermal insulation and impact resistance, commonly used in packaging and construction. Polyurethane foam provides superior flexibility and cushioning, making it ideal for furniture, bedding, and automotive seating.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Polystyrene is a synthetic aromatic hydrocarbon polymer derived from the monomer styrene, featuring a rigid, glassy structure with a benzene ring attached to every other carbon atom in the backbone, which imparts its characteristic brittleness and thermal insulation properties. Polyurethane is formed through the reaction of polyols and diisocyanates, resulting in a versatile polymer network with urethane linkages (-NH-CO-O-) that provide elasticity, durability, and varying density based on formulation. The chemical composition differences affect foam properties: polystyrene foams tend to be lightweight and rigid due to their simple linear chains, while polyurethane foams offer flexibility and resilience owing to their cross-linked, segmented polymer structure.
Manufacturing Processes Explained
Polystyrene foam production primarily involves polymerization of styrene monomers using a suspension or emulsion process, followed by expansion through heat application, creating lightweight, rigid foam beads ideal for insulation and packaging. Polyurethane foam manufacturing uses a chemical reaction between polyols and diisocyanates, mixed with blowing agents to create flexible or rigid foam with superior cushioning and thermal properties. Both processes require precise control of temperature and reaction time to optimize cell structure and foam density for targeted applications.
Physical Properties and Performance
Polystyrene foam exhibits high rigidity, excellent insulation properties, and resistance to moisture, making it ideal for packaging and thermal insulation. Polyurethane foam offers superior flexibility, greater impact absorption, and higher durability under mechanical stress, which suits applications requiring cushioning and shock resistance. Comparing density, polystyrene typically ranges from 20-50 kg/m3, while polyurethane foams vary widely from 25-150 kg/m3, influencing their respective compression resistance and thermal conductivity.
Insulation Efficiency and Thermal Conductivity
Polystyrene foam typically has a thermal conductivity ranging from 0.030 to 0.040 W/m*K, making it an effective insulator for building applications and packaging. Polyurethane foam offers superior insulation efficiency with thermal conductivity values as low as 0.020 to 0.025 W/m*K, resulting in better energy savings and enhanced temperature control. The lower thermal conductivity of polyurethane foam translates to higher R-values per inch, making it more efficient in reducing heat transfer compared to polystyrene foam.
Durability and Longevity in Applications
Polystyrene foam offers moderate durability with good resistance to moisture and impact, making it suitable for insulation and packaging applications where lightweight and cost-effectiveness are key. Polyurethane foam excels in longevity due to its superior thermal insulation properties and robust resistance to wear, chemicals, and deformation, making it ideal for high-performance automotive, furniture, and construction uses. The choice between polystyrene and polyurethane depends on the specific application's durability demands and expected lifespan, with polyurethane providing enhanced durability for long-term, heavy-duty applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polystyrene foam, widely used in packaging and insulation, is non-biodegradable and poses significant challenges in waste management due to its persistence in landfills and potential to release toxic chemicals when burned. Polyurethane foam, commonly found in furniture and automotive applications, can be produced with bio-based polyols, improving its sustainability profile, though it still faces issues related to chemical additives and limited recyclability. Innovations in recycling technologies and the development of greener raw materials are critical in reducing the environmental impact of both foams, with polyurethane showing slightly better potential for sustainable lifecycle improvements.
Cost Comparison and Market Availability
Polystyrene foam generally offers a lower cost per unit compared to polyurethane, making it a popular choice for budget-sensitive projects and large-scale packaging applications. Polyurethane foam, while typically more expensive, provides superior insulation properties and durability, which can justify its higher price in automotive and construction markets. Market availability favors polystyrene due to its widespread manufacturing and use in various industries, whereas polyurethane's specialized production limits its accessibility but supports niche applications requiring advanced performance.
Common Uses in Industry and Everyday Products
Polystyrene foam is widely utilized in packaging materials, insulation panels, and disposable food containers due to its rigidity and moisture resistance. Polyurethane foam finds extensive applications in furniture cushions, automotive seating, and thermal insulation because of its flexibility and durability. Both materials are integral to construction and consumer goods, with polystyrene favored for lightweight structural support and polyurethane chosen for comfort and impact absorption.
Choosing the Right Foam: Key Considerations
Polystyrene foam offers rigid, lightweight insulation ideal for packaging and construction, whereas polyurethane foam provides superior flexibility, cushioning, and thermal insulation, making it suitable for furniture and automotive applications. Consider factors such as density, compression strength, thermal resistance (R-value), and application-specific requirements to determine the optimal foam type. Environmental impact and recyclability also play critical roles in selecting between polystyrene's rigidity and polyurethane's versatility for long-term performance and sustainability.
Infographic: Polystyrene vs Polyurethane for Foam Product
 azmater.com
azmater.com